
What is Emotional Intelligence in AI?
Understanding Emotional Intelligence in Humans vs. Machines
Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to recognize, understand, and manage emotions effectively. For humans, it includes empathy, interpersonal skills, and self-awareness. When applied to AI systems, EI involves creating agents that can recognize user emotions and respond empathetically, mimicking human-like emotional intelligence.
Unlike humans, AI doesn’t “feel” emotions—it identifies patterns. These patterns are derived from voice tone, facial expressions, word choice, or even typing speed. By bridging these data points with programmed responses, AI systems replicate empathetic behaviors.
Core Components of AI-Driven Emotional Intelligence
Emotionally intelligent AI relies on three pillars:
- Emotion Recognition: Identifying user emotions using facial recognition, sentiment analysis, or physiological signals.
- Emotion Interpretation: Contextually understanding these emotions and their triggers.
- Emotion Response: Generating relevant, empathetic outputs to address user needs effectively.
These elements combine to create smoother, more intuitive interactions between users and machines.
How Emotionally Intelligent AI Works
Role of NLP and Sentiment Analysis
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is the backbone of emotional AI. It enables systems to analyze text and speech, uncovering emotional undertones. Combined with sentiment analysis, AI can differentiate between joy, frustration, or sadness, tailoring its responses accordingly.
For example, an AI customer service agent could detect frustration in a user’s tone and shift its language to be more soothing and solution-focused.
Machine Learning Models for Emotional Detection
AI’s emotional intelligence thrives on data. Machine learning models process thousands of emotional cues, training on datasets like emotional lexicons or audio clips with labeled emotions. Over time, these systems become adept at predicting nuanced emotional states.
Advanced tools like multimodal analysis integrate inputs from various sources—voice, text, and visuals—offering a holistic emotional interpretation.
Applications of Emotionally Intelligent AI
AI in Mental Health Support: Virtual Therapists
AI-powered chatbots, like Woebot and Wysa, provide real-time support for mental health challenges. By recognizing emotions through text or speech, these systems offer empathetic, non-judgmental conversations, often acting as a bridge until professional help is accessible.
For individuals facing anxiety or stress, emotionally intelligent AI can deliver immediate support, guiding users through therapeutic exercises or mindfulness activities.
Retail and Customer Service: Personalization at Scale
Emotionally aware AI systems transform customer interactions by personalizing responses based on mood. For instance, a chatbot could suggest uplifting products to a user expressing frustration or dissatisfaction.
Brands leveraging this tech often see improved customer retention rates and satisfaction scores.
Education: Enhancing Student Engagement
In virtual classrooms, emotionally intelligent AI tracks student emotions via facial expressions or engagement metrics. If a student appears confused or disinterested, the system can adapt by simplifying content or offering encouragement.
The Ethics of Emotionally Intelligent AI

Privacy Concerns in Emotion Data Collection
To interpret emotions, AI systems gather sensitive data—voice recordings, videos, or even biometric information. This raises privacy concerns. How secure is the data? Who has access? Transparency in these processes is vital to maintaining user trust.
Transparency and Trust in AI Interactions
Emotionally intelligent AI must be upfront about its capabilities. Users need to know if their emotions are being analyzed and how that data is being used. Without clear communication, trust in these systems can erode quickly.
Avoiding Manipulation with Emotional Cues
When designed ethically, emotionally intelligent AI empowers users. However, there’s a thin line between support and manipulation. Overly persuasive systems could exploit emotional states for profit, such as upselling during moments of vulnerability. Safeguards are crucial.
Benefits of Emotionally Intelligent AI
Building Trust with Users Through Empathy
Empathy creates a bond between AI and users, fostering trust. When users feel understood, they’re more likely to engage with the system. This emotional connection sets emotionally intelligent AI apart from standard chatbots.
Boosting Engagement and Satisfaction
Personalized interactions lead to higher satisfaction. Emotionally intelligent AI adapts to user needs in real-time, making experiences more intuitive and enjoyable.
