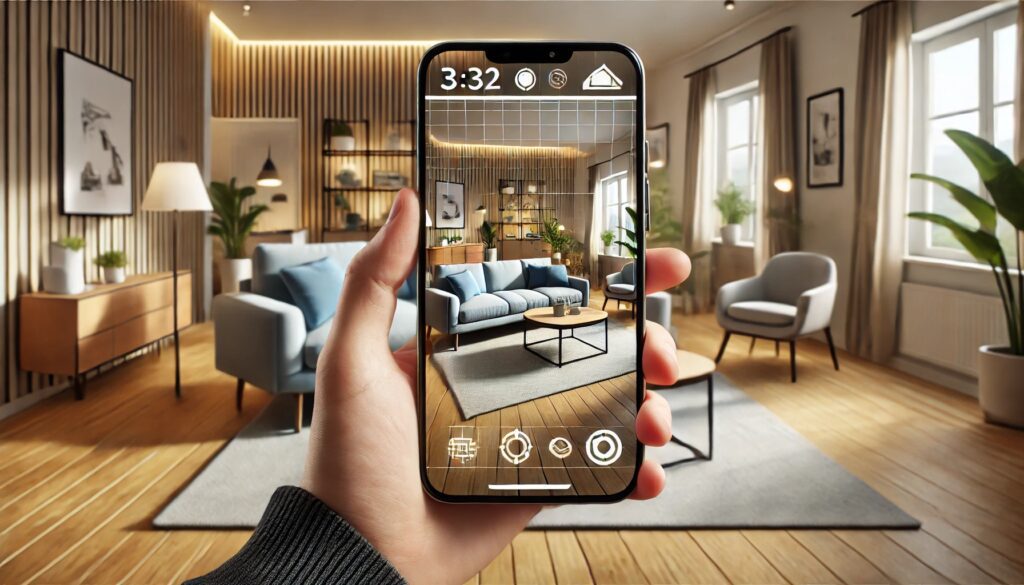
Augmented Reality (AR) becoming a hotbed of innovation in entertainment, e-commerce, education, and more. For AR experiences to truly engage, UX/UI and 3D designers have to work closely, crafting immersive and interactive environments.
Let’s explore how these design disciplines collaborate to make AR not only functional but thrilling for users.
Understanding the Basics: What Makes AR Different?
AR Blurs the Line Between Real and Digital
In AR, virtual elements blend with real-world settings, transforming how users interact with digital content. Unlike VR, where users enter a fully virtual world, AR overlays digital information on the real world, so designers need to create experiences that adapt seamlessly to different physical environments.
UX/UI Must Be Intuitive and Non-Intrusive
The challenge for UX/UI designers is making AR intuitive. Since users navigate with gestures and voice, they need clear indicators and seamless transitions. The goal? A natural flow that doesn’t overwhelm or distract from reality but guides users effortlessly.
3D Designers Bring Virtual Elements to Life
3D designers play a crucial role by adding realistic textures, lighting, and depth to virtual objects, making them appear as though they belong in the real world. It’s not just about aesthetics but creating believable and consistent interactions with the user’s environment.
Key UX/UI Principles for AR Design
Accessibility and Ease of Use
For any AR experience to be successful, it must be accessible. UX designers need to consider factors like ease of entry, guidance, and how users will interact. They use familiar icons and cues that simplify navigation, whether through a phone screen or smart glasses.
Minimal Distractions for Maximum Engagement
One of the biggest pitfalls in AR is visual overload. Since AR enhances reality, adding too much information can distract rather than enhance. Designers use a minimalist approach, focusing on showing only what’s relevant in the moment, while keeping the overall interface light.
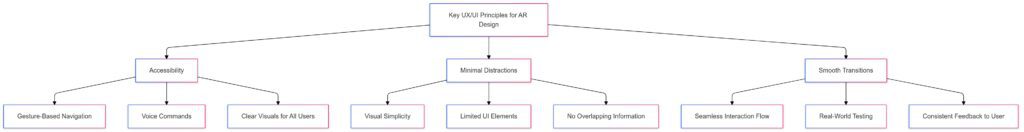
Smooth Transitions Keep Users Immersed
Transitions are critical. Moving from one screen to another, or introducing new digital elements, has to feel smooth and natural. UX designers use transitions that mimic real-life physics, like fading or sliding, to make the experience immersive.
