With companies worldwide aiming to reduce their environmental impact, Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is emerging as a powerful ally in this mission.
By improving efficiency and reducing resource waste, RPA helps organizations streamline workflows and tackle sustainability challenges.
Understanding RPA’s Role in Sustainability
What is RPA and How Does It Work?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) uses software “robots” to automate repetitive tasks that typically require human effort. These robots handle tasks like data entry, processing transactions, and managing databases, allowing teams to focus on more strategic projects. Through digital transformation, RPA enhances operational efficiency, and its automation capabilities offer a way to reduce environmental impacts across sectors.
RPA doesn’t just simplify tasks—it can significantly cut down on resource waste. By automating mundane processes, organizations can save energy and reduce their carbon footprint. Automation makes it possible to reduce manual, resource-heavy tasks, ultimately helping companies work more sustainably.
The Environmental Impact of Digital Efficiency
Every digital transaction consumes energy, from processing emails to running cloud-based applications. By using RPA to streamline workflows, businesses can reduce the cumulative energy cost of these transactions. This isn’t only beneficial for cost reduction—it directly aligns with environmental goals by lowering energy consumption and carbon emissions.
Some industries, particularly those with high data-processing needs, can significantly benefit. Banks, insurers, and retailers, for example, can achieve notable environmental savings by reducing the processing time and energy required for large data operations.
Leveraging RPA to Optimize Resource Allocation
Automation technologies help organizations become more resource-efficient by optimizing how they allocate energy, labor, and time. For instance, automated systems can consolidate operations that were once fragmented, reducing the need for duplicated resources. When fewer resources are needed, less waste is generated, contributing to a circular economy and fostering more sustainable practices within the organization.
By shifting to automated workflows, companies not only increase productivity but also eliminate the need for excessive hardware, which reduces the overall environmental burden of their operations.
Real-World Applications of RPA in Sustainable Practices
Reducing Paper Usage with Digital Workflows
One of the most straightforward ways RPA supports sustainability is by digitizing paper-intensive processes. Traditional administrative workflows, from invoice processing to record-keeping, typically rely heavily on paper. By automating these workflows, companies can make substantial reductions in their paper usage, contributing directly to forest conservation and reducing waste in landfills.
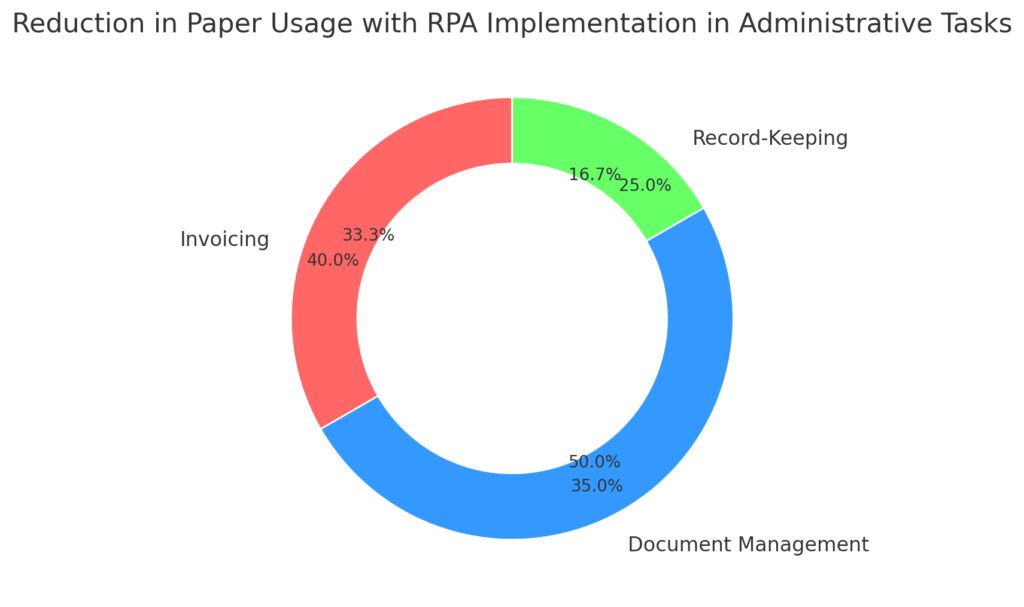
Outer Ring (Before RPA): Shows paper usage in each area before automation, with distinct colors.
Inner Ring (After RPA): Highlights the reduction in paper consumption for Invoicing, Document Management, and Record-Keeping post-automation.
