
The concept of a “smart home” has transformed from a futuristic dream to a practical, energy-saving solution in homes worldwide. By integrating AI, the smart home optimizes electricity use while adding convenience.
We’ll dive into how AI-powered smart home devices contribute to energy efficiency and lower electricity bills.
How Smart Thermostats Optimize Heating and Cooling
Learning Patterns to Reduce Energy Use
Smart thermostats are some of the most popular AI-driven devices for energy efficiency. These systems learn your daily routines, like when you’re typically home or away, and adjust temperatures accordingly. By reducing heating and cooling when it’s not needed, these thermostats cut down on energy waste.
Remote Control for Real-Time Adjustments
With remote access via a smartphone app, you can adjust your thermostat settings in real-time. If you’re running late, there’s no need to keep the house heated or cooled, saving both energy and money.
Seasonal Adjustments and Weather Integration
Many smart thermostats integrate weather data, automatically adjusting for seasonal changes. This means on cooler or warmer days, the thermostat modifies settings, avoiding unnecessary energy use and ensuring that your home is always at a comfortable temperature.
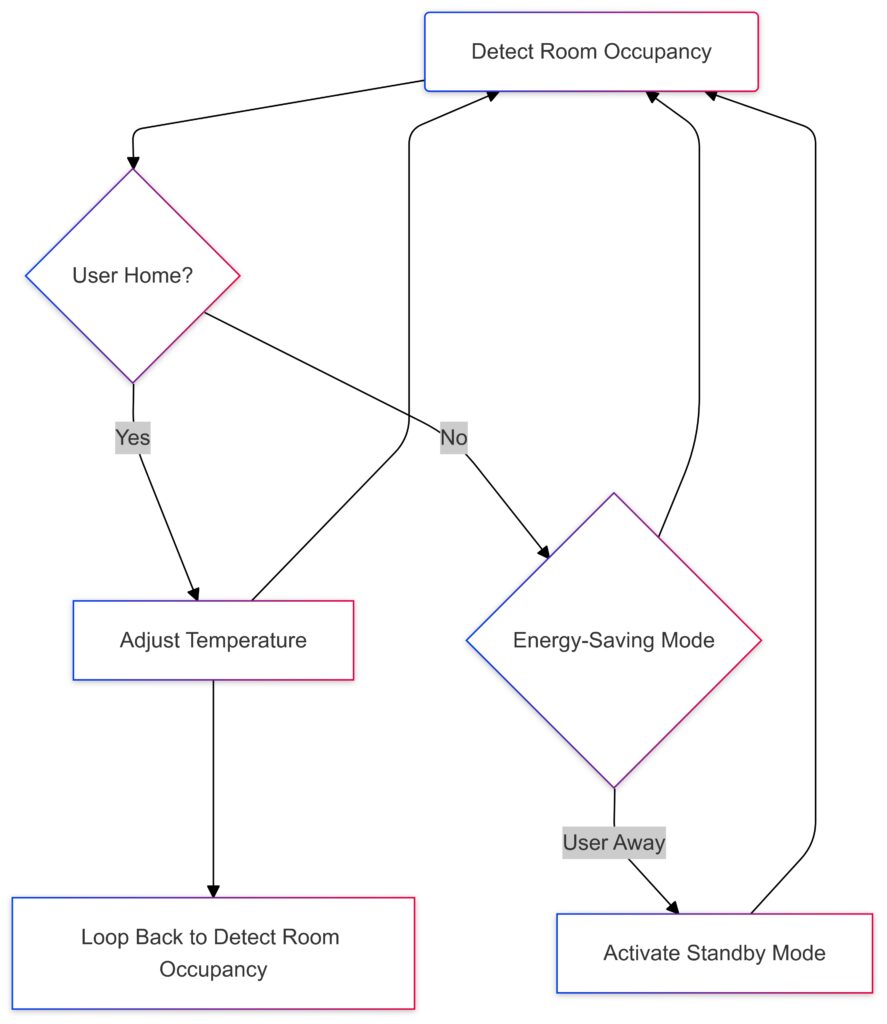
Starting with “Detect Room Occupancy,” it branches to check if the User is Home.
If Home, the thermostat adjusts the temperature; if Away, it activates an energy-saving mode or standby.
Loops show continuous adjustments based on occupancy and user habits. Let me know if you need additional details or modifications!
