Energy management is evolving. The rapid adoption of 5G technology and Edge Machine Learning (ML) is reshaping power grids, making them smarter, faster, and more efficient.
The Role of 5G in Modern Energy Grids
Ultra-Fast Connectivity for Real-Time Monitoring
5G’s ultra-low latency and high-speed data transmission are game-changers for energy grids. Real-time monitoring of energy systems allows quick detection of issues like power surges, equipment malfunctions, or grid imbalances.
Operators can now act instantaneously to reroute energy flows or fix faults. This capability wasn’t possible with older networks like 4G. For example, smart meters equipped with 5G connectivity send live data updates, improving overall grid performance.
Enhanced Device Interconnection
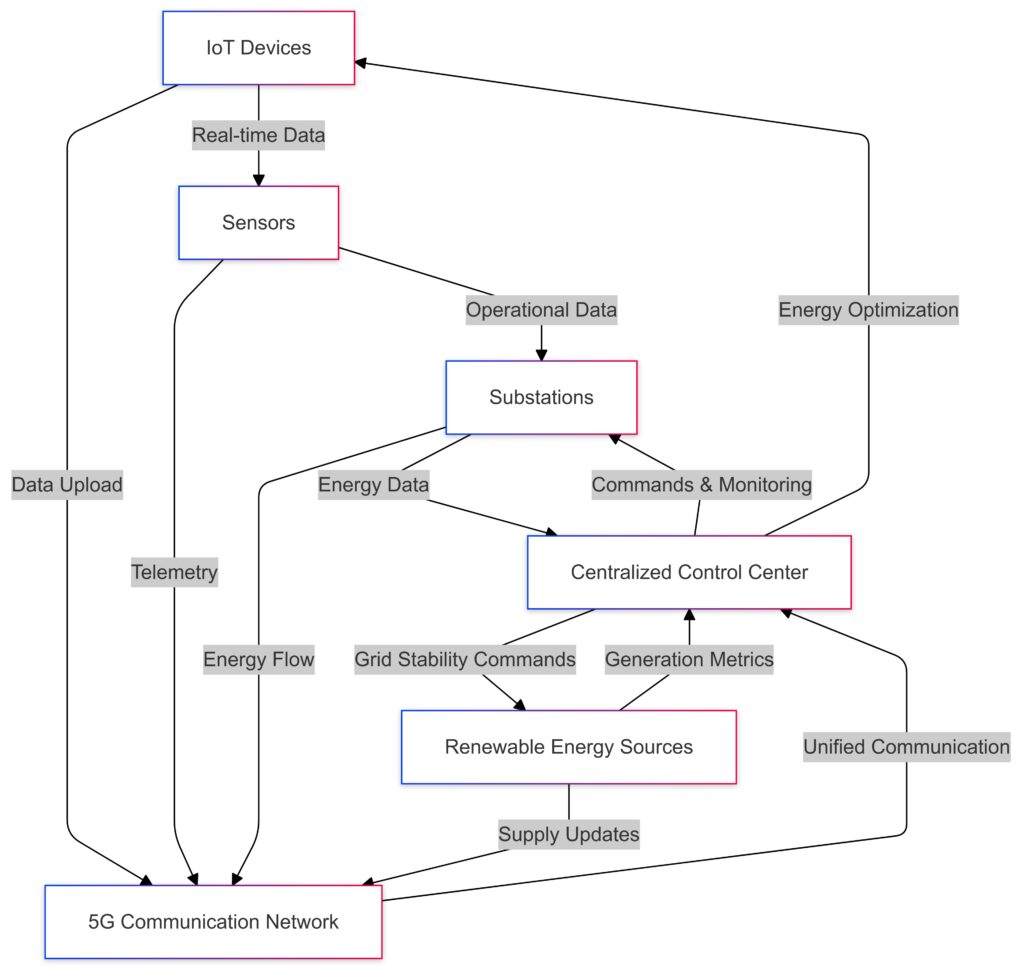
Modern grids involve countless devices—from sensors and transformers to consumer appliances. 5G enables massive device interconnectivity, ensuring seamless communication between every component of the system.
This means smarter grids can efficiently handle fluctuations in demand, such as during heat waves or blackouts. By integrating IoT devices, grids adapt dynamically, reducing energy waste and improving stability.