3D Design Essentials: Building Realism and Interactivity
Realistic Textures and Lighting
3D objects need to feel part of the user’s environment. Lighting and textures help bridge the gap, creating a sense of reality. For instance, a virtual chair in a user’s room should reflect light accurately and cast shadows in a way that aligns with the room’s actual lighting.
Depth and Scale Are Key to Believability
A common design hurdle is achieving realistic depth and scale. If a virtual object is too small or doesn’t interact with the environment properly, it breaks the illusion. Designers use real-world measurements and scale models to ensure objects appear realistic, no matter the user’s perspective.
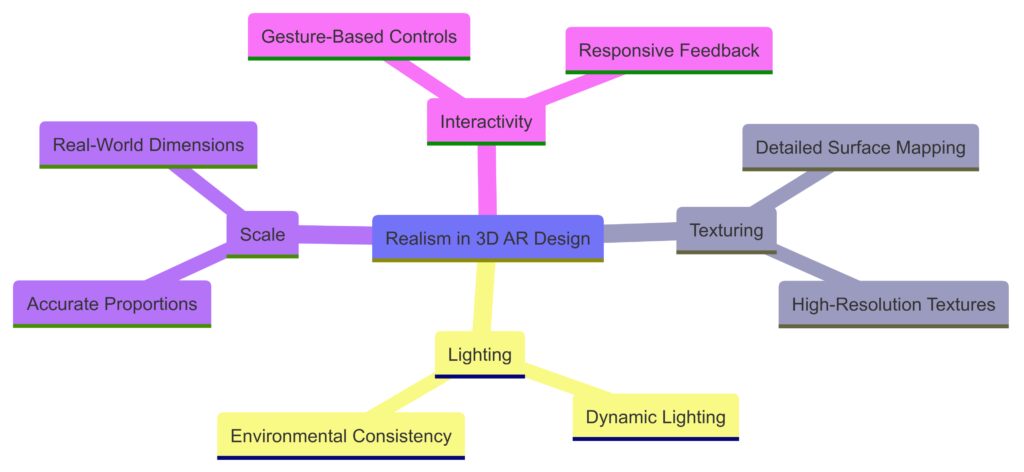
Interactive Elements for Engaging Experiences
AR shines when objects aren’t just visual but interactive. 3D designers create objects that respond to user actions, such as a character that waves back or a virtual product that spins when tapped. Interactivity makes the experience feel personal and keeps users engaged.
UX/UI and 3D Designers Collaborate to Create Cohesive Experiences

Defining User Flows and Mapping Real-World Interactions
UX designers outline how users will interact, while 3D designers bring the vision to life. They work together to define user flows that align with real-world actions. For instance, in an AR shopping app, a user should be able to place virtual furniture in their home. This flow requires both UX expertise in navigation and 3D accuracy for scaling.
Testing and Iteration for a Seamless Experience
Testing in AR is a must. AR environments are dynamic, so designers constantly test how elements behave in different lighting and physical settings. Feedback loops allow UX/UI and 3D designers to refine textures, adjust navigation, and improve object interactions based on real-world usage.
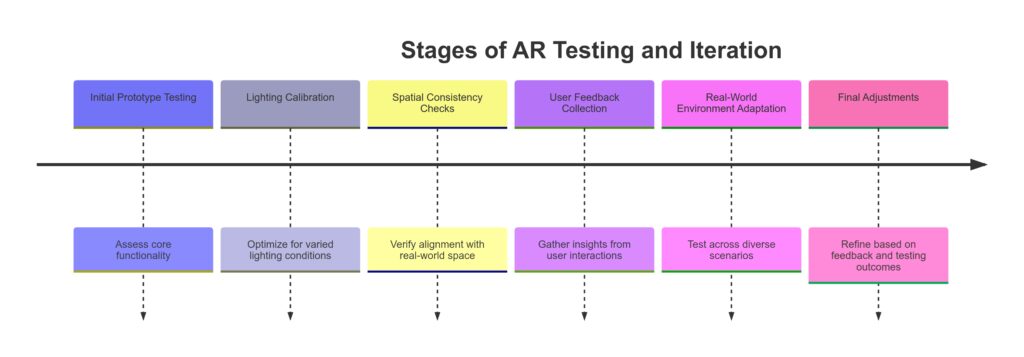
Adapting to Platform Limitations
Each AR platform has unique specifications, from processing power to display quality. Designers must adapt their creations to suit these limitations while maintaining a high-quality experience. For instance, mobile AR apps need lightweight graphics to run smoothly, while headset-based AR might allow for richer, more complex visuals.
