With advanced robotics, machines are becoming critical allies in saving lives during crises. These cutting-edge technologies are reshaping how emergencies are handled, offering speed, precision, and tireless reliability. Let’s explore how emergency response robots are transforming safety standards and providing innovative solutions.
How Robots are Saving Lives in Natural Disasters
Swift Deployment in Disaster Zones
Natural disasters like earthquakes and hurricanes demand immediate action. Robots equipped with sensors and cameras can navigate through rubble or floodwaters, reaching areas unsafe for humans.
- Drones scan vast terrains for survivors, providing aerial views.
- Ground robots clear paths and assess structural stability.
- AI integration ensures real-time decision-making during rescue missions.
By acting as the first responders, these robots not only speed up disaster relief but also minimize risks for human teams.
Advanced Search and Rescue Capabilities
Robots excel in search and rescue, particularly in places humans cannot reach. Miniature robots, such as snake-like bots, slither through tight crevices to locate trapped victims.
- Thermal imaging helps identify body heat in pitch-black conditions.
- Audio sensors detect faint cries or tapping sounds.
- Autonomous systems reduce delays by working 24/7 without fatigue.
These features dramatically increase survival rates in disaster scenarios.
Restoring Critical Infrastructure
Beyond saving lives, robots aid in restoring vital services. They repair power lines, clean debris, and assess roadways for usability.
For example, robotic arms can mend ruptured pipelines or place temporary barriers, ensuring communities quickly regain essential utilities.
Robots Tackling Industrial Emergencies
Firefighting Robots Combat High-Risk Blazes
Industrial fires, chemical spills, and explosions are dangerous for human responders. Robots like fireproof drones or tank-like bots are equipped to extinguish flames and manage toxic substances.
- They use infrared sensors to detect hotspots.
- High-pressure water jets or foam suppress fires effectively.
- Gas detectors keep teams informed of hazardous levels.
These bots are invaluable in protecting responders and mitigating large-scale industrial accidents.
Managing Hazardous Material Spills
Dealing with hazardous spills requires precision. Robots ensure cleanup without exposing humans to dangerous chemicals.
- Remotely controlled bots handle materials like radioactive waste.
- Sensors analyze contamination levels to guide cleanup efforts.
- Autonomous vacuums and arms streamline toxic waste collection.
Using robotics here reduces health risks while ensuring strict compliance with safety regulations.
Enhanced Incident Response in Oil Rigs
On offshore oil rigs, emergencies like gas leaks or platform fires pose unique challenges. Submersible robots operate underwater to inspect pipelines, while aerial drones monitor above.
Their round-the-clock vigilance prevents small problems from snowballing into major disasters.
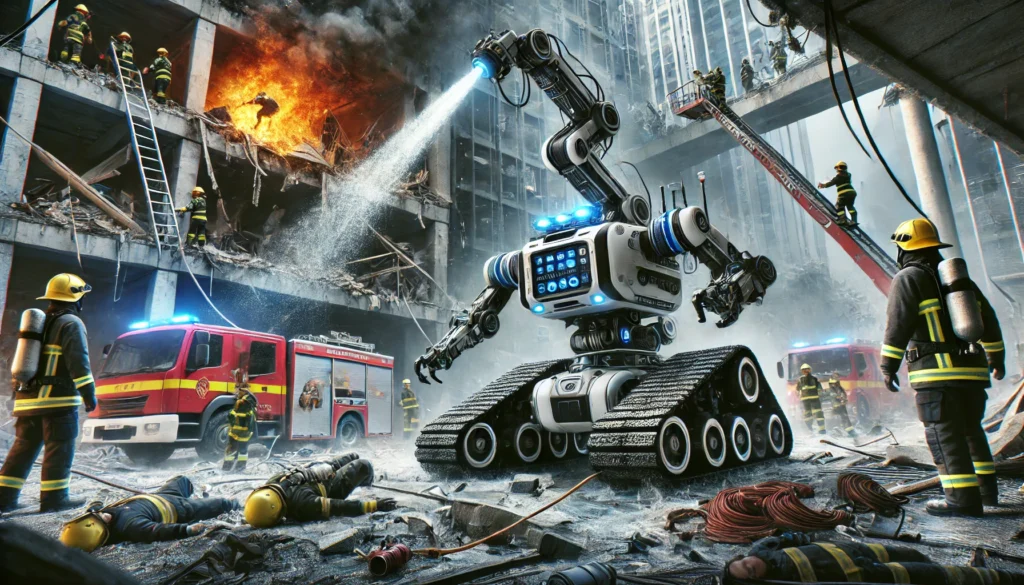

Robots Redefining Medical Emergency Responses
Robotic Ambulances and Evacuation Aids
Robotic ambulances and autonomous evacuation systems are game-changers in medical emergencies. These vehicles navigate traffic and dangerous terrains to reach victims faster.