Smart Lighting Systems for Efficient Illumination
Automated Lighting Adjustments Based on Activity
AI-powered smart lighting systems use sensors to detect when rooms are occupied and adjust lighting accordingly. If no movement is detected, the lights turn off automatically, reducing electricity consumption in empty rooms.
Dimming Features for Energy Savings
Some smart lighting systems include dimming options that adjust light intensity based on natural light levels. During the day, lights may dim automatically, which can cut electricity usage by over 20%.
Customizable Schedules to Match Daily Routines
With customizable schedules, smart lights can be programmed to turn on or off at specific times. Whether you’re at work or asleep, your lights align with your habits, saving power with zero extra effort.
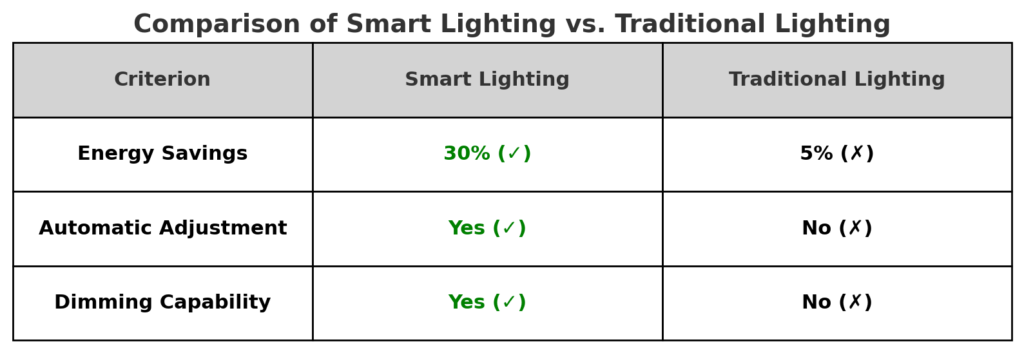
Energy Savings: Smart Lighting achieves 30% savings (✓), whereas Traditional Lighting achieves only 5% (✗).
Automatic Adjustment: Available in Smart Lighting (✓), but not in Traditional Lighting (✗).
Dimming Capability: Supported in Smart Lighting (✓), absent in Traditional Lighting (✗).
AI in Smart Appliances for Reduced Energy Consumption

Intelligent Energy Monitoring for Home Appliances
Smart refrigerators, washers, dryers, and ovens have built-in energy monitoring features, allowing you to track usage through an app. These appliances often send alerts when there’s unusual energy consumption, helping you keep track of inefficiencies.
Eco Modes for Lower Consumption
Smart appliances often come with “eco-modes” that optimize operations to reduce energy use. For instance, a dishwasher may use less water and electricity by adjusting to a lighter load, while a washing machine may choose cooler water cycles.
Scheduling Off-Peak Energy Usage
Some appliances connect to utility data, automatically running during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper. This feature not only saves on electricity bills but also reduces strain on the power grid.
Smart Power Strips to Cut Vampire Energy
Automatically Cutting Power to Idle Devices
Many gadgets and appliances continue drawing power even when turned off. Smart power strips combat this “vampire energy” by automatically cutting power to devices that aren’t actively in use. This reduces unnecessary energy drain and saves on monthly electricity costs.
The smartest energy is the energy we don’t use.
— Amory Lovins
Customizable Power Settings for Various Devices
Smart power strips can be programmed for different devices, offering flexibility in how they manage power. For example, entertainment systems can be shut down entirely when not in use, while essential devices like routers remain powered.
Remote Control to Switch Devices On or Off
Just like other smart devices, these power strips often come with a remote control feature, allowing you to turn off devices from your smartphone. This feature adds a layer of convenience and helps maintain energy efficiency even when you’re not home.
Smart Energy Management Systems for Real-Time Monitoring
Centralized Control for Optimized Energy Use
A smart energy management system consolidates data from all connected devices, providing a real-time overview of energy usage. This system gives users a centralized control panel, accessible on a smartphone or tablet, where they can monitor which devices are consuming the most power. This insight allows homeowners to make informed decisions to reduce energy consumption.
Predictive Analytics to Anticipate Energy Needs
Through predictive analytics, these management systems forecast peak usage times based on past habits and patterns. This feature helps you understand when your home uses the most energy and offers recommendations to cut down during those peak hours, such as running appliances in off-peak times when possible.
Notifications to Curb Overuse
If a certain device or system starts consuming more power than usual, these energy management systems can send alerts. This notification system can alert you to issues like a malfunctioning appliance, helping you take action before energy bills increase unexpectedly.