Emerging Tools and Technologies That Shape AR Design
Software for Seamless Collaboration

Tools like Unity and Unreal Engine allow 3D and UX/UI designers to collaborate within a shared space, optimizing how assets look and perform in real-time. Collaboration platforms like Figma enable UX designers to map interactions that can be quickly tested and modified, aligning with 3D assets.
Leveraging AI for Adaptive AR Elements
AI is transforming AR by making objects smarter and more responsive. AI algorithms can adjust textures based on lighting or anticipate user gestures, creating a smoother and more intuitive experience. Designers use these capabilities to increase realism without adding complexity.
Eye-Tracking and Haptics for Enhanced Interaction
With the rise of eye-tracking and haptics, designers can make interactions even more immersive. Eye-tracking helps anticipate where users are looking, enabling designers to display relevant information at the right moment. Meanwhile, haptics adds a tactile dimension, allowing users to “feel” virtual objects.
The Future of AR Design: What’s Next for UX/UI and 3D Designers?
Expanding Beyond Mobile to Smart Glasses
Smart glasses will soon be the main device for AR, pushing designers to rethink how they display information when users aren’t restricted by a small screen. Designers are preparing for a shift towards always-on, contextual AR, where digital and real-world elements blend seamlessly.
Personalized AR Experiences Using User Data
AR design is moving towards personalized experiences, where content changes based on individual preferences, locations, and habits. UX and 3D designers are working on experiences that feel tailor-made, from virtual fashion that aligns with a user’s style to AR tours that highlight personal interests.
Multi-User AR for Social Experiences
Collaborative AR experiences are on the horizon, with applications in social media, gaming, and virtual meetings. Designers will need to tackle challenges of synchronization and interaction across devices to make shared AR experiences smooth and engaging.
Final Thoughts: Blending Art, Technology, and User Experience in AR
Designing for AR is a journey of blending reality and imagination, where UX/UI and 3D designers co-create experiences that captivate. As AR technology evolves, designers are tasked with finding innovative ways to make interactions feel natural, realistic, and fun. The future of AR holds boundless opportunities for these creative minds to transform how we see and interact with the world around us.
Ready to dive deeper?
Learn about the latest tools for AR design on platforms like Unity or explore AR design insights at sources like AugmentedReality.org.
FAQs
How is designing for AR different from traditional UX/UI?
Designing for AR blends digital and real-world experiences, requiring unique attention to interaction, depth, and adaptability. In AR, designers focus on seamless overlays that work with a user’s physical environment, unlike traditional interfaces that remain on a flat screen.
What are key principles for UX/UI in AR?
For UX/UI in AR, it’s crucial to maintain minimalism, clarity, and easy navigation. Designers aim to make interactions intuitive, using cues that guide users without overwhelming them. Transitions must also be smooth to keep the user immersed and engaged.
Why is realism so important in 3D AR design?
Realism in 3D is essential to make virtual objects feel believable in the real world. Realistic textures, accurate lighting, and scale create an immersive experience that tricks the brain into perceiving virtual objects as real.
What tools do designers use for creating AR experiences?
Designers commonly use Unity, Unreal Engine, and Figma for AR projects. These platforms support collaborative design, 3D modeling, and real-time testing, enabling UX/UI and 3D designers to iterate quickly and align the visual and interactive elements of AR experiences.
How do designers test AR experiences?