Many companies are also using cloud storage to archive documents digitally rather than physically, cutting down the need for paper files and storage space. Implementing RPA-powered digital processes creates a more sustainable office environment and aligns with broader environmental policies.
Lowering Energy Consumption in IT Operations
Data centers are among the largest consumers of energy, with IT operations contributing significantly to a company’s carbon footprint. By deploying RPA to manage IT workflows—such as batch processing, system monitoring, and data migration—companies can optimize server use, reducing the energy required to power large-scale IT operations.
For example, automation can reduce the need for 24/7 server activity by scheduling tasks only when required, which means less power consumption during off-peak hours. RPA helps minimize resource drain and keep IT operations sustainable by using computational power more strategically.
Supply Chain Optimization for Reduced Emissions
In logistics and manufacturing, RPA is used to automate supply chain management processes that can lead to a decrease in carbon emissions. Automating inventory management, order processing, and distribution scheduling can help companies reduce emissions associated with transportation and warehousing.
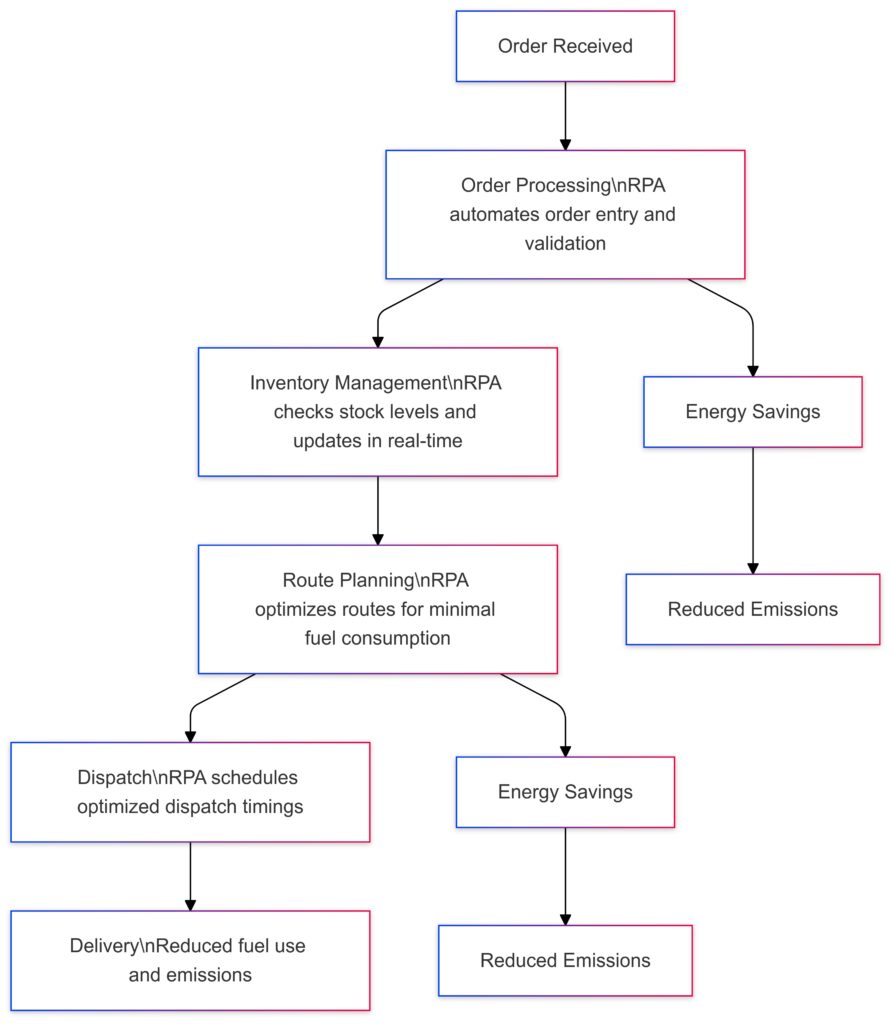
Order Processing: RPA automates order entry and validation, improving speed and accuracy.
Inventory Management: RPA checks stock levels in real-time, ensuring efficient stock use and avoiding excess storage energy.
Route Planning: RPA optimizes routes for minimal fuel consumption, reducing emissions.
Dispatch Scheduling: RPA coordinates optimal dispatch timings to avoid peak traffic, further lowering fuel usage.
Each step incorporates Energy Savings and Emissions Reduction, with RPA especially enhancing route planning and dispatch logistics for sustainability.
