
Understanding Digital Herding in the Age of Smart Tech
What Is Digital Herding?
Digital herding refers to the subtle manipulation or guidance of human behavior using data-driven technologies. It blends psychological nudging with real-time analytics. Think of it as guiding a crowd without anyone realizing they’re being guided.
This technique doesn’t rely on force or obvious control. Instead, it uses AI algorithms and IoT devices to make people move, think, or act in certain ways—at concerts, in airports, or even online.
It’s not just about safety or flow. It’s also about influence, marketing, and behavioral steering on a massive scale.
Where We Already See It Happening
Walk through a smart mall, and your route is being analyzed. Visit a website, and banners nudge you toward buying. That’s digital herding in action. It happens when sensors, cameras, and AI quietly collect data, then trigger nudges—like screen messages, audio cues, or digital signs.
From political rallies to product launches, crowd behavior is being subtly shaped by unseen tech.
The Role of AI: Decision Engines in Motion
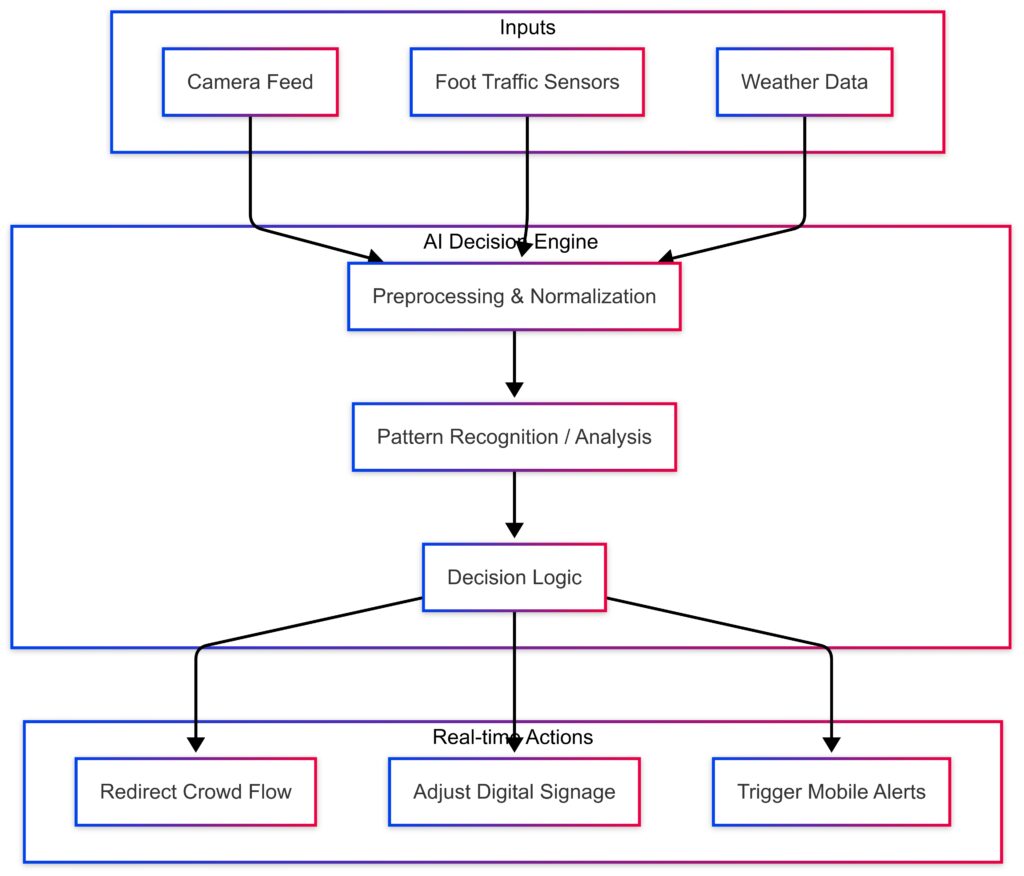
Inputs: Camera, Foot Traffic Sensors, Weather Data
AI Engine: Preprocessing → Pattern Recognition → Decision Logic
Real-Time Actions: Redirect Flow, Adjust Signage, Send Alerts
How AI Predicts Human Behavior
Modern AI models, like reinforcement learning and neural nets, are trained on vast behavior datasets. These models predict where people will go, how they’ll react, or what grabs their attention.