- Self-driving ambulances transport patients without delay.
- Built-in medical tools, like ventilators and defibrillators, provide care en route.
- AI-driven triage systems prioritize critical cases.
These technologies significantly improve survival odds during the “golden hour” after a traumatic injury.
Precision in Pandemic Response
During pandemics, robots minimize human contact, reducing the risk of infection spread. From sanitizing public spaces to delivering medical supplies, they’ve proven indispensable.
- UV-light bots disinfect hospitals and clinics.
- Delivery robots transport medications and essentials to isolated patients.
- Automated testing kiosks and diagnostic tools boost testing efficiency.
These robots ensure health workers stay safe while maintaining care quality.
Assisting in Field Hospitals
In disaster-struck areas, field hospitals are chaotic. Medical robots manage logistics, perform routine checks, and even assist in surgeries.
- Robotic nurses monitor patient vitals and administer medications.
- Portable robotic surgical units perform minimally invasive operations.
- AI software predicts patient needs, optimizing resource allocation.
By automating repetitive tasks, they free healthcare professionals to focus on saving lives.
Revolutionizing Urban Emergency Preparedness
Smart Surveillance and Early Warning Systems
Robots paired with smart sensors detect emergencies before they spiral out of control. These systems monitor environmental changes, infrastructure stress, or unusual activity.
- AI drones patrol urban areas, identifying fire risks or structural weaknesses.
- Robots equipped with seismic sensors alert communities about impending earthquakes.
- Flood bots predict water levels, prompting timely evacuations.
This proactive approach prevents disasters, safeguarding lives and property.
Enhancing Traffic Incident Response
Traffic accidents require quick and efficient action. Robots are transforming responses through automation.
- Crash-site drones provide real-time visual updates to traffic authorities.
- Robotic road sweepers clear debris, ensuring traffic resumes swiftly.
- Autonomous vehicles assist injured passengers while emergency teams mobilize.
Such technologies streamline rescue operations and reduce accident-related delays.
Robots in Building Evacuations
During fires or collapses, robots guide individuals safely out of harm’s way. Intelligent evacuation bots map safe routes and lead groups to exits.
- Smoke-detecting drones ensure no one is left behind.
- Robotic stair climbers assist the elderly or disabled during emergencies.
- Emergency lighting robots provide visibility in smoke-filled environments.
This personalized assistance makes evacuations faster and more effective.
The Future of Emergency Response Robotics
AI-Driven Command Centers
Emergency response is evolving through AI-integrated robots, which streamline command operations. These robots interpret vast amounts of data and deliver actionable insights in real time.
- Predictive algorithms identify potential threats before they materialize.
- Coordinated systems ensure resources are deployed efficiently.
- Multilingual bots bridge communication gaps during global crises.
These advancements improve decision-making during time-critical situations.
Space Exploration Robots in Terrestrial Crises
Robots designed for space exploration, like Mars rovers, are being repurposed for extreme environments on Earth.
- Their rugged designs navigate disaster zones untouched by other machines.
- Extreme-temperature bots work in fires or freezing conditions.
- Autonomous systems require minimal human intervention, ideal for prolonged operations.
Such tech brings solutions to situations that were once insurmountable.
Next-Generation Drone Swarms
Drones are evolving into cooperative swarms, enhancing coverage and efficiency during emergencies. These robotic networks:
- Map expansive disaster zones rapidly.
- Deliver critical supplies like medicine or food to remote areas.
- Provide synchronized surveillance for coordinated rescue operations.
Their collaborative approach can transform responses to large-scale crises.
Ethical Challenges in Robotic Emergency Response
Balancing Automation with Human Oversight
As robots take on larger roles, ethical concerns emerge about decision-making in life-and-death situations.
- Who is accountable for errors—developers or operators?
- Should robots prioritize one life over another in critical scenarios?
- How do we ensure transparency in automated decisions?
These are key questions as robots grow more autonomous in emergencies.
Protecting Data Privacy
Emergency response robots collect vast amounts of data during operations. Safeguarding this information from misuse or breaches is critical.
- Clear regulations should define data use during crises.
- Encrypted systems ensure secure transmission of sensitive information.
- Stakeholders must balance efficiency with ethical handling of personal data.
Addressing these concerns ensures trust in robotics for public safety.
Maintaining Accessibility
While advanced, robotics must remain accessible to all communities, not just the affluent. Bridging gaps in resource allocation ensures equitable disaster responses globally.