Testing is an ongoing process that involves real-world trials in varied environments to refine textures, lighting, and user interactions. Designers often perform testing in natural light and in spaces similar to where users might engage with the AR app, ensuring a smooth and consistent experience.
Are AR experiences adaptable across different devices?
Yes, though it’s a challenge. AR designs need to account for device limitations such as screen size, resolution, and processing power. Mobile AR apps, for instance, may need lighter graphics for smooth performance, while AR for headsets can allow more detailed visuals and interactions.
What’s next for UX/UI and 3D design in AR?
As AR expands beyond mobile into smart glasses and shared experiences, designers are exploring always-on interfaces, multi-user interaction, and personalized content. Innovations like AI and eye-tracking will make AR interactions even more responsive and immersive, paving the way for new applications in social media, retail, and beyond.
How do UX/UI and 3D designers collaborate on AR projects?
UX/UI and 3D designers work closely to create a unified experience. UX/UI designers focus on interaction flows and user guidance, while 3D designers handle object realism, depth, and environmental adaptation. Together, they map user journeys, ensuring virtual elements align visually and functionally in real-world contexts.
What role does AI play in AR design?
AI enhances AR by enabling adaptive elements and more natural interactions. For example, AI can adjust virtual lighting to match real-time surroundings or anticipate user gestures for smoother, intuitive responses. It also allows for personalization, presenting content that aligns with a user’s habits or preferences.
Can AR experiences be personalized for individual users?
Yes, personalization is becoming a big focus in AR. Designers are using user data to customize experiences, tailoring what users see based on their interests, past interactions, or even their location. This makes AR feel more relevant and engaging for each individual.
How does eye-tracking improve AR experiences?
Eye-tracking technology enables AR apps to recognize where a user is looking, helping to present relevant information exactly when it’s needed. For example, if a user’s gaze focuses on a product, the app can display extra details, creating a more personalized and intuitive interaction.
Why are smooth transitions so important in AR?
In AR, abrupt changes or lags can disrupt immersion and feel unnatural. Smooth transitions, like fading or sliding effects, help virtual elements blend with real-world surroundings, enhancing the sense of presence and making interactions feel more natural.
How do designers balance realism with performance in AR?
Designers often face a trade-off between visual quality and app performance. For mobile devices, they may simplify 3D models or reduce textures to keep the app running smoothly, while higher-powered devices can support richer graphics. The key is finding the right balance for a seamless, engaging experience across devices.
What are the main challenges in designing AR experiences?
AR design challenges include managing device limitations, maintaining realism across varied environments, and creating intuitive interactions that feel natural. Testing in multiple real-world settings and iterating based on feedback is essential to tackle these challenges.
How does haptic feedback enhance AR experiences?
Haptic feedback provides a tactile layer to AR, allowing users to “feel” interactions through subtle vibrations or force feedback. This can make virtual objects feel more real and responsive, adding a dimension of physicality to digital elements that deepens immersion.
How do designers ensure that AR objects align accurately in real-world environments?
To achieve precise alignment, designers use spatial tracking and object anchoring technologies. These tools analyze a user’s surroundings and place virtual objects in specific locations, ensuring that objects remain fixed in place even as the user moves. Depth-sensing and object recognition technologies also help AR elements interact realistically with the real world.
Why is lighting consistency so crucial in AR?
Lighting consistency makes AR objects feel believable. If a virtual object’s lighting doesn’t match the environment, it looks out of place and disrupts immersion. Designers use dynamic lighting and shading techniques that adapt to the real-time environment, like shadows that fall correctly and highlights that mimic natural light.
How does depth perception impact AR design?
Depth perception is key for making virtual objects appear naturally integrated with real-world settings. Without it, objects might look “flat” or poorly placed. Designers use depth cues such as overlapping, shadow casting, and size scaling to make virtual items appear correctly in relation to their physical surroundings, enhancing realism.
Can AR support multiple users at once?
Yes, multi-user AR is possible and increasingly popular. This allows users to share the same AR experience in real-time, which is especially useful for games, collaborative design, and social applications. Designers tackle synchronization and lag issues to ensure a smooth, unified experience across devices, making shared AR interactions feel seamless.