For instance, RPA can optimize delivery routes, reducing the fuel consumption of trucks, or automate demand forecasting to prevent overproduction and excess inventory. By lowering emissions and reducing waste, companies can better align their operations with sustainability goals.
Enhancing Sustainable Reporting with RPA
Automating Data Collection for Environmental Reporting
Companies are increasingly accountable for their environmental footprint, and reporting standards have become more stringent. However, collecting and analyzing data for sustainability reports can be time-intensive and prone to errors. RPA simplifies this process by automating data collection from multiple sources, including energy usage metrics, waste output, and carbon emissions data.
By implementing RPA for automated data collection, companies can efficiently compile accurate reports that comply with environmental regulations. This not only supports transparency but also helps organizations track their progress toward sustainability goals in real-time, enabling quicker response to any deviations from their targets.
Improving Accuracy in Compliance Reporting
Compliance with environmental standards is critical, and manual reporting processes can sometimes result in errors that lead to regulatory penalties. RPA improves the accuracy of sustainability compliance reporting by standardizing data collection methods and automating calculations for emissions, waste, and energy consumption metrics.
Through automation, companies can ensure that their reporting meets ISO standards or the guidelines of the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), reducing the risk of inaccuracies.
Promoting a Green Workplace Through RPA
Minimizing Employee Commute with Remote Automation
With the rise of remote work, companies are embracing RPA to further reduce their carbon footprint. By automating tasks that employees typically handle on-site, RPA allows for more remote operations, cutting down on daily commutes. This approach can result in significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions associated with commuting and support employees in maintaining a lower carbon lifestyle.
RPA technology enables secure, seamless operations from anywhere, reducing the need for physical office presence and the associated energy consumption. For organizations with hybrid work models, RPA is a powerful tool to enhance efficiency while supporting a more eco-friendly workplace culture.
Smart Energy Management in Office Spaces
For organizations that require physical office spaces, energy management is a key area where RPA can make a difference. Automation software can monitor and control lighting, heating, and cooling systems to reduce unnecessary energy use. For example, RPA systems can adjust thermostat settings based on real-time occupancy data, ensuring that office spaces are only heated or cooled as needed.
By integrating RPA with IoT sensors, companies can create smart energy systems that automatically reduce energy consumption during off-hours, lowering electricity bills and reducing the environmental impact of office operations.
Encouraging Paperless Work Environments
As companies move towards paperless office initiatives, RPA plays a central role in transitioning away from traditional paperwork. Tasks that once required physical documents, such as approvals, invoices, and contract management, can now be digitized and automated. RPA tools can route, approve, and archive documents in secure digital storage systems, eliminating the need for printed copies.
This shift not only conserves paper but also reduces the need for physical storage space and the associated costs. A paperless environment also enhances data security, since digital documents are easier to track, encrypt, and control access to, ultimately supporting a sustainable and secure office model.
Long-Term Benefits of RPA for Sustainable Business Growth
Reducing Operational Waste and Optimizing Resources
By eliminating inefficiencies, RPA minimizes waste throughout business operations. For example, when companies use RPA to automate procurement or production scheduling, they can more accurately predict demand, preventing overproduction and reducing surplus inventory that often goes to waste. Smarter resource management results in less energy, water, and raw materials consumed, contributing to the overall sustainability of operations.
Additionally, by automating routine tasks, companies reduce the need for single-use office supplies and unnecessary equipment, fostering a more streamlined, eco-friendly workplace.
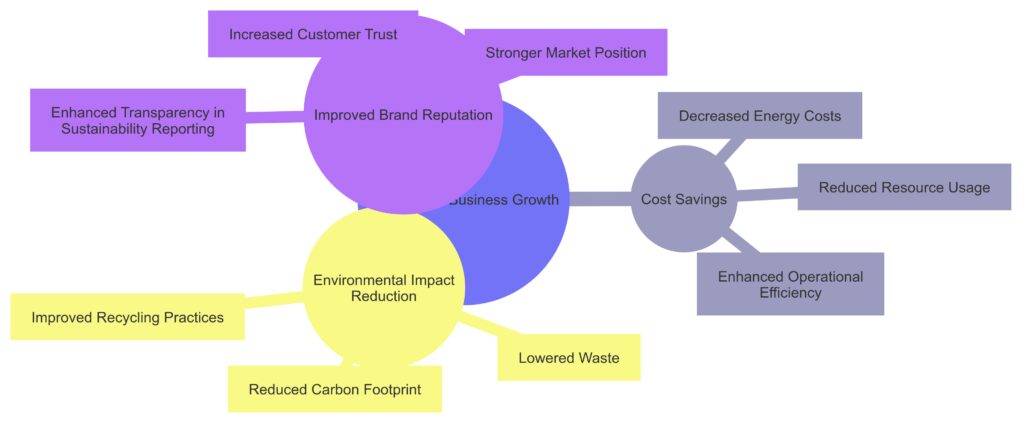
Environmental Impact Reduction: Lowering waste, reducing the carbon footprint, and improving recycling practices.