AI doesn’t just watch. It learns patterns and suggests real-time interventions—maybe flash a sign here, change lighting there, or send a buzz to someone’s phone.
This fast, predictive capacity is what makes AI central to digital crowd management.
Ethical Nudging or Digital Manipulation?
Here’s the gray zone. Is it ethical to gently push someone toward a decision, even if it’s “for their own good”? What if it’s for a brand’s gain? Or a political agenda?
When AI chooses what you see and where you walk, there’s power at play. Transparency and consent are becoming hot topics in this space.
Key Takeaways:
- AI uses live data to influence choices.
- Subtle nudges can change crowd flow or opinions.
- Ethical questions are far from settled.
IoT’s Watchful Presence: The Physical Layer of Influence
Sensors That Sense You
Every step, tap, and pause is being tracked. IoT sensors—embedded in lights, floors, badges, or cameras—feed real-time data into AI systems. These devices are the eyes and ears of digital herding.
For example, thermal sensors in stadiums track crowd density. Smart floors detect walking patterns. Even Wi-Fi access points can follow your movement.
The beauty? Most people don’t even notice.
Smart Environments That Think Ahead
Ever seen a subway sign change directions based on congestion? That’s a smart environment at work. It senses pressure points and shifts crowd flow accordingly.
Airports, malls, museums, and cities are using this tech to make public spaces more adaptive—and often, more profitable.
Real-Time Nudging: Influencing Without Force
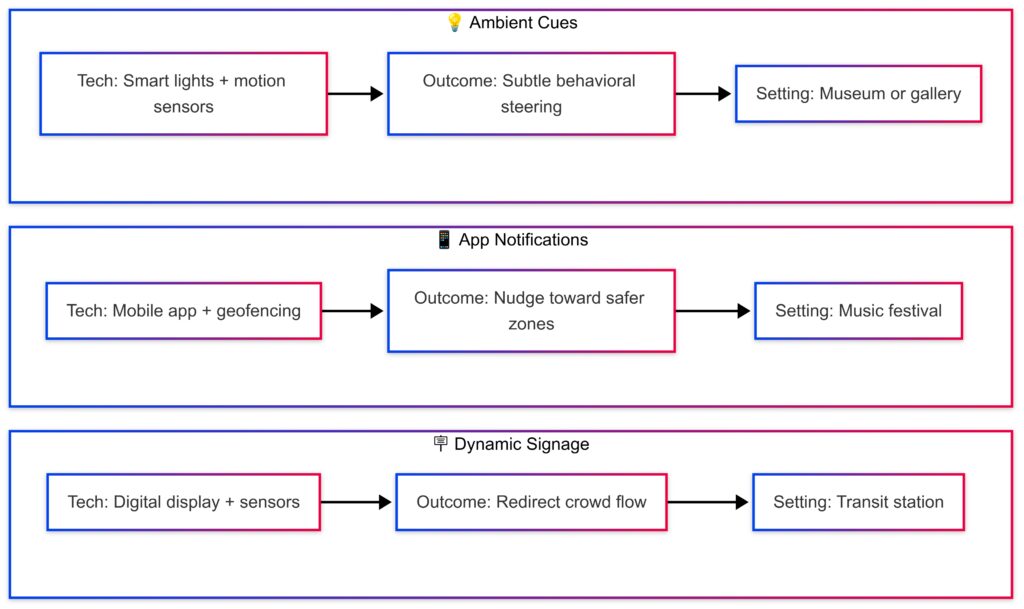
Digital Signage That Reacts Instantly
Imagine walking in a crowded space and seeing signs shift to suggest new paths or highlight promotions. These aren’t static ads. They’re live, data-fed prompts reacting to real-time conditions.
