Introduction
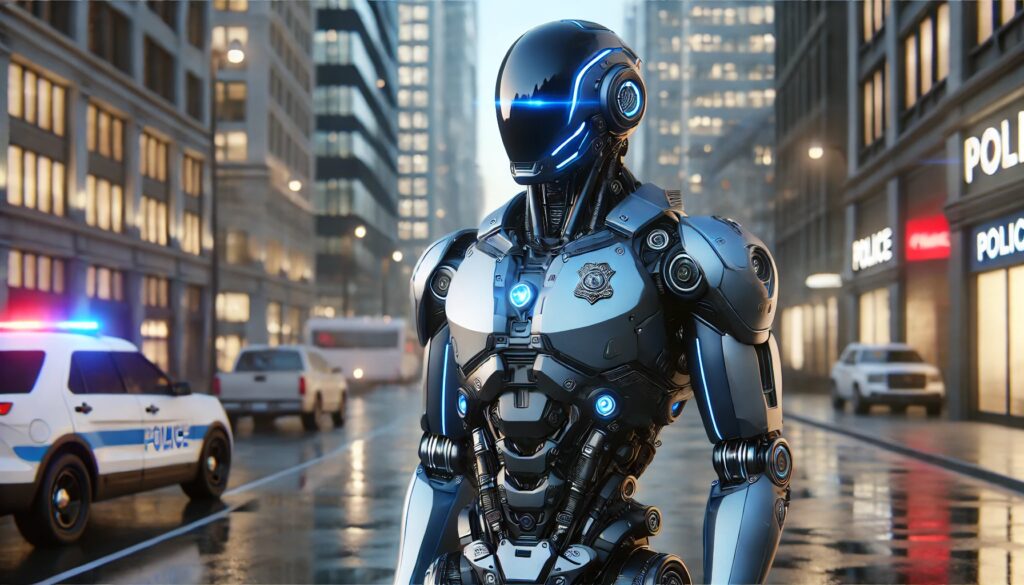
The dawn of robotic law enforcement signals a transformative era in policing. As technological innovations continue to surge, police robots are increasingly becoming integral to modern law enforcement strategies. These advanced machines, equipped with cutting-edge capabilities, are reshaping how police departments approach crime prevention, public safety, and emergency response. But what exactly do these police robots entail, and how are they likely to influence the future of policing?
Defining Police Robots: More Than Just Machines
Police robots are sophisticated mechanical devices programmed to assist law enforcement officers in various capacities. These robots range from simple remote-controlled devices to highly autonomous systems powered by artificial intelligence. Their roles are diverse, encompassing tasks such as surveillance, bomb disposal, crowd control, and even direct interaction with the public. The versatility of these robots allows them to undertake duties that would be too dangerous, tedious, or time-consuming for human officers.
A Closer Look: Types of Police Robots
1. Surveillance Drones
Surveillance drones are arguably the most widespread type of police robot. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are used for aerial monitoring, providing a bird’s-eye view of large areas during public events, protests, or in high-crime zones. They are equipped with high-resolution cameras, thermal imaging, and sometimes even facial recognition software, making them invaluable tools in tracking suspects and gathering intelligence.
2. Bomb Disposal Robots
Bomb disposal robots are perhaps the most established form of robotic assistance in policing. These robots are designed to approach, examine, and neutralize explosive devices safely. They are often equipped with manipulators, x-ray systems, and disruptors that can be used to safely disarm or detonate bombs from a distance, protecting human life in the process.
3. Patrol Robots
Patrol robots are a newer development in robotic law enforcement. These robots are designed to patrol designated areas, such as airports, shopping malls, and public parks, scanning for unusual activities or potential threats. Some advanced models can interact with the public, providing directions, answering questions, or even issuing tickets for minor offenses like littering.
4. Rescue and Reconnaissance Robots
In disaster-stricken areas or in situations where the environment is too hazardous for human officers, rescue robots play a critical role. These robots can navigate through rubble, toxic environments, or areas under gunfire to locate and assist victims. They often come equipped with sensors and cameras that relay crucial information back to rescue teams, allowing for more coordinated and effective responses.