Bridging Communication Gaps in Diverse Contexts
Emotionally intelligent AI can help in multicultural or multilingual environments. By focusing on universal emotional cues, such as facial expressions or tone, these systems create a common ground for communication.
Challenges in Developing Emotionally Intelligent AI
Technical Complexities in Emotion Detection
Detecting human emotions is no small feat. Human emotions are layered, context-driven, and often ambiguous. Training AI to interpret them accurately requires advanced multimodal analysis that integrates text, tone, and visual cues. However, this process demands extensive computing power and precision algorithms, which are still evolving.
For instance, sarcasm in speech or cultural nuances in facial expressions can easily confuse AI, highlighting gaps in the current systems.
Limitations of Datasets and Bias Risks
Emotionally intelligent AI relies on large datasets to learn. These datasets, however, often come with inherent biases. For example, if training data predominantly features Western facial expressions, the AI may struggle to recognize emotions in people from other regions.
Ensuring inclusivity in data sourcing is crucial to building fair systems that serve a global audience.
Balancing Emotional Accuracy with Real-Time Processing
In practical applications, emotionally intelligent AI must process emotions in real time. This demands a delicate balance between emotional accuracy and computational efficiency. Delays in responses or inaccurate interpretations could erode user trust.
Real-World Examples of Emotionally Intelligent AI
AI-Powered Assistants Like Replika
Replika, a popular AI chatbot, exemplifies emotionally intelligent AI. Designed as a personal companion, it uses sentiment analysis and user feedback to tailor conversations, offering empathetic responses that feel deeply personal.
For many, Replika serves as an emotional outlet, providing comfort and understanding in a non-judgmental environment.
Automotive Applications in Enhancing Road Safety
Emotion AI is making waves in the automotive industry. Driver-monitoring systems, like those developed by Affectiva, assess a driver’s emotional state—detecting fatigue, frustration, or distraction. These insights enable vehicles to trigger safety alerts or adapt driving assistance features.
Emotionally Responsive AI in Smart Homes
Smart home assistants, such as Alexa or Google Nest, are integrating emotional intelligence to better serve their users. By analyzing voice tone or daily patterns, these systems can adjust lighting, recommend music, or suggest activities to uplift moods.
The Role of Emotion AI in Business Growth
Driving Customer Loyalty Through Personalized Experiences
Emotionally intelligent AI plays a pivotal role in customer retention. By understanding and responding to individual emotions, businesses can create memorable, personalized experiences. For instance, an AI chatbot sensing customer frustration could expedite issue resolution, boosting brand loyalty.
Streamlining HR and Employee Wellness Programs
In the workplace, AI tools equipped with emotional intelligence are revolutionizing HR practices. From analyzing employee engagement surveys to detecting burnout through communication patterns, these systems help organizations foster healthier work environments.
AI-driven wellness programs, offering personalized mindfulness tips or resources, also support employee well-being.
Innovations in Market Research with Emotional Insights
Emotionally intelligent AI offers marketers a goldmine of insights. By tracking consumer reactions to ads or products in real time, businesses can refine their strategies. Emotional heatmaps, for example, reveal which parts of an ad evoke the strongest reactions, enabling targeted improvements.
Future Technologies Enhancing Emotional AI
Advances in Wearables for Real-Time Emotion Tracking
Wearable devices like smartwatches and fitness bands are being equipped with sensors to monitor heart rate, skin temperature, and other physiological indicators of emotion. These real-time inputs feed into AI systems, offering more accurate emotional interpretations.
The Impact of Quantum Computing on Emotion Recognition
Quantum computing holds the potential to revolutionize emotional AI. With its unparalleled processing power, quantum computers could analyze vast emotional datasets faster and more accurately, enabling systems to handle complex, nuanced emotions.
Integration with AR/VR for Immersive Empathetic Experiences
Imagine a virtual reality platform where the AI responds to your emotional state in real-time, creating fully immersive empathetic experiences. AR/VR, combined with emotion tracking, could transform therapy, gaming, and education by adapting environments to users’ feelings.