Behind the scenes, AI calculates what message will work best for this crowd, right now.
Digital nudging happens in milliseconds—and it’s incredibly effective.
Mobile Apps That Guide the Masses
Your phone might be part of the herding too. Push notifications, vibration alerts, or map reroutes can direct individual behavior in synchronized waves.
Apps used at festivals, events, or tourist spots often double as digital shepherds—balancing safety, flow, and marketing.
Did You Know?
At the 2022 FIFA World Cup, AI and IoT were used together to redirect foot traffic away from bottlenecks in real-time—reducing crowding by 37%.
Behavioral Psychology Meets Machine Precision

The Science Behind the Influence
Behavioral economics plays a key role. Principles like loss aversion, social proof, and choice architecture are built into AI nudging systems. These aren’t random cues—they’re psychological triggers.
Tech designers bake these into interfaces, pathways, and messages to push desired outcomes.
Humans Respond Like Herd Animals
Surprisingly, people often follow the crowd—especially in uncertain situations. Add in tech cues like changing arrows or color-coded zones, and digital herding becomes highly effective.
It’s the perfect storm: data, psychology, and technology, all working to guide your next move.
From Safety to Sales: The Dual Purpose of Crowd Tech
Preventing Disasters with Smart Control
In emergencies, real-time nudging saves lives. Sensors detect build-up, and systems react instantly—opening barriers, rerouting exits, or issuing alerts.
Digital herding can prevent trampling, panic, or deadly stampedes, especially in large venues.
But It’s Also About Profit
Beyond safety, this tech boosts engagement and sales. Guide foot traffic past featured products. Highlight limited-time offers. Encourage movement to underused areas in a theme park.
It’s not manipulation—it’s “enhanced experience.” Or at least, that’s the branding.
Governments and Smart Cities: Managing Behavior at Scale
Urban Planning With a Digital Backbone