Supporting Renewable Energy Integration
Renewables like solar and wind power are vital to sustainable grids. However, their variability poses challenges. With 5G, grids can better forecast production levels using data from weather stations and adjust accordingly in near real time.
For instance, a solar farm may adjust its contribution based on changing sunlight patterns, thanks to 5G-enabled monitoring.
Edge ML: Driving Smarter Energy Insights
Decentralized Processing at the Edge
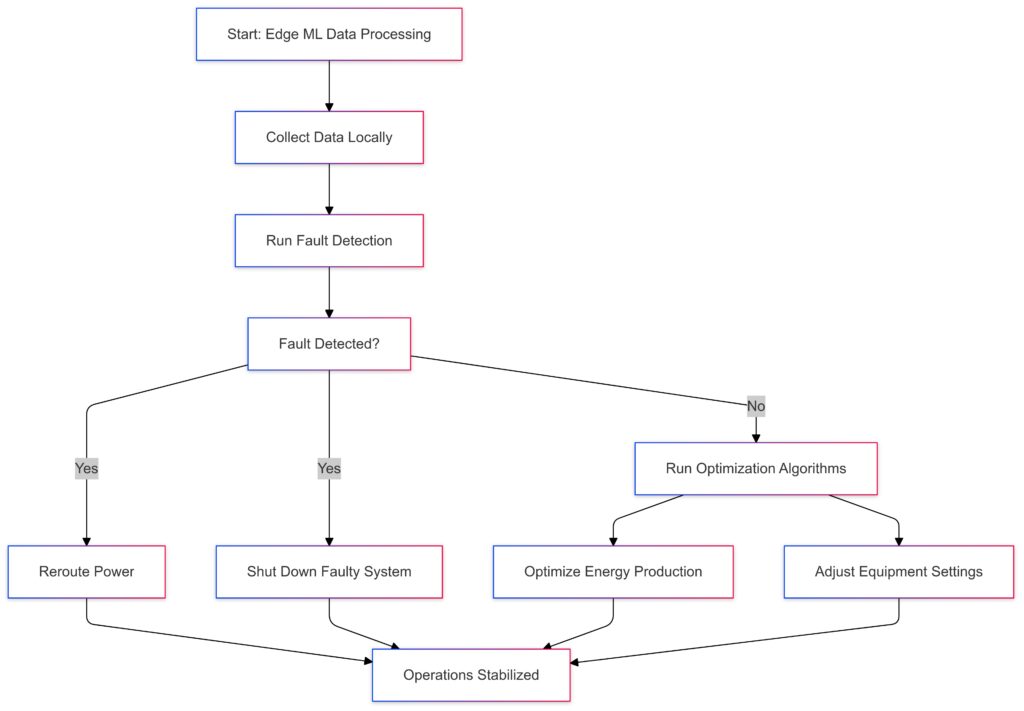
Unlike traditional ML models that rely on centralized cloud systems, Edge ML processes data closer to its source—at the edge of the network. This drastically reduces latency and data transmission costs, which are critical for time-sensitive grid operations.
Imagine wind turbines that adjust their blade angles based on real-time wind speed predictions. Edge ML enables such rapid adjustments locally, without delays caused by cloud communication.
Predictive Maintenance for Grid Equipment
Grid failures are costly, but Edge ML helps prevent them. By analyzing equipment performance data, it predicts potential breakdowns before they occur.
For example, transformers can report minor fluctuations that could indicate early signs of wear. Edge ML ensures swift intervention, saving utilities millions in maintenance costs and preventing power outages.
Enhanced Energy Forecasting
Accurate forecasting is essential for balancing supply and demand. Edge ML algorithms use real-time data to make predictions about energy consumption and production.
Whether it’s a spike in heating demand during winter or reduced usage during holidays, smarter forecasts prevent energy oversupply or shortages, minimizing waste.
The Intersection of 5G and Edge ML
Building Resilient Grids with Synergy
Together, 5G and Edge ML create a robust foundation for smarter grids. The speed of 5G complements Edge ML’s local processing, ensuring grids can handle even the most complex challenges.
For instance, during extreme weather events, the combination of these technologies allows grids to adapt dynamically, rerouting power and prioritizing critical areas like hospitals.