Improved Brand Reputation: Enhancing transparency in sustainability reporting, boosting customer trust, and strengthening market position.
Building a Sustainable Brand Image
As consumers increasingly favor environmentally responsible companies, RPA can support brand reputation by demonstrating a commitment to sustainability. Businesses that automate to reduce waste, conserve energy, and limit emissions can leverage these initiatives in their brand messaging, positioning themselves as leaders in environmental stewardship.
Moreover, RPA-driven improvements in compliance reporting allow companies to showcase their eco-friendly practices transparently, which helps attract eco-conscious customers and investors. This sustainable image not only improves public perception but also opens doors to green partnerships and certifications, further enhancing business growth.
Scaling Sustainable Practices Across Departments
RPA is a scalable solution, making it easy to extend sustainable practices across multiple departments and locations. For instance, companies can initially automate key processes within their HR, finance, or customer service departments and then expand RPA to other areas such as logistics or production. This scalability allows organizations to implement sustainable practices consistently, fostering a unified, environmentally conscious culture.
By scaling RPA solutions, companies can amplify their impact, ensuring that sustainable operations are practiced across the organization, from local offices to global divisions.
Overcoming Challenges to Sustainable RPA Implementation
Balancing Initial Investment with Long-Term Gains
While the benefits of RPA for sustainability are significant, the initial investment can be a barrier. Some companies may hesitate to adopt RPA due to upfront costs for software, training, and system integration. However, these costs are often outweighed by long-term savings on resources and reduced waste.
To ease this transition, companies can begin by targeting high-impact areas for automation, such as paper reduction or energy management. By tackling smaller projects first, businesses can generate initial savings that justify further RPA investment, allowing for a gradual, cost-effective transition.
Ensuring Compatibility with Existing Systems
Successful RPA implementation relies on compatibility with existing IT systems, which can sometimes pose a challenge. Legacy systems may not integrate seamlessly with RPA tools, making it difficult to fully automate processes. However, many RPA providers offer flexible, customizable solutions that can work alongside various software platforms and hardware setups.
Companies can mitigate this challenge by partnering with experienced RPA vendors who can tailor solutions to their unique technology stack. By ensuring compatibility, organizations can enjoy the benefits of automation without requiring a complete overhaul of existing systems.
Managing the Environmental Impact of RPA Infrastructure
While RPA reduces resource consumption, it still requires an IT infrastructure to operate, which itself consumes energy. As companies increase their use of automation, they must manage the energy demands of these digital tools to avoid offsetting the environmental gains. Implementing RPA in conjunction with green IT practices—such as cloud-based systems powered by renewable energy—can help companies minimize RPA’s energy footprint.
By adopting sustainable data practices, businesses can fully leverage RPA’s environmental benefits while ensuring that their automation strategy aligns with a greener IT infrastructure.
Future Trends: RPA Innovations Supporting Sustainability
AI-Enhanced RPA for Smarter Environmental Solutions
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) advances, integrating AI with RPA can take automation’s impact on sustainability to a new level. AI-enhanced RPA can analyze large data sets to identify patterns in energy use, resource consumption, and waste production, enabling organizations to make smarter environmental decisions.
For example, an AI-powered RPA system could predict periods of high energy demand and automatically adjust operations to optimize energy use. This predictive capability helps companies proactively manage resources, reduce waste, and further lower their carbon footprint. Such intelligent automation will play a central role in sustainable business innovation as industries evolve.
Integrating RPA with IoT for Real-Time Monitoring
The Internet of Things (IoT) can transform RPA from a tool for static tasks into a dynamic solution for real-time environmental monitoring. By integrating RPA with IoT devices, organizations can gather live data on factors like water consumption, waste levels, and greenhouse gas emissions. This data enables RPA to make immediate adjustments, such as shutting off unused equipment or optimizing energy-intensive machinery.
IoT-driven RPA can also be used in smart buildings to monitor and control lighting, heating, and ventilation systems, ensuring these systems operate at peak efficiency without manual intervention. With IoT-powered automation, companies can better control their environmental impact on a continuous basis.