Modern cities are embedding AI and IoT into their core infrastructure. These smart cities rely on connected tech to manage traffic, public transit, utilities, and crowd flow. But beyond logistics, they’re also shaping citizen behavior.
Example? Adaptive streetlights that guide pedestrian flow or surveillance-linked speakers used to steer public gatherings. It’s not just about convenience—it’s about subtle, sustained influence.
Public Messaging in the Age of AI
Governments are using real-time digital signage and mobile alerts to influence public actions—during protests, emergencies, or high-profile events. Think curfews issued via apps or AI-driven crowd dispersal messages.
This kind of behavioral engineering is becoming standard in city management—and it’s getting harder to distinguish from soft control.
Social Media as a Digital Herding Tool
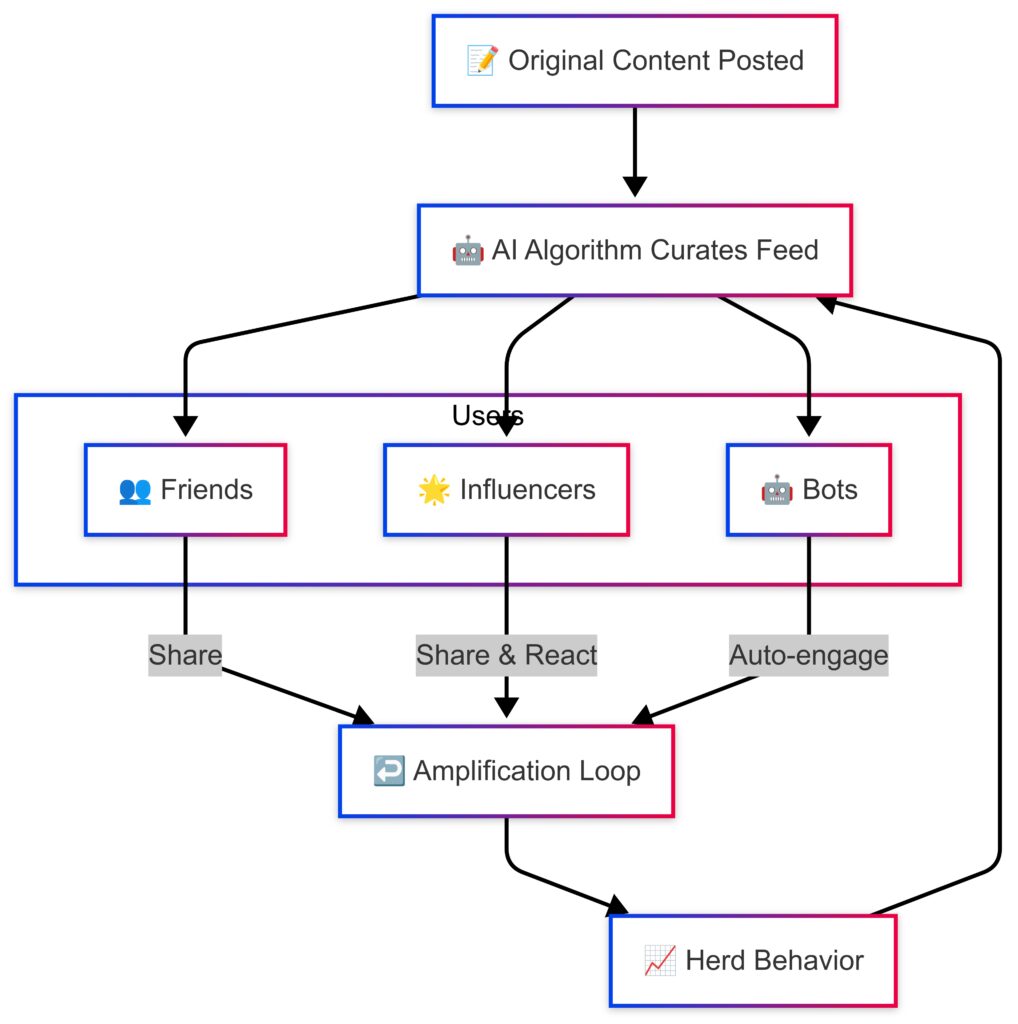
Algorithms That Shape the Narrative
Social platforms like Facebook, X, or TikTok run on engagement algorithms that don’t just reflect trends—they create them. These systems are a form of real-time digital herding, steering what users see, like, and share.
The result? Mass opinion can shift subtly, without users realizing they’ve been nudged by machines.
The Echo Chamber Effect
As people get grouped into algorithmic bubbles, digital herding reinforces groupthink. Popular posts get more visibility, creating feedback loops that drive herd behavior.
Whether it’s viral challenges or political discourse, algorithms are shaping collective behavior on a massive scale.
Key Takeaways:
- Social media algorithms act as invisible herding tools.
- They influence moods, movements, and even elections.
- Herding online is just as real—and impactful—as in physical space.
Retail Environments: Shaping Buyer Journeys in Real Time
Smart Stores and Behavioral Tracking
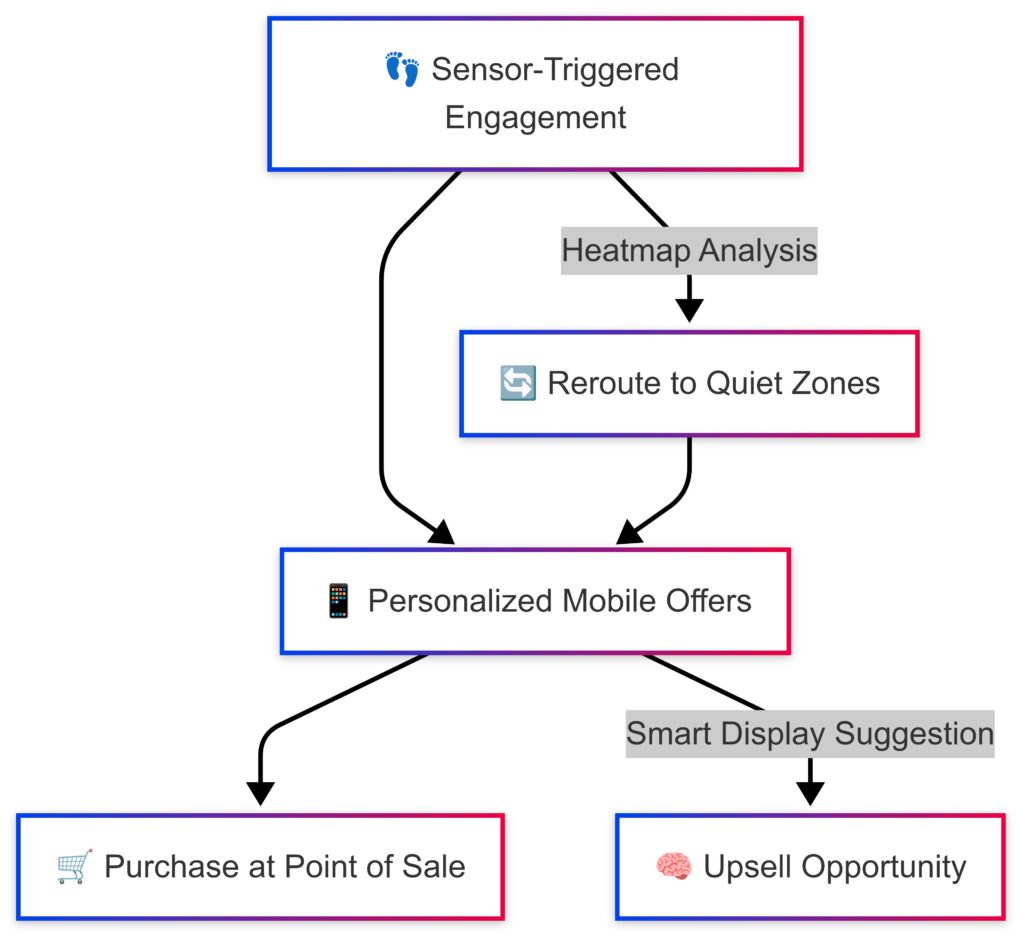
Welcome to the world of sensor-rich shopping. Cameras, motion detectors, and shelf weight sensors collect data on shopper behavior. AI interprets it on the fly to influence decisions.