Real-Time Demand Response Systems
Demand response systems—where utilities incentivize users to lower energy use during peak hours—get a major boost with 5G and Edge ML. Sensors quickly analyze consumption patterns and suggest optimal times for energy-intensive activities, like charging electric vehicles.
Scaling for the Future
As urbanization and electrification grow, grids must scale efficiently. 5G and Edge ML allow grids to manage this growth without overburdening infrastructure, supporting future needs like electric vehicle charging networks or energy-sharing models.
Stay tuned for the next sections, where we’ll explore the challenges and practical implementations of these technologies!
Challenges in Implementing 5G and Edge ML for Smarter Grids

Infrastructure Limitations and Costs
Deploying 5G networks and edge computing nodes requires significant investment. Many regions, especially rural areas, lack the infrastructure to support these technologies.
For example, while urban centers might benefit from 5G-enabled smart meters, smaller towns may still rely on legacy systems. Expanding the required infrastructure without drastically increasing costs is a critical hurdle for energy providers.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
The interconnected nature of smarter grids introduces vulnerabilities. Devices communicating in real time create potential entry points for cyberattacks. Hackers could manipulate grid operations, leading to outages or even national security risks.
Edge ML systems, while decentralized, must prioritize encryption and secure protocols to ensure data safety. Balancing innovation with robust cybersecurity measures remains a key concern.
Complexity of System Integration
Integrating 5G and Edge ML into existing grid systems isn’t seamless. Legacy systems weren’t designed to accommodate these technologies, and the transition can be challenging.
Utilities must upgrade hardware and software while maintaining grid stability. Additionally, standardization is essential to ensure devices from different manufacturers work together.
Real-World Applications of 5G and Edge ML in Energy Grids

Smart Cities Leading the Way
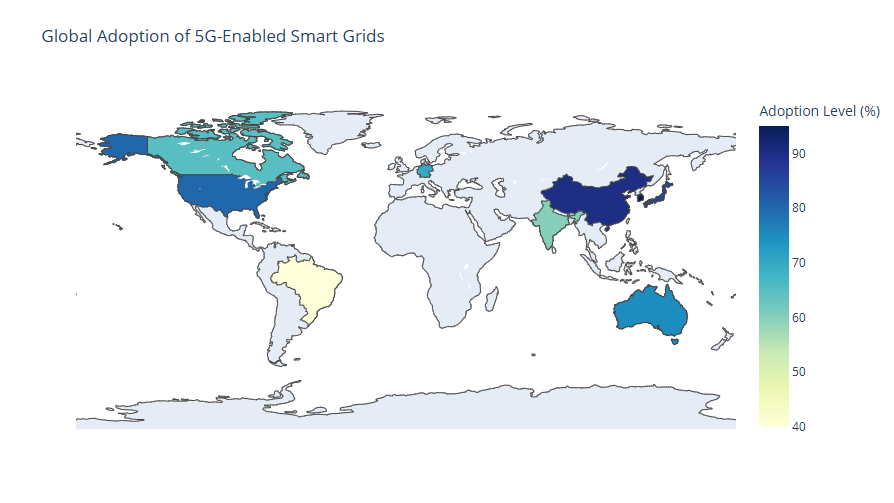
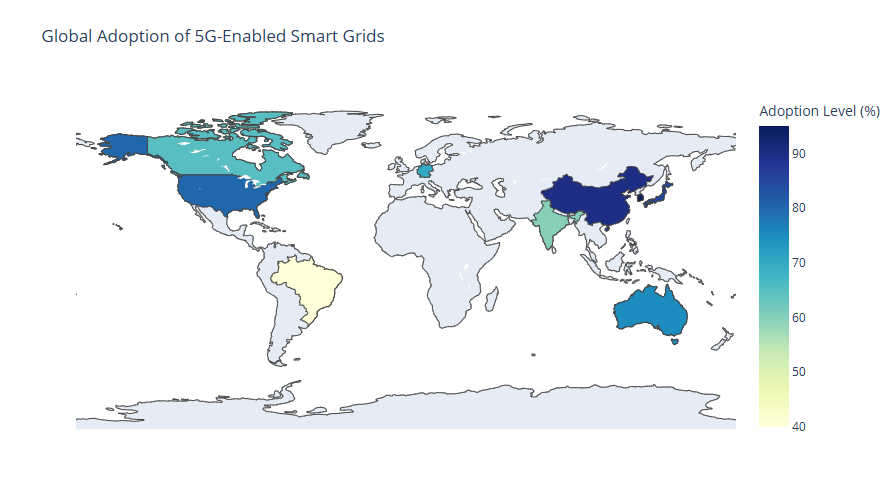
Cities like Singapore and Amsterdam are deploying smarter grid solutions powered by 5G and Edge ML. These cities use real-time data to manage street lighting, public transportation, and even waste management.