Criticism and Controversies Surrounding Emotional AI
Fear of Dehumanization in Relationships with Machines
Critics argue that emotionally intelligent AI may blur the line between human and machine interactions. As users grow attached to empathetic AI companions, concerns about replacing genuine human connections arise.
The Potential for Misuse in Surveillance or Control
Emotion recognition technologies, when misused, can invade privacy. Governments or corporations could exploit these tools for surveillance, using emotional data to monitor dissent or manipulate behavior.
Philosophical Debates: Can Machines Truly “Care”?
While emotionally intelligent AI mimics care and empathy, it lacks genuine emotional experience. This raises ethical and philosophical questions: Can something that doesn’t feel emotions ever truly understand them?
Emotionally Intelligent AI and Social Impact
Reducing Stigma Around Mental Health Support
Emotionally intelligent AI is reshaping mental health care by providing judgment-free spaces for users to express themselves. Virtual therapists offer anonymity and accessibility, reducing the stigma often associated with seeking help. For many, these tools serve as a crucial first step toward healing.
Organizations are also leveraging emotion AI to gauge employee mental health trends, promoting healthier workplace environments.
Empowering Accessibility for Neurodivergent Individuals
AI systems with emotional intelligence can adapt their interactions to meet diverse needs. For neurodivergent users, these technologies simplify communication by recognizing subtle emotional cues or adjusting tone and complexity in conversations.
For example, chatbots designed for users with autism can maintain consistency and clarity, creating a less overwhelming communication experience.
Fostering Inclusivity Through Empathetic Tech
By recognizing universal emotional cues, emotionally intelligent AI transcends cultural and linguistic barriers. These systems make interactions more inclusive, allowing people from different backgrounds to connect without fear of misunderstanding.
The Role of AI in Enhancing Human-Emotional Intelligence
Helping Users Understand Their Emotions
Emotionally intelligent AI can act as a mirror, reflecting users’ emotional states back to them. By analyzing tone or behavior patterns, these systems help individuals identify feelings they may not recognize on their own, promoting self-awareness.
Encouraging Emotional Self-Regulation
AI tools, such as mindfulness apps, use emotional cues to suggest calming exercises, breathing techniques, or meditations. By guiding users through emotional regulation, these systems encourage healthier emotional responses over time.
Bridging Emotional Gaps in Global Communications
Emotionally intelligent AI offers solutions for cross-cultural communication challenges. By focusing on emotional universals—such as happiness, anger, or sadness—these tools foster better understanding between individuals from vastly different cultures or languages.
Comparing Emotionally Intelligent AI with Humans
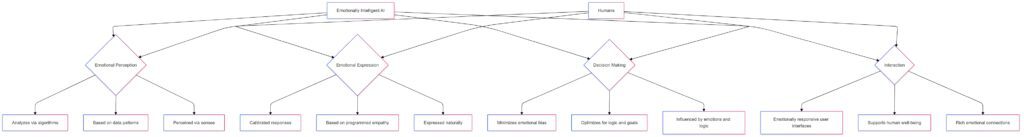
Strengths: Scalability and Consistency
Unlike humans, emotionally intelligent AI is tireless and consistent. It can handle thousands of interactions simultaneously, maintaining the same level of empathetic behavior without fatigue. This scalability is especially valuable in areas like customer service or mental health support.
Weaknesses: Lack of Genuine Emotional Depth
Despite its capabilities, emotionally intelligent AI lacks the authenticity of human emotion. Its responses are programmed, not felt, which limits its ability to offer true emotional support. Users may find interactions helpful but still prefer the depth of human connection.
Complementing Human Capabilities Rather Than Replacing Them
The goal of emotionally intelligent AI is not to replace humans but to complement them. By handling routine emotional tasks, AI frees up humans to focus on deeper, more meaningful connections, enhancing overall emotional well-being.
Future Predictions for Emotionally Intelligent AI
Expansion Into New Industries Like Healthcare and Law
Emotion AI is poised to transform industries beyond its current scope. In healthcare, emotionally intelligent systems could provide bedside support for patients. In law, AI might mediate disputes by assessing emotional states and offering balanced solutions.
