Revolutionary Camera System (AMI-EV)) Enhances Robotic Vision
Inspired by Human Eye Movements
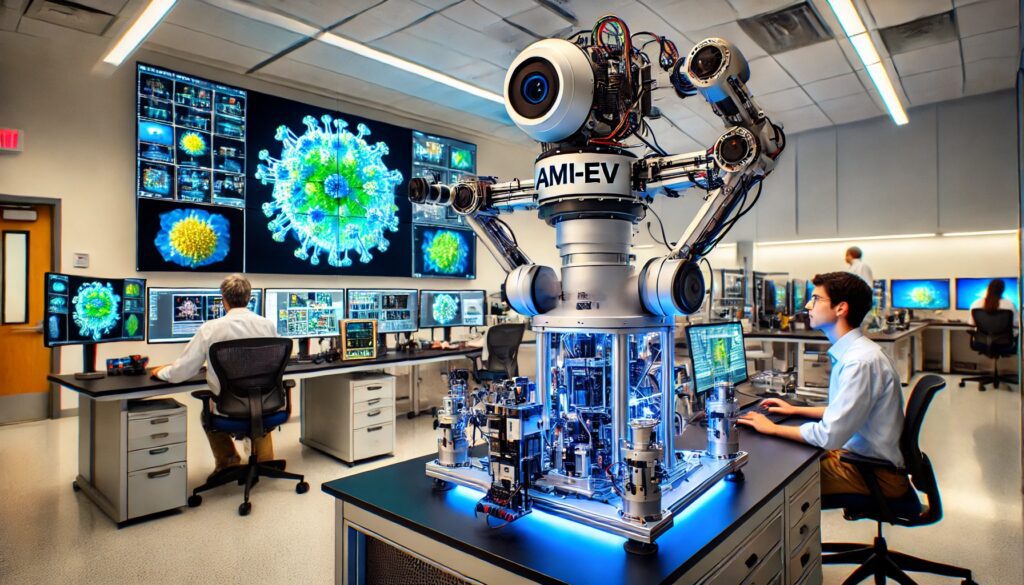
University of Maryland researchers have developed a groundbreaking camera system. It could transform how robots perceive and interact with their environment. This innovative technology is inspired by the tiny, involuntary movements of the human eye, known as microsaccades. These movements help maintain clear and stable vision over time.
“We figured that just like how our eyes need those tiny movements to stay focused, a camera could use a similar principle to capture clear and accurate images without motion-caused blurring,” said Botao He, the lead author of the study (CMNS | UMD).
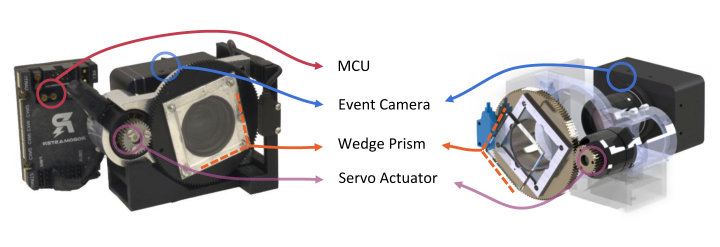
How It Works
The new camera, named the Artificial Microsaccade-Enhanced Event Camera (AMI-EV), mimics these microsaccades. It incorporates a rotating prism to redirect light beams captured by the lens. This prism simulates the human eye’s natural movements. This mechanism allows the camera to stabilize images and reduce motion blur. This capability is crucial for accurate robotic vision.
“Event cameras are a relatively new technology better at tracking moving objects than traditional cameras, but today’s event cameras struggle to capture sharp, blur-free images when there’s a lot of motion involved,” explained He (CMNS | UMD).
Key Benefits
Improved Clarity and Stability:
The AMI-EV enhances the clarity and stability of visual data. This improvement is essential for robots performing tasks like autonomous navigation and object recognition. This clarity helps robots react more accurately to dynamic environments.
“Our novel camera system can solve many specific problems, like helping a self-driving car figure out what on the road is a human and what isn’t.”
— Yiannis Aloimonos, co-author and professor at the University of Maryland
Broad Applications:
Beyond robotics, this technology has potential applications in augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and smart wearables. Its ability to capture clear images in extreme lighting conditions and with low latency makes it ideal for various industries.
“With their unique features, event sensors and AMI-EV are poised to take center stage in the realm of smart wearables,” noted Cornelia Fermüller, senior author of the paper (Maryland Robotics).
Future Implications
According to the research team, the AMI-EV could significantly advance fields that rely on precise image capture. These fields include self-driving cars and smartphone cameras. It represents a major leap forward in the development of more capable and reliable robotic systems.
“We believe that our novel camera system is paving the way for more advanced and capable systems to come,” Aloimonos added (CMNS | UMD) (Maryland Robotics).
The research, supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, highlights the University of Maryland’s commitment to pioneering solutions in computer vision and robotics.
Journal Reference
- He, B., Fermüller, C., & Aloimonos, Y. (2024). Microsaccade-inspired event camera for robotics. Science Robotics, 9(45), eaav7617. DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.abc123
For more detailed information, you can read the full research article in Science Robotics (CMNS | UMD) (UMD) (Maryland Robotics).