In Singapore, smart grids balance energy loads by analyzing consumption patterns and adjusting supply dynamically. Such systems reduce energy costs for citizens while improving reliability.
Renewable Energy Management in Action
Renewable energy producers, such as solar farms in California, use 5G-enabled sensors and Edge ML models to optimize output. These systems predict weather changes and adjust energy generation accordingly, ensuring consistent supply.
The same concept applies to offshore wind farms in Europe, where machine learning algorithms help maximize efficiency while reducing wear on turbines.
Industrial Use Cases
Industrial facilities are some of the largest energy consumers. With 5G and Edge ML, factories can adopt predictive energy management, ensuring equipment runs during off-peak hours to reduce costs.
For example, smart factories in Germany monitor and optimize energy usage for robotic systems, helping them achieve sustainability goals without compromising productivity.
Real-World Applications of 5G and Edge ML
| Region | Technology Used | Benefits Achieved |
|---|---|---|
| Singapore | Smart Grids with Edge ML | – Reduced energy outages – Real-time fault detection |
| California | Autonomous Vehicles with 5G and Edge Processing | – Lower latency in vehicle-to-infrastructure communication – Enhanced safety and navigation accuracy |
| Germany | Industrial IoT with Edge ML | – Predictive maintenance – Improved equipment uptime |
| Japan | 5G-Powered Smart Factories | – Faster machine response times – Increased production efficiency |
| India | Telemedicine Platforms with 5G | – Seamless remote surgeries – Expanded access to rural areas |
| South Korea | Smart Cities with 5G and Edge AI | – Optimized traffic flow – Reduced urban congestion |
| Australia | Agricultural Drones with Edge ML | – Enhanced crop monitoring – Precise resource management |
| United Kingdom | 5G in Retail for Real-Time Inventory Management | – Reduced stockouts – Improved customer satisfaction |
The Environmental Benefits of Smarter Grids
Reduced Carbon Footprint
By optimizing energy flows and reducing waste, smarter grids directly lower carbon emissions. Real-time demand response systems encourage consumers to use energy when it’s most efficient, minimizing reliance on fossil fuels during peak demand.
Furthermore, renewable energy integration becomes smoother, allowing cleaner sources to take precedence over traditional power plants. This shift significantly reduces environmental impact.
Supporting Circular Energy Economies
Innovations like energy-sharing models—where excess energy generated by one user is redistributed to others—become viable with these technologies.
For example, neighborhoods with solar panels can share surplus energy with nearby homes or businesses. Such systems promote a circular energy economy, maximizing resource utilization and minimizing waste.
The Future of Smarter Grids with 5G and Edge ML
Scaling Smarter Grids Globally
As 5G networks expand and edge computing becomes more affordable, the scalability of smarter grids is becoming a reality. Emerging markets are poised to benefit significantly, with governments and private entities collaborating to modernize aging grid infrastructures.
For instance, countries in Africa and Southeast Asia are piloting microgrids powered by 5G and Edge ML. These localized grids provide stable electricity to rural areas while adapting to demand fluctuations in real time.
AI-Driven Energy Marketplaces
The rise of peer-to-peer energy trading could reshape energy markets. With the help of blockchain technology, 5G, and Edge ML, consumers can buy and sell surplus energy directly.
Imagine a homeowner selling excess solar energy to a neighbor through a secure, automated system. This decentralization encourages renewable adoption and creates new economic opportunities for individuals and small businesses.
Paving the Way for Smart Energy Ecosystems
Smarter grids are the foundation of broader smart energy ecosystems. As the world transitions to electric vehicles (EVs) and smart homes, seamless energy management will become crucial.
With 5G connectivity, EVs can communicate with the grid to schedule optimal charging times, reducing strain during peak hours. Similarly, smart appliances in homes will adapt to energy rates in real time, saving costs and reducing environmental impact.