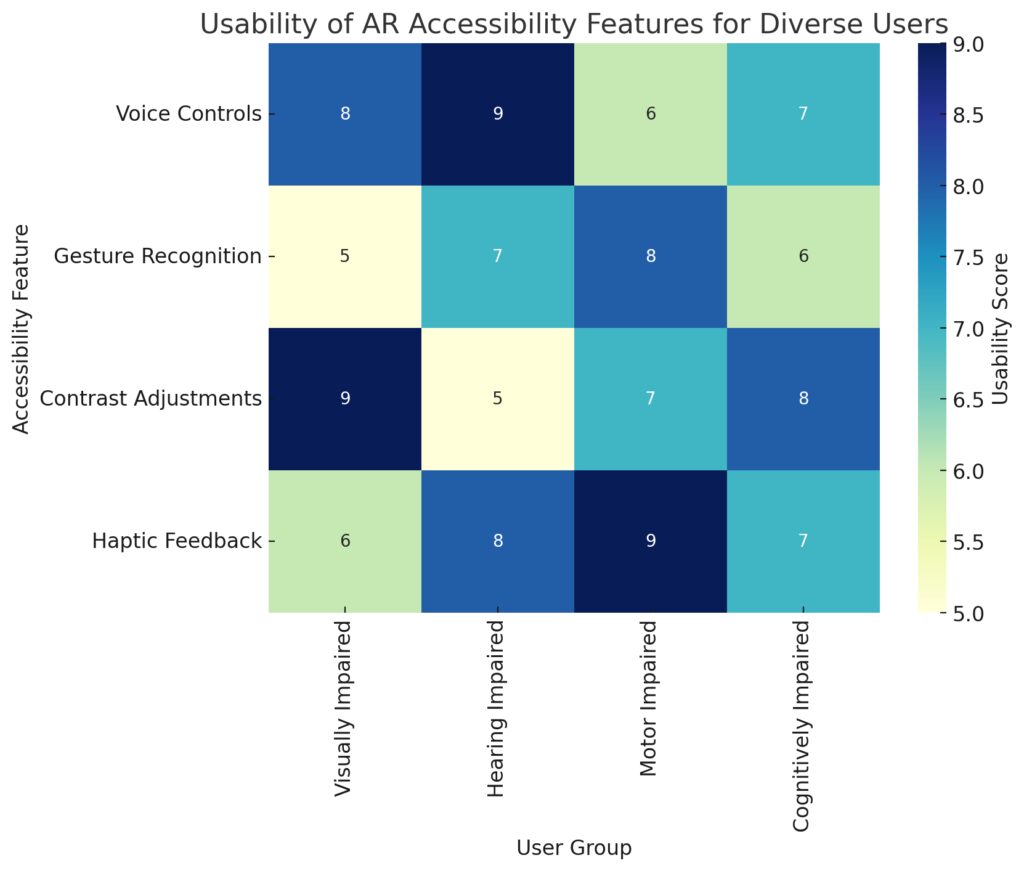
How do designers approach accessibility in AR?
Accessibility in AR involves making experiences intuitive and usable for people of all abilities. Designers consider voice control, gesture recognition, and simple visual cues to make interactions accessible. They also design with customizable text sizes, colors, and contrast levels to support users with visual impairments.
What are some common applications of AR in e-commerce?
AR in e-commerce allows users to “try before they buy,” enhancing shopping experiences by letting customers place virtual products in their homes. This is especially popular in furniture and home decor, as well as fashion, where users can try on clothes or accessories virtually. It’s a powerful way to help customers make informed decisions.
How do UX/UI designers handle navigation in AR environments?
Navigation in AR can be challenging since traditional screen-based menus don’t always work. Designers often rely on gesture-based controls, voice commands, and icon cues to guide users. They ensure that controls are easy to find but unobtrusive, so users can explore the real and virtual worlds without interruption.
What are the ethical considerations in AR design?
Ethics in AR design focus on privacy, consent, and user safety. Since AR can capture and display real-world environments, designers must be careful with data handling and transparency. There’s also an emphasis on responsible use, ensuring AR elements don’t interfere with a user’s surroundings or create distractions that could pose safety risks.