Advantages of Police Robots: Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
The integration of police robots into daily operations brings about several key advantages. Safety is paramount; by deploying robots in potentially life-threatening situations, police departments can significantly reduce the risks faced by human officers. For example, robots can be sent ahead into dangerous environments—such as during a hostage situation or when dealing with hazardous materials—thus minimizing the need for officers to expose themselves to harm.
Additionally, efficiency is greatly enhanced through the use of robots. Unlike humans, robots do not tire and can work around the clock, providing continuous monitoring and rapid response. Advanced sensors and cameras on these robots can detect subtle anomalies that might escape the notice of a human observer, leading to quicker identification of threats and more effective law enforcement.
The Ethical Dilemma: Privacy, Accountability, and Job Displacement
While the benefits of police robots are significant, their deployment raises several ethical concerns. Privacy is a major issue, especially with surveillance robots capable of constant monitoring and recording. The potential for overreach is high, and without stringent regulations, these robots could infringe on citizens’ rights to privacy, leading to public distrust.
Accountability is another critical concern. In situations where robots are given a degree of autonomy—such as identifying suspects or using non-lethal force—questions arise about who is responsible if something goes wrong. If a robot mistakenly injures a person or makes an incorrect decision, it is unclear who should be held accountable—the officer controlling the robot, the department that deployed it, or the manufacturer?
Moreover, there is the issue of job displacement. As robots take on more tasks traditionally performed by human officers, there is a growing fear that this could lead to reduced employment opportunities in the law enforcement sector. However, many experts argue that robots are meant to complement human efforts rather than replace them, enabling officers to focus on more complex and nuanced aspects of policing.
Real-World Applications: How Police Robots Are Used Today
Around the globe, police robots are already making a significant impact. In the United States, for instance, the NYPD has deployed a robotic dog, known as Spot, for reconnaissance in situations too dangerous for human officers, such as during standoffs or in hazardous environments. Similarly, in China, robot patrol officers are becoming a common sight in airports and train stations, where they monitor for suspicious behavior and assist with crowd control.
In Dubai, the police force has gone a step further by introducing a robot officer designed to engage with the public. These robots can provide directions, offer information, and even report crimes. This initiative is part of Dubai’s broader plan to have robots make up 25% of its police force by 2030.
The Challenges Ahead: Regulation and Public Trust
As robotic law enforcement becomes more prevalent, the need for regulation is increasingly evident. Ensuring that these technologies are used ethically and responsibly will be crucial to maintaining public trust. Governments and law enforcement agencies must work together to establish clear guidelines on how and when robots can be deployed, ensuring that their use does not infringe on civil liberties.
Public education will also play a vital role in this process. By informing citizens about the capabilities and limitations of police robots, law enforcement can foster greater understanding and acceptance of this new technology.
The Future of Police Robots: What Lies Ahead?
The future of police robots is likely to see even more advanced and autonomous systems. With continued developments in artificial intelligence and machine learning, future robots may be capable of more complex decision-making processes, allowing them to act more independently in the field. This could include autonomous patrols, real-time crime prediction, and even engagement in negotiations during hostage situations.
However, with these advancements will come increased scrutiny. Policymakers, technologists, and the public will need to engage in ongoing discussions about the role of robots in society, ensuring that their integration into law enforcement serves the public good and respects individual rights.
Conclusion
The rise of police robots marks a new chapter in law enforcement, one that promises to enhance safety, efficiency, and effectiveness. However, this technological revolution also brings with it significant ethical and practical challenges. As we move forward, it will be crucial to strike a balance between leveraging the benefits of these robots and addressing the concerns they raise. The future of policing may indeed be robotic, but it will require careful consideration, regulation, and public engagement to ensure it evolves in a way that serves everyone.
For more in-depth information on police robots and their impact on modern law enforcement, check out the resources below.