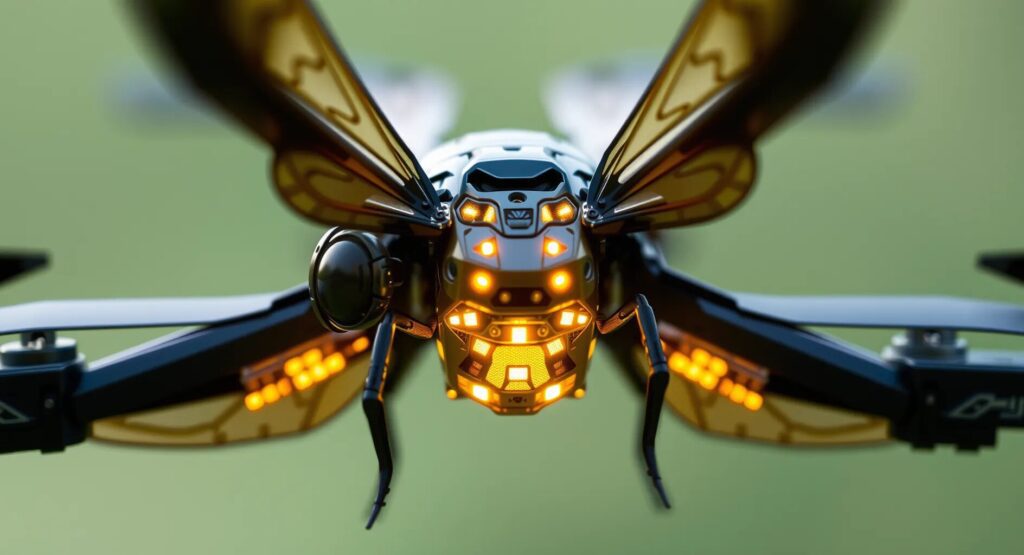
Imagine a world where the survival of crops doesn’t hinge on the uncertain activity of bees. Instead, a fleet of tiny, sophisticated drones, guided by artificial intelligence, ensures that every flower gets its fair share of pollen. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the next frontier in agriculture. AI-powered pollinator drones are poised to not just supplement, but possibly surpass natural pollinators in efficiency and reliability, revolutionizing the way we think about food production and environmental sustainability.
The Pollination Crisis: A Deeper Look
Pollination is a critical process in the growth cycle of many crops. Without it, the fruits, seeds, and vegetables we rely on simply wouldn’t exist. But the pollination crisis is real and growing. Over the past few decades, there has been a dramatic decline in bee populations worldwide, largely due to Colony Collapse Disorder (CCD), pesticide use, habitat destruction, and the spread of diseases among pollinators.
The implications of this decline are profound. Bees and other pollinators contribute to the pollination of over 35% of global crops, including those that provide essential nutrients to the human diet. Without them, many of the foods we take for granted—like apples, almonds, and coffee—could become scarce or even disappear, leading to higher prices and food insecurity.
While efforts are being made to conserve and protect natural pollinators, there’s growing recognition that technology must play a role in addressing this crisis. Enter the AI-powered pollinator drones.
The Mechanics: How AI-Powered Pollinator Drones Operate
AI-powered pollinator drones are a marvel of modern engineering. These drones are typically small, lightweight, and designed to mimic the flight patterns and pollination techniques of bees. But what sets them apart is their ability to perform these tasks with machine-like precision and adaptability.
1. Advanced Vision Systems
At the core of these drones is an advanced vision system that allows them to identify flowers with incredible accuracy. Using a combination of machine learning and computer vision, these drones can distinguish between different species of plants, recognize when a flower is ready for pollination, and even determine the best angle to approach the flower for effective pollination.
2. Autonomous Navigation
Equipped with GPS, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and a suite of sensors, these drones can autonomously navigate complex environments. They can maneuver through dense foliage, avoid obstacles, and even adapt to changing weather conditions. This level of autonomy is crucial for large-scale deployment, as it allows the drones to operate with minimal human intervention.
3. Pollen Collection and Distribution
The actual process of pollination is where these drones truly shine. They use electrostatic forces or tiny brushes to collect pollen from one flower and transfer it to another. The drones can be programmed to target specific plants, ensuring that cross-pollination occurs only between compatible species. This level of control can significantly increase the efficiency of pollination, leading to higher crop yields.
4. Data Analytics and Crop Monitoring
While pollinating, the drones also collect valuable data on the health of plants, soil conditions, and environmental factors. This data is transmitted in real-time to farmers, who can use it to make informed decisions about watering, fertilization, and pest control. Over time, this data can be used to refine the drone’s algorithms, making them even more effective.

Beyond Pollination: The Wider Implications of AI Drones in Agriculture
The use of AI-powered pollinator drones isn’t just about solving the pollination crisis—it’s about rethinking how we approach agriculture altogether. These drones are part of a broader trend toward precision agriculture, where technology is used to optimize every aspect of farming.
1. Optimizing Crop Yields
With their ability to pollinate more efficiently and gather detailed data on crop health, these drones can help farmers maximize their yields. In regions where natural pollinators are scarce or unreliable, the use of drones could make the difference between a successful harvest and a failed one.
2. Reducing Chemical Dependency
One of the most exciting possibilities is the potential to reduce the need for chemical inputs like pesticides and fertilizers. By providing precise, targeted pollination, these drones can help crops grow more robustly, making them less susceptible to pests and diseases. The data collected by the drones can also be used to identify problem areas in a field, allowing for more targeted and efficient use of chemicals.
3. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
In addition to boosting crop yields, AI-powered pollinator drones can contribute to more sustainable farming practices. By reducing the need for pesticides, they can help protect local ecosystems and biodiversity. Moreover, their ability to operate in challenging conditions means that they can be used in areas where traditional farming methods are less effective, potentially opening up new areas for cultivation without harming natural habitats.

Ethical Considerations and Challenges
Despite their promise, the deployment of AI-powered pollinator drones raises several ethical and practical questions. One of the most significant concerns is the potential impact on natural pollinators. While drones can supplement or even replace bees in some contexts, they should not become a substitute for efforts to conserve natural pollinator populations.
1. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Balance
Natural pollinators play a crucial role in maintaining biodiversity by pollinating a wide range of plants, many of which are not cultivated by humans. If drones were to completely take over the role of pollinators in agricultural settings, there could be unintended consequences for wild ecosystems. It’s essential to strike a balance between using technology and preserving the natural processes that sustain our environment.
2. Accessibility and Affordability
Another challenge is ensuring that this technology is accessible to all farmers, not just large industrial operations. Small-scale and subsistence farmers, particularly in developing countries, may struggle to afford these drones or lack the technical expertise to use them effectively. Making this technology affordable and user-friendly will be crucial to its widespread adoption.
3. Regulation and Safety
As with any new technology, the widespread use of AI-powered pollinator drones will require careful regulation to ensure safety and ethical use. This includes setting standards for drone operation, protecting privacy, and ensuring that the use of drones does not disrupt local communities or wildlife.
The Road Ahead: Integrating AI and Nature
The future of AI-powered pollinator drones is bright, but it must be approached with care and foresight. These drones offer an innovative solution to the pollination crisis and have the potential to transform agriculture. However, their success will depend on our ability to integrate this technology with broader efforts to protect and restore natural ecosystems.
In the long run, the goal should be a harmonious relationship between technology and nature, where drones and bees work side by side to ensure that our crops—and our planet—continue to thrive. By embracing AI-powered pollinator drones while also investing in the conservation of natural pollinators, we can build a more sustainable and resilient agricultural system.
As we move forward, it’s clear that the intersection of technology and agriculture holds immense potential. But it’s not just about the drones themselves—it’s about the bigger picture. We must think critically about how we use this technology to address not only the immediate challenges of food production but also the long-term health of our environment. The future of farming may very well depend on our ability to strike this balance.
In a world where AI-powered pollinator drones are becoming a reality, it’s not just about replacing bees—it’s about innovating responsibly, ensuring that we don’t lose the natural beauty and biodiversity that make our planet unique. The journey ahead will require collaboration, creativity, and a deep respect for both technology and nature. But if we get it right, the rewards could be nothing short of revolutionary.
Resources
Here are some valuable resources that can provide further insights into AI-powered pollinator drones and their implications for agriculture and the environment:
Books
- “The Bee-Friendly Garden: Design an Abundant, Flower-Filled Yard that Nurtures Bees and Supports Biodiversity” by Kate Frey and Gretchen LeBuhn
- While this book focuses on natural pollinators, it provides essential background on the importance of pollination and the challenges faced by bees, offering context for why alternative solutions like pollinator drones are being developed.
- “Precision Agriculture Technology for Crop Farming” by Qin Zhang
- This book delves into various precision agriculture technologies, including AI and robotics, providing a broader understanding of how technologies like pollinator drones fit into the future of farming.
- “Robotics in Agriculture and Forestry” by Francisco Rovira-Más, Ali Roshanianfard, and Emilio Moltó
- A comprehensive look at the role of robotics in modern agriculture, including drones and their applications in crop management, soil health monitoring, and more.
Research Papers and Articles
- “Pollination in the Anthropocene: How Pollinator Declines and Climate Change Are Impacting Pollination” by Helen M. Phillips et al. (2020)
- This paper explores the current state of pollinators, the challenges they face, and why alternative solutions, including technology, may become increasingly important.
- “The Use of Drones in Agriculture: Future Prospects” by M. Zhang, H. Su, and H. Wang (2019)
- A detailed examination of the various uses of drones in agriculture, including their potential role in pollination.
- “Artificial Pollination by UAVs: A Review of Robotic Pollination Methods” by Paolo Arena et al. (2021)
- This article reviews the current advancements in robotic pollination methods, including the use of drones, offering a technical perspective on the state of the art.
Websites and Online Resources
- FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization) – Pollination Services
- Link to FAO Pollination Services
- Provides comprehensive resources and reports on the importance of pollination, the threats to natural pollinators, and the need for innovative solutions.
- PrecisionAg
- Link to PrecisionAg
- A leading resource for the latest news, research, and insights into precision agriculture technologies, including drones and AI applications in farming.
- The Bee Informed Partnership
- Link to Bee Informed Partnership
- Focuses on research and education around bee health, offering insights into why alternative pollination methods are being explored.
Videos and Documentaries
- “The Pollinators” (Documentary)
- A documentary that explores the challenges facing bees and other natural pollinators, providing context for why technological solutions are being developed.
- TED Talks – “What Happens If All The Bees Die?” by Emma Bryce
- Link to TED Talk
- This talk explores the critical role of bees in our ecosystem and what could happen if we don’t find solutions to their decline.
- “Future Farming: How AI is Revolutionizing Agriculture”
- Link to YouTube Video
- A video discussing how AI, including drones, is transforming agriculture, with a focus on sustainability and efficiency.