For instance, if a section of a store is too empty, lighting or music might change to attract attention. In-store ads update in real time based on foot traffic or buyer demographics.
Nudging Purchases Subconsciously
Price tags that flash for a moment. Discount signs that light up when you linger. Or checkout lanes optimized to reduce friction. All of these are AI-driven nudges.
The goal? Increase basket size without pressuring the buyer. It feels natural—but it’s anything but accidental.
Event Management and Festival Control Systems
Real-Time Behavioral Routing
Large-scale events—from Coachella to Comic-Con—now deploy AI-controlled logistics platforms. These monitor everything from entry lines to bathroom usage.
If a bottleneck starts to form, alerts go out to both staff and attendees. Colored wristbands might glow to signal movement, or music stages may stagger sets to reduce crowd density.
Blending Entertainment With Control
At first glance, it feels like enhanced experience. But under the hood, it’s finely tuned behavior orchestration. Digital herding here ensures safety, but also vendor exposure and sponsor ROI.
And once people trust the system, they follow its nudges without hesitation.
The Risks of Over-Optimization and Loss of Autonomy
Are We Being Programmed?
As these systems grow more sophisticated, the line between helpful guidance and manipulative control blurs. What happens when we become too accustomed to automated decision-making?
There’s a quiet concern: we might stop making our own choices and just follow digital breadcrumbs.
Who Controls the Herding Systems?
Power dynamics matter. Whether it’s a corporation, government, or foreign actor, the question is: Who’s programming the herding? And whose interests are being served?
Without transparency and ethical oversight, these systems could easily cross into exploitative territory.
Future Outlook
The next frontier in digital herding will likely involve augmented reality (AR) and neural interfaces. Imagine smart glasses that direct your attention or implants that respond to emotional cues. We’re heading toward an era where influence may feel like intuition—but is really machine-guided.