Blockchain and RPA for Transparent Sustainability Tracking
Blockchain, known for its secure, transparent data tracking, is an emerging technology in sustainability. Combined with RPA, blockchain can provide a verifiable record of sustainability metrics, from resource use to emissions data. This transparency is invaluable for companies needing to verify their compliance with environmental regulations or prove their sustainability claims to stakeholders.
RPA can automate the collection of data that blockchain secures, making sustainability reporting more reliable and accessible. Through blockchain and RPA, companies can establish trust in their sustainability practices, which helps in building credibility with eco-conscious consumers and investors alike.
The Broader Impact of RPA on Global Sustainability Goals

Contributing to Carbon Neutrality and Climate Goals
With countries worldwide committing to net-zero emissions, RPA provides businesses with an actionable path to contribute to these climate targets. By reducing emissions across supply chains, operations, and IT systems, RPA helps companies align with global initiatives like the Paris Agreement.
In sectors like manufacturing and logistics, automation can lead to substantial carbon reductions. For example, automated energy management in production facilities can reduce emissions, while RPA-enabled route optimization in logistics reduces transportation fuel use. Together, these efficiencies make significant contributions to carbon neutrality goals.
Supporting Circular Economy Principles
The circular economy seeks to reduce waste by keeping resources in use for as long as possible through recycling, reusing, and repurposing. RPA can facilitate circular practices by automating resource recovery, tracking product life cycles, and optimizing recycling processes. For instance, automation in inventory management can help minimize excess production, which reduces waste.
In addition, RPA can monitor and record the use of raw materials, ensuring resources are effectively tracked from production to end-of-life. By encouraging sustainable resource use, RPA promotes circular economy principles, helping industries transition from a linear to a circular model.
Empowering Sustainable Decision-Making in Organizations
Data-driven decision-making is essential for effective sustainability strategies, and RPA enhances this by automating real-time data collection and analysis. Organizations can use RPA-generated insights to make informed choices about energy use, resource allocation, and waste reduction. For instance, an RPA system can continuously analyze production efficiency, helping decision-makers adjust strategies based on current environmental performance.
With RPA, organizations can move from reactive to proactive sustainability strategies, where they anticipate challenges and adjust accordingly. This adaptability is crucial for businesses aiming to remain competitive while adhering to environmental standards and fostering a culture of sustainability.
Why RPA is Essential for a Sustainable Future
As businesses face increasing pressure to operate sustainably, RPA is proving to be an essential tool in the journey toward greener practices. By streamlining operations, reducing resource consumption, and supporting sustainable reporting, RPA directly addresses many environmental challenges that companies face today.
Looking forward, automation technologies like RPA are likely to become even more integral to sustainable business practices as they continue to evolve alongside AI, IoT, and blockchain. The future of sustainability in business will depend heavily on innovation, and RPA is well-positioned to help organizations meet their environmental goals while enhancing efficiency and growth.
In a world where sustainability is no longer optional, RPA offers a practical, scalable solution for businesses committed to making a positive environmental impact. By embracing RPA, companies can support a more sustainable future, proving that automation and environmental responsibility can go hand in hand.
FAQs
What are some challenges of implementing RPA for sustainability?
Some challenges include the initial investment required for RPA setup, compatibility issues with existing systems, and managing the energy demands of RPA infrastructure. Companies can address these by starting with high-impact areas, partnering with flexible RPA providers, and implementing green IT practices to minimize the environmental impact of RPA.
Can RPA support circular economy practices?
Yes, RPA can facilitate circular economy practices by automating processes that track product lifecycles, manage resource recovery, and reduce overproduction. RPA helps optimize resource use and minimize waste, aligning company operations with circular economy principles.
How will future technologies like AI and IoT impact RPA’s role in sustainability?
Future technologies like AI and IoT will enhance RPA’s impact on sustainability by enabling real-time monitoring, predictive analytics, and intelligent decision-making. For example, AI can help RPA optimize energy use based on usage patterns, while IoT can provide live data for immediate adjustments, making RPA-driven operations even more sustainable.
Is RPA a long-term sustainable solution for businesses?
Absolutely. RPA offers a scalable, flexible, and efficient way for companies to meet long-term sustainability goals. As businesses face growing environmental responsibilities, RPA provides a practical solution to streamline operations, reduce emissions, and foster sustainable practices across all departments.
How can RPA support remote work to reduce environmental impact?