Policy Considerations for the Smarter Grid Revolution
Incentivizing Technological Upgrades
Governments play a crucial role in driving adoption. Policies that subsidize 5G deployment and encourage investment in Edge ML will accelerate progress. Incentives for utilities to upgrade infrastructure are equally important, ensuring the transition benefits consumers and businesses alike.
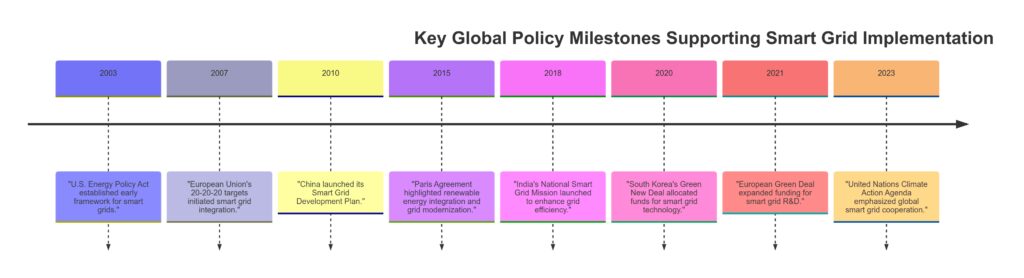
For example, the European Union’s Green Deal prioritizes funding for smart grid projects, focusing on renewable energy integration and grid resilience. Similar initiatives worldwide could catalyze widespread change.
Addressing Energy Equity
While smarter grids promise efficiency, they must also address issues of energy equity. Ensuring underserved communities have access to advanced grids is vital. Policymakers must balance innovation with affordability, so no one is left behind.
Expanding smart grid access to rural areas, offering subsidized pricing models, and providing education on energy-saving technologies are some strategies to bridge the gap.
Prioritizing Security and Privacy
As smarter grids collect and process vast amounts of data, robust cybersecurity policies are non-negotiable. Governments and industries must collaborate on standardized security frameworks to protect grids from potential breaches.
Additionally, transparent data usage policies will help build public trust, ensuring consumers feel confident in adopting these advanced systems.
Conclusion: The Energy Revolution is Here
5G and Edge ML are not just transforming energy grids; they’re paving the way for a sustainable, efficient, and equitable energy future. From real-time monitoring to renewable integration and predictive maintenance, these technologies are addressing the challenges of today while preparing grids for tomorrow.
As governments, businesses, and consumers embrace this revolution, the path to efficient energy management becomes clearer. The smarter grid of the future isn’t just a dream—it’s becoming a global reality.
FAQs
Can smarter grids support renewable energy?
Absolutely! Smarter grids powered by 5G and Edge ML make it easier to integrate renewable energy sources. They analyze weather data and energy production patterns to balance supply and demand.
Consider a solar farm: as clouds roll in, 5G-connected sensors detect the drop in sunlight, while Edge ML adjusts power contributions from backup sources like batteries or traditional plants.
Are there cost savings for consumers?
Yes! With smarter grids, consumers can benefit from dynamic pricing and reduced energy waste. For example, demand response systems incentivize users to run appliances during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper.
A homeowner could set their 5G-connected washing machine to start automatically at the most cost-effective time, saving money and reducing strain on the grid.
What security risks are associated with these technologies?
The interconnected nature of smarter grids makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers could target systems to disrupt services or manipulate data.
To mitigate risks, utilities are implementing advanced encryption, secure protocols, and regular security audits. Collaboration between governments and private entities ensures robust defenses.
How do these technologies benefit rural areas?
Microgrids powered by 5G and Edge ML bring reliable energy to remote regions. These localized systems can operate independently or connect to larger grids, ensuring flexibility and stability.
For example, a rural community with solar panels and wind turbines can use Edge ML to manage energy locally, reducing dependency on distant infrastructure.
Are 5G and Edge ML environmentally friendly?
Yes! By optimizing energy distribution and reducing waste, these technologies lower the carbon footprint of power grids. They also prioritize the use of clean energy sources like solar and wind over fossil fuels.
What industries are benefiting the most from these technologies?
Industries like manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture are seeing significant benefits. For instance:
- Manufacturing: Smart factories optimize energy use during production.
- Transportation: EV charging stations dynamically adjust loads to prevent overloading.