AI as Emotional Educators for Children
Imagine AI companions teaching children how to manage emotions, resolve conflicts, or build empathy. These tools could help future generations grow up with stronger emotional intelligence, shaping kinder and more understanding societies.
The Long-Term Vision of Symbiotic Human-AI Relationships
In the future, emotionally intelligent AI could become a seamless extension of human life, coexisting as emotional advisors, companions, and educators. This symbiosis would combine AI’s efficiency with human empathy to create an emotionally balanced world.
How to Prepare for an Emotionally Intelligent AI Future
Embracing Emotional AI in Daily Life
From mental health apps to empathetic customer service bots, emotionally intelligent AI is becoming part of everyday life. Learning to engage with these systems effectively will enhance their benefits.
Advocating for Ethical AI Practices
As users, we must demand transparency and fairness in emotion AI technologies. Ethical regulations will ensure that these tools serve humanity without infringing on privacy or autonomy.
Upskilling for Careers in Emotional Tech Innovation
The rise of emotional AI opens up exciting career opportunities. Skills in machine learning, psychology, and user experience design will be invaluable in creating empathetic technologies for the future.
FAQs
Is emotional AI better than humans at recognizing emotions?
Emotion AI excels at processing vast amounts of emotional data consistently and efficiently, but it lacks genuine emotional depth. For example, while AI can detect sadness in a user’s text message and suggest solutions, it doesn’t “feel” compassion—it simulates empathetic behaviors.
Human interactions, on the other hand, involve intuition and life experiences, which AI cannot replicate. Emotionally intelligent AI works best as a complement to human empathy, not a replacement.
Where is emotionally intelligent AI currently used?
Emotionally intelligent AI is widely used in mental health support, customer service, and education.
- In mental health, apps like Wysa and Woebot provide emotionally aware chat support to guide users through anxiety or stress.
- In customer service, chatbots analyze customer sentiment to adjust their tone and actions, ensuring a more satisfying experience.
- In education, tools like AI tutors gauge students’ frustration or confusion and adapt teaching methods accordingly.
It’s also emerging in areas like automotive safety, where emotion AI detects driver fatigue or anger to prevent accidents.
What are the ethical concerns of emotionally intelligent AI?
There are three primary concerns:
- Privacy Issues: Emotion AI requires sensitive data, like voice recordings or facial expressions, to function. Mismanagement of this data can lead to privacy violations.
- Manipulation Risks: Companies could exploit AI’s emotional capabilities to upsell products or influence decisions during vulnerable moments.
- Trust Transparency: Users need to be informed when their emotions are being analyzed. Lack of transparency can erode trust in the technology.
For example, an emotionally intelligent sales bot might detect hesitation and push a limited-time offer, pressuring customers to buy. Such scenarios highlight the need for ethical safeguards.
Can emotionally intelligent AI help with mental health?
Yes, emotionally intelligent AI has shown great promise in mental health support. Tools like Replika and Wysa are designed to offer empathetic interactions, using sentiment analysis to recognize when users feel down or anxious.
For example, if a user expresses feeling overwhelmed, the AI might suggest breathing exercises, share positive affirmations, or guide them through Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) techniques. While these tools are not a replacement for professional therapy, they can provide valuable support, especially in moments of immediate need.
Can emotionally intelligent AI understand sarcasm or humor?
Emotionally intelligent AI struggles with nuances like sarcasm or humor because these often rely on cultural context, tone, or intent, which can be ambiguous. For instance, the sentence, “Great, another Monday!” could be genuine enthusiasm or sarcasm depending on the speaker’s tone or facial expression.
Some advanced models combine natural language processing (NLP) with contextual learning to improve in these areas, but they still lag behind human comprehension. Developers continue to refine systems to recognize these subtleties better, using multimodal data like tone and body language.
How does emotional AI enhance customer experiences?
Emotion AI personalizes interactions based on emotional cues, creating more satisfying customer experiences. For example:
- Retail: A chatbot detects frustration in a customer’s message and immediately offers assistance with a discount or faster resolution.
- Hospitality: Smart assistants in hotels recognize when guests sound tired and adjust their tone, offering quick solutions without unnecessary formalities.