RPA allows many tasks traditionally performed on-site to be automated and completed remotely, supporting a remote workforce and reducing the need for employee commutes. This shift lowers greenhouse gas emissions associated with daily travel and reduces office resource use, such as energy and paper, contributing to an overall reduction in the organization’s environmental footprint.
Is RPA energy-intensive, and how do companies manage this?
While RPA does require energy to operate, it’s typically less than the cumulative energy used in manual, repetitive tasks that involve equipment, paper, and in-person logistics. Companies can manage RPA’s energy needs by using cloud-based solutions powered by renewable energy sources and by optimizing RPA tools to run only when necessary, reducing any excess power use.
How does RPA integrate with other green IT initiatives?
RPA can be integrated with green IT strategies by pairing it with cloud computing, IoT devices, and AI-driven energy management systems. This integration allows RPA to work within energy-efficient infrastructures, helping to further reduce overall power consumption. Additionally, RPA can automate processes that monitor and adjust other IT systems to ensure optimal energy usage, supporting a sustainable tech ecosystem.
Can RPA assist in environmental compliance?
Yes, RPA can be programmed to gather, track, and analyze data required for environmental compliance with various standards, such as ISO or GRI. By automating compliance reporting, RPA reduces human error and ensures accurate tracking of sustainability metrics. This not only helps companies avoid regulatory issues but also enables proactive improvements in their environmental practices.
How does RPA impact waste reduction in production?
In production, RPA can automate inventory management, demand forecasting, and supply chain operations to reduce overproduction, which minimizes waste. By only producing and storing the necessary amount of goods, companies can avoid excessive resource use and reduce waste, which is especially important in industries like manufacturing, retail, and food production.
Is RPA effective for small businesses pursuing sustainability goals?
Yes, RPA can be very effective for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) seeking sustainable practices. Many RPA solutions are scalable and customizable, allowing smaller businesses to automate high-impact areas without needing significant upfront investment. By streamlining tasks like document processing and energy monitoring, RPA helps SMEs reduce costs and operate sustainably.
How can RPA help in tracking Scope 3 emissions?
RPA can automate the data collection process needed to track Scope 3 emissions, which include indirect emissions from supply chains, product use, and waste disposal. By gathering and analyzing data from suppliers and partners, RPA supports companies in gaining insights into their total environmental impact, including emissions generated outside their direct operations.
How does RPA promote sustainable digital transformation?
RPA enables digital transformation by automating manual, resource-heavy processes and migrating to digital, paperless workflows. This shift reduces reliance on physical resources, encourages a digital-first approach, and supports broader sustainability goals within the organization. By adopting RPA, companies build a foundation for further digital advancements that are aligned with environmental responsibility.
Resources
Environmental Benefits of RPA in Business Operations
- Description: This article explores how RPA reduces carbon emissions, minimizes waste, and improves energy efficiency across various sectors.
- Link: Deloitte Insights on RPA and Sustainability
The Role of RPA in Achieving a Circular Economy
- Description: A detailed examination of how RPA supports circular economy practices, including resource recovery, waste reduction, and efficient inventory management.
- Link: World Economic Forum – Circular Economy and Digital Transformation
How IoT and RPA Combine for Sustainable Solutions
- Description: This resource explains the synergy between RPA and IoT in promoting sustainable, real-time energy monitoring, equipment management, and automated systems.
- Link: IBM – IoT and RPA for Sustainable Operations
Sustainability Reporting with RPA: Enhancing Transparency and Accuracy
- Description: Focuses on how companies can use RPA to automate data collection, improve compliance reporting, and meet global environmental standards.
- Link: Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
AI-Enhanced RPA for Predictive Sustainability
- Description: Learn how AI-powered RPA improves resource allocation, predicts energy needs, and reduces waste through smart automation.
- Link: McKinsey & Company on AI and Sustainability
RPA in the Supply Chain: Reducing Carbon Footprint
- Description: An analysis of how RPA optimizes supply chain logistics, reducing emissions associated with transportation and warehousing.
- Link: Supply Chain Dive – RPA in Logistics and Sustainability
Green IT Practices with RPA Integration
- Description: This guide outlines best practices for implementing RPA alongside green IT initiatives, focusing on energy efficiency and sustainable IT infrastructure.
- Link: Green IT Guide by TechRepublic
Future Trends in RPA and Environmental Impact
- Description: Provides insights into emerging technologies like blockchain, IoT, and AI, and how they are shaping the future of sustainable automation.
- Link: Forbes – The Future of RPA and Sustainability