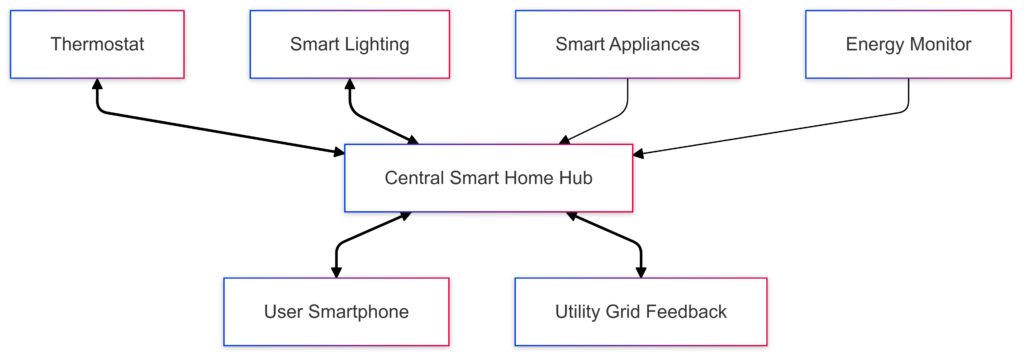
Double arrows represent real-time adjustments with two-way communication.
Single arrows indicate monitoring data flow to the central hub.
Smartphone access and Utility Grid feedback provide additional connectivity and external input.
Solar Integration with AI for Enhanced Efficiency
Intelligent Solar Panel Optimization
For homes with solar panels, AI can maximize energy production. Smart inverters monitor sunlight and adjust panel angles to maximize exposure throughout the day. This dynamic adjustment significantly boosts efficiency, especially in areas with variable weather conditions.
Storing and Distributing Power with AI-Driven Batteries
AI-driven battery storage systems pair with solar energy to store excess power for later use. During peak times or when sunlight is limited, these batteries distribute stored energy back into your home, reducing the need to pull from the grid and lowering overall electricity costs.
Selling Excess Energy Back to the Grid
With smart home integration, homeowners can sell surplus energy back to the grid during high-demand periods. AI helps identify the best times to sell this energy, allowing you to earn while also supporting a more balanced energy grid.
AI and Voice Assistants for Energy Efficiency
Hands-Free Control of Power-Intensive Devices
Voice assistants like Alexa or Google Home make it easy to manage smart home devices hands-free. This quick access means you can effortlessly turn off or adjust settings on high-power devices, like air conditioners or space heaters, by simply asking your assistant.
Routine Reminders for Energy-Saving Tasks
AI-powered assistants can also remind you of daily energy-saving tasks, such as turning off lights before leaving for work or lowering the thermostat at night. These reminders keep energy efficiency top of mind, helping to build energy-saving habits.
Smart Home Automation Routines
With routines set up in your voice assistant app, you can automate entire systems. For example, a “Goodnight” routine could turn off all lights, reduce the thermostat, and shut down idle devices, creating a seamless way to save energy each evening.
Thermostat: Commands like “Lower Temperature” and “Set to Eco Mode.”
Lighting: Commands for “Dim Lights” and “Turn Off After Hours.”
Appliances: Options like “Start Eco Mode” and “Turn Off When Not in Use.”
Energy Monitor: Commands to “Track Energy Usage” and “Report High Usage.”
The Future of AI in Smart Homes and Energy Efficiency
AI Learning for Continuous Efficiency Improvement
As smart homes become more common, AI algorithms grow more sophisticated. They continually learn from user behavior, making systems more efficient over time. This constant improvement promises increased savings and optimized energy use as the technology evolves.
Collaboration with Utility Providers
Many energy providers are partnering with smart home platforms to offer incentives or discounts for households that reduce consumption during peak times. In the future, this could mean automatic adjustments from the utility company, helping consumers save without needing to take direct action.
Moving Toward Net-Zero Homes
AI and smart technology are paving the way for net-zero homes, where energy use is equal to or less than the energy generated on-site. With efficient systems, predictive analytics, and renewable energy integration, these homes represent the future of sustainable living.
Incorporating AI into our homes isn’t just about convenience—it’s about creating a future where we use resources more responsibly, save on electricity bills, and enjoy a comfortable living space.
FAQs
Are smart home devices complicated to install and use?