These developments showcase a future where robots and humans collaborate seamlessly to save lives and mitigate risks, revolutionizing emergency preparedness on all fronts.
FAQs
How are robots powered during emergencies?
Most emergency response robots are battery-powered, with designs that prioritize energy efficiency. Some models use solar panels or have backup power systems to ensure uninterrupted operation.
Example: A search-and-rescue drone may be equipped with swappable batteries, allowing it to stay in the air for hours during rescue missions.
What types of sensors are commonly used in emergency robots?
Robots often include thermal cameras, gas detectors, seismic sensors, and LIDAR systems to detect heat, toxic chemicals, ground vibrations, and map surroundings.
Example: During a chemical spill, a robot with gas sensors and cameras can detect dangerous fumes and relay live footage to safety teams.
Are there any drawbacks to using robots in emergencies?
While robots are powerful tools, they can face limitations, such as difficulty navigating extreme terrain or communication issues in remote areas. Regular maintenance is also crucial to ensure reliability.
Example: In a dense forest fire, a drone may struggle with thick smoke, reducing visibility and GPS signal effectiveness.
What role do robots play in disaster recovery?
Robots assist in recovery by clearing debris, repairing critical infrastructure, and restoring utilities like power and water.
Example: Robotic arms can mend broken power lines, ensuring electricity is restored to affected areas faster after a hurricane.
Are emergency response robots sustainable?
Yes, many robots are designed with sustainability in mind. Energy-efficient systems and reusable materials are prioritized to reduce their environmental footprint.
Example: Solar-powered surveillance drones used during flood monitoring are both eco-friendly and cost-effective, making them sustainable options for long-term use.
How do robots assist during pandemics?
Robots play a vital role in pandemics by reducing human contact and ensuring efficient operations in high-risk zones. They disinfect areas, deliver supplies, and even perform diagnostic tasks.
Example: In hospitals, UV-disinfecting robots clean patient rooms and surgical suites, minimizing exposure to pathogens.
Can emergency response robots operate autonomously?
Yes, many robots are equipped with AI systems that allow for autonomous operation. They can perform tasks like navigating terrain, avoiding obstacles, and making real-time decisions without human input.
Example: Autonomous drones used in wildfire monitoring can identify hotspots and direct firefighters to critical areas without needing constant oversight.
What training is required to operate emergency robots?
Operators typically require specialized training to control emergency robots effectively. Training covers remote operation, interpreting sensor data, and understanding robot capabilities.
Example: Firefighters may train with robotic fire extinguishers to learn how to direct them into hazardous areas and control water pressure remotely.
Are there robots designed specifically for underwater emergencies?
Yes, underwater robots, or ROVs (Remotely Operated Vehicles), are used for operations like rescuing trapped divers, repairing offshore rigs, or investigating shipwrecks.
Example: During an oil spill, an underwater robot can inspect and seal a ruptured pipeline without endangering divers.
How do robots communicate in remote or disaster-stricken areas?
Robots often use satellite connections, mesh networks, or radio frequencies to maintain communication in areas with limited or damaged infrastructure.
Example: Drones surveying an earthquake site may create a mesh network to relay real-time data back to rescue teams.
What industries benefit the most from emergency response robots?
Robots are valuable in various industries, including firefighting, healthcare, oil and gas, mining, and construction. Each sector utilizes specific designs tailored to its unique challenges.
Example: Mining companies use robotic vehicles to monitor air quality and extract trapped workers during underground accidents.
How do robots handle ethical dilemmas in emergencies?
Robots rely on programmed decision-making algorithms to address dilemmas. However, ethical challenges like prioritizing who to save remain a topic of debate and development.
Example: A rescue robot may face a decision between saving a trapped individual or preventing an unstable structure from collapsing further.
What innovations are shaping the future of emergency robots?
Future developments include swarming drones, AI-enhanced predictive systems, and robots designed for extreme environments like volcanoes or arctic conditions.
Example: Scientists are developing firefighting drones that work in synchronized swarms to contain massive wildfires more efficiently.
How can smaller communities access emergency robots?
Programs and grants often help smaller or underfunded communities acquire robots. Partnerships with tech companies or NGOs also make these tools more accessible.
Example: Rural areas prone to flooding may receive robotic flood monitoring systems funded by government disaster-prevention programs.
Can emergency robots work alongside rescue animals?
Yes, robots and rescue animals can complement each other. While dogs rely on their keen senses, robots provide data and access to hazardous zones animals cannot enter.
Example: A search-and-rescue dog might locate a survivor, while a robot delivers supplies or creates a path for rescuers to follow.
For further reading on emergency response robots, check out the following resources:
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
- International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems
- Robotics Business Review
- Neuro-Symbolic Integration