- Healthcare: Emotionally intelligent virtual assistants calm patients by responding with empathy to anxiety or fear during medical inquiries.
This ability to adapt in real time builds trust and loyalty among users.
What are some futuristic applications of emotionally intelligent AI?
Emotionally intelligent AI is set to expand into exciting areas, such as:
- Healthcare: Emotionally aware robots providing bedside care to patients, offering comforting words, and alerting staff if distress is detected.
- Education: Virtual tutors detecting when students are disengaged and adjusting lessons to re-capture attention or reduce stress.
- Law: AI mediators assessing emotional cues during negotiations or conflict resolution, offering fair and neutral recommendations.
- Entertainment: Personalized movies or games that adapt storylines in real time based on the viewer’s emotional responses.
These applications could revolutionize how we interact with technology across multiple industries.
What are the main challenges in scaling emotionally intelligent AI?
Scaling emotionally intelligent AI comes with several challenges:
- Emotion Complexity: Human emotions are layered, often blending states like frustration and curiosity, making detection and interpretation difficult.
- Real-Time Processing: Large-scale deployment requires AI to interpret emotions instantaneously, which demands substantial computing power and optimized algorithms.
- Cultural Bias: Emotions are expressed differently across cultures, and datasets often lack diversity, leading to biased systems.
- Ethical Barriers: Privacy concerns and fears of misuse limit widespread adoption.
For instance, a global e-commerce company might deploy emotion AI for customer interactions, but inaccuracies in detecting non-Western emotional cues could alienate users instead of helping them.
Can emotionally intelligent AI help in team collaborations?
Yes, emotionally intelligent AI can foster better team collaboration by analyzing communication patterns and suggesting improvements. For example:
- Workplace Monitoring Tools: AI detects burnout or disengagement in employee emails or Slack messages and recommends interventions like mental health days.
- Virtual Meeting Assistants: Emotionally aware assistants analyze participants’ facial expressions during meetings and provide feedback on engagement levels.
- Conflict Resolution: AI mediators suggest neutral, empathetic language to de-escalate tense discussions.
By promoting emotional awareness, AI helps teams function more harmoniously and efficiently.
Can emotionally intelligent AI create stronger human-AI bonds?
Absolutely. Emotionally intelligent AI fosters trust and rapport by responding empathetically to users’ needs. For example:
- Virtual Companions: AI like Replika or XiaoIce builds long-term relationships with users by adapting to their emotional states and personalities.
- Gaming Characters: Emotionally intelligent NPCs (non-player characters) respond to players’ moods, creating a more immersive experience.
- Healthcare Robots: Emotionally aware robots, such as ElliQ, help seniors combat loneliness by initiating empathetic conversations or suggesting activities.
These connections make technology feel more human, enhancing user satisfaction and engagement.
Resources
Articles & Reports
- “The Ethics of AI Emotion Recognition” – Harvard Business Review
Explore how emotion AI can balance innovation with ethical considerations.
Read here - “Emotion AI: The Future of Human-Machine Interaction” – MIT Technology Review
Insightful analysis of real-world applications and future trends in emotionally intelligent AI.
Read here - “Bridging Emotional Gaps with AI” – World Economic Forum
A report on how emotional AI fosters inclusivity in global communication.
Read here
Books
- “Artificial Intelligence: A Guide to Emotion AI” by Kate Crawford
Covers the basics and ethical dilemmas of emotion AI technology. - “Human + Machine: Reimagining Work in the Age of AI” by Paul Daugherty & H. James Wilson
Explores how AI complements human intelligence, including emotional capabilities. - “Emotion AI: The Impact on Society” by Rana el Kaliouby
Written by the co-founder of Affectiva, a pioneer in emotion AI.
Organizations & Tools
- Affectiva
A leading company specializing in emotional AI for industries like automotive and healthcare.
Visit Affectiva - OpenAI Research on Emotion AI
Regularly updated research articles exploring AI advancements.
Learn more - Woebot Health
An AI-driven platform offering empathetic mental health support through chatbots.
Visit Woebot