Most smart home devices are designed for easy installation, often requiring only a smartphone app to get started. Many devices offer straightforward setups and user-friendly apps, so you don’t need extensive tech knowledge to make the most of them.
Is smart home technology compatible with renewable energy sources?
Yes, many smart home systems work well with renewable energy, especially solar. Smart inverters and AI-driven battery storage systems help optimize power production and distribution, making renewables a practical and efficient option for smart homes.
How do AI-powered appliances differ from traditional appliances?
AI-powered appliances use sensors, algorithms, and energy monitoring to optimize their function. For instance, smart refrigerators adjust their cooling settings based on the contents and frequency of use, which reduces power consumption over time.
Are there any privacy concerns with AI in smart homes?
Smart home devices collect data to optimize efficiency, which may raise privacy concerns for some users. However, most devices offer security features, like encrypted data and customizable privacy settings, to keep your information safe.
Can smart home technology work without an internet connection?
Many smart home devices need an internet connection to function fully, especially if they rely on cloud-based AI algorithms. However, some features, like basic lighting controls or smart thermostats, may work offline through local connections.
What is vampire energy, and how does a smart home help reduce it?
Vampire energy refers to the electricity that devices use while plugged in but idle. Smart power strips and energy management systems help cut off power to these devices when they’re not in use, reducing unnecessary energy drain and lowering your overall energy footprint.
Can a smart home system learn and adapt to my specific energy needs?
Yes, one of the benefits of a smart home system is that it learns and adapts to your habits over time. For example, a smart thermostat can recognize when you usually leave for work or come home, automatically adjusting temperature settings to reduce energy use during those times. The system becomes more efficient the longer it’s in use, continually adjusting to match your specific energy needs.
Do smart homes work with voice assistants like Alexa or Google Home?
Absolutely! Most smart home devices are compatible with popular voice assistants like Alexa, Google Home, and Apple HomeKit. This compatibility allows you to control everything from lighting to appliances with voice commands, making it convenient to manage energy-efficient settings even when your hands are full.
Are there any tax credits or incentives for installing smart home energy systems?
Yes, in many regions, governments and utility companies offer tax credits, rebates, and incentives for energy-efficient upgrades, including smart home systems. These incentives vary by location, so it’s a good idea to check with your local government or utility provider to see what options are available.
How much maintenance does a smart home system require?
Smart home systems typically require minimal maintenance. However, regular software updates ensure that devices are running efficiently and securely. For devices with moving parts, like smart thermostats or smart window shades, occasional checks might be needed, but most systems are designed for long-term, low-maintenance use.
What are eco-modes, and how do they save energy?
Eco-modes are energy-saving settings available on many smart appliances, such as dishwashers, washing machines, and refrigerators. When activated, eco-modes optimize appliance functions to use minimal energy and water, helping reduce electricity consumption without sacrificing performance.
Can I monitor my energy usage remotely?
Yes, most smart home systems allow for remote monitoring through smartphone apps. You can track real-time energy consumption, adjust settings, and receive alerts if certain devices are using more energy than usual—all from wherever you are.
Do smart home systems support solar and battery storage options?
Yes, many smart home systems integrate seamlessly with solar panels and battery storage. AI optimizes the distribution of solar power within the home and manages battery usage, storing excess energy for later use. This setup helps maximize efficiency and reduce reliance on grid electricity.
How does predictive analytics work in a smart home?
Predictive analytics in a smart home uses data on your habits and patterns to anticipate energy needs. For instance, based on previous usage, a smart energy management system might adjust your thermostat before you arrive home or power down devices when you typically go to bed. This predictive capability helps save energy by only using it when necessary.
Can smart home devices help reduce peak electricity demand?
Yes, some smart home systems work with utility companies to reduce energy usage during peak times, known as demand response programs. When energy demand is high, your smart system might adjust settings to use less electricity, helping stabilize the grid and often earning you savings or rebates in the process.
Resources
EnergySage: Guide to Solar Integration with Smart Homes
EnergySage is a platform focused on solar energy, with resources on integrating solar panels with smart home systems. Their website covers the basics of solar power, AI-powered battery storage, and how solar can work seamlessly within a smart home environment. Check out EnergySage’s Solar Integration Guide
Smart Electric Power Alliance (SEPA): Demand Response Programs
The Smart Electric Power Alliance (SEPA) provides information on how smart homes can reduce electricity demand during peak hours. They offer resources on demand response programs, how they work, and how homeowners can benefit by participating in these programs. Learn More About SEPA and Demand Response