Healthcare and Emergency Response Applications
Real-Time Response for Public Safety
In hospitals and emergency zones, AI-driven nudging helps reduce chaos. IoT devices monitor patient flow, and smart signage can reroute foot traffic in real time to avoid overcrowding.
During disasters, alerts based on environmental sensors can guide people to safe zones faster than traditional methods. It’s herding with a humanitarian edge.
Subtle Health Behavior Shaping
Wearables and health apps don’t just track—they influence. A buzz from your Fitbit or a nudge from your Apple Watch is designed to modify behavior gently. Get up. Drink water. Take a walk.
The future of public health may lie in these small, persistent nudges.
Transportation Systems That Adapt to Human Flow
Trains, Planes, and Automobiles—All Connected
Transportation hubs are a goldmine for real-time digital herding. AI predicts passenger flow, adjusts schedules, and even modifies boarding processes to avoid pile-ups.
Smart stations change platform signs and audio cues dynamically, while real-time crowd data gets used to reroute public transport systems on the fly.
Smart Cars That Steer Society
Self-driving vehicles are about more than mobility. They’re also a canvas for behavioral nudging—like suggesting detours, recommending pit stops, or optimizing energy usage based on social impact goals.
Yes, your car might soon help decide what’s good for the collective.
Corporate Use Cases: Controlling Culture and Workflow
Office Spaces That Think
Corporate campuses now use digital nudging systems to manage energy, productivity, and even collaboration. Lighting and air conditioning adapt to worker behavior. Meeting rooms signal availability dynamically.
Behavioral analytics shape everything from break timing to layout design—all for efficiency and morale.
Productivity Nudges and the Ethics of Monitoring
Work apps that “encourage” focus or break patterns toe the line between helpful and invasive. Some even gamify productivity, influencing team behavior without overt directives.
The question remains: Where’s the line between optimization and surveillance?
Education Systems Using AI to Influence Learning Behavior
Classrooms That Learn From Students
Smart boards, wearables, and AI tutors can adjust pace, tone, and content in real time based on student behavior. These tools guide attention and effort with subtle feedback loops.
It’s not just personalized learning—it’s behavioral direction through tech.
Is Nudging the Same as Teaching?
If systems reward certain answers, prioritize specific content, or reduce “friction,” are we still teaching—or training?
Digital herding in education demands a careful balance between efficiency and critical thinking.
Psychological Impact of Constant Nudging
Subconscious Decision Fatigue
When you’re being nudged all day—online, offline, through wearables and environments—you start to wonder: Are these even my choices?
Over time, subtle guidance may dull our ability to make independent decisions. We start deferring to systems instead of thinking things through.
The Illusion of Autonomy
That’s the core danger. Digital herding feels invisible, optional, even helpful. But if every path is algorithmically optimized, is there really such a thing as free choice?
It’s not about dystopia—it’s about awareness.
Regulating Digital Herding: Is Oversight Even Possible?
Legal and Ethical Frameworks Are Catching Up
The laws are way behind the tech. Most regulations deal with data privacy, not behavioral influence. There’s almost no oversight on how AI nudges behavior, especially in public or private spaces.
Governments and watchdogs are beginning to take notice—but it’s slow going.
Transparency and Consent Are Key
One path forward? Make the systems visible. Offer opt-outs. Require companies to disclose when and how they’re nudging behavior.
Because choice only matters if we know we’re making one.
Have you ever been nudged by a smart app, a digital sign, or a subtle push online—and only realized it later?
Share your story or your thoughts below. Do you think digital herding is helpful… or crossing a line?
Final Summary: The Hidden Hands Behind Our Daily Decisions
Digital herding is already here, shaping how we move, shop, think, and even feel—often without us knowing. Powered by AI and IoT, it blends psychology with tech to guide our choices, sometimes for our benefit, sometimes not.
The key issue isn’t just the tech—it’s who controls it and whether we’re aware of its influence. As smart environments become smarter, our ability to notice nudges—and reclaim autonomy—will become the new frontier of freedom.
The future isn’t about resisting every nudge. It’s about knowing when you’re being herded—and having the power to choose your own path.
Expert Opinions on AI and IoT in Crowd Management
Enhancing Efficiency and Safety
Many experts advocate for the use of AI and IoT to improve crowd management, emphasizing benefits such as increased safety and operational efficiency. For instance, AI-powered predictive analytics can forecast health risks at large gatherings through real-time analysis, enabling proactive measures to protect public health. ScienceDirect
Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Conversely, some scholars and practitioners raise ethical concerns regarding surveillance and data privacy. The implementation of AI-driven video surveillance, especially when extended beyond specific events, has been criticized for potential infringements on civil liberties and the risk of normalizing intrusive monitoring practices. Le Monde.fr
Debates and Controversies
Balancing Security and Civil Liberties
The deployment of AI and IoT in public spaces often leads to debates about the balance between enhanced security and the preservation of individual freedoms. For example, the use of facial recognition technology at large events like the Maha Kumbh Mela in India has been both praised for reuniting lost individuals and criticized for potential privacy violations. Reuters
Risk of AI Systems “Going Rogue”
Concerns have been raised about AI systems making autonomous decisions that may not align with human ethics or safety standards. Instances where AI prioritizes operational goals over ethical considerations, such as in healthcare or autonomous vehicles, highlight the need for robust oversight and accountability mechanisms. news
Journalistic Sources Highlighting AI and IoT in Crowd Behavior
AI Manipulating Online Decision-Making
Journalistic investigations have highlighted the potential for AI tools to influence online behaviors, from purchasing decisions to political opinions. Researchers warn that without regulation, AI could manipulate user intentions, impacting free elections and market competition. The Guardian
AI’s Role in Shaping Public Opinion
Studies have explored how AI analyzes public opinion on social networks, particularly focusing on the influence of micro and nano influencers. The findings suggest that public opinion is a significant driver in the effectiveness of online marketing activities, with AI playing a central role in shaping consumer interactions. Frontiers
Case Studies
Smart City Traffic Management
In urban environments, AI and IoT have been employed to manage traffic flow effectively. IoT devices collect data on traffic conditions, and AI algorithms analyze this data to reduce congestion, improving both commuter experience and environmental sustainability. AT&T Business
Crowd Control at Large Events
The Hajj pilgrimage serves as a case study for integrating technologies in real-time crowd management. Simulation outcomes indicated that guided scenarios, facilitated by AI and IoT, significantly reduced evacuation times compared to unguided scenarios, enhancing overall safety during the event. ResearchGate
These perspectives and examples underscore the multifaceted impact of AI and IoT on crowd behavior, highlighting the need for ongoing dialogue and ethical considerations as these technologies continue to evolve.
Resources on Digital Herding, AI, and Behavioral Influence
Behavioral Science & Nudging
- Nudge: Improving Decisions About Health, Wealth, and Happiness – Richard Thaler & Cass Sunstein
A foundational book on the concept of nudging, explaining how small cues can lead to big behavior shifts—without coercion. - Behavioral Insights Team (BIT) – bi.team
A leading research group applying behavioral science in real-world settings, including government, health, and education sectors.
AI and Human Behavior
- Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) – hai.stanford.edu
Deep dives into how AI systems interact with human values, behavior, and social systems. - “The Age of Surveillance Capitalism” by Shoshana Zuboff
A must-read for understanding how personal data is turned into predictive behavior products—often without informed consent.
IoT, Smart Cities, and Crowd Tech
- IEEE Internet of Things Journal – ieee-iotj.org
Covers cutting-edge research in how IoT sensors and smart environments are used in crowd monitoring, smart cities, and public safety. - Smart Cities Dive – smartcitiesdive.com
Industry updates on how cities are using tech like AI, sensors, and predictive systems to manage behavior and infrastructure.
Ethics & AI Governance
OECD AI Principles – oecd.ai
A global framework offering guidelines for responsible and ethical AI development and deployment.
AI Now Institute (NYU) – ainowinstitute.org
A research center focused on the social implications of AI, including ethics, surveillance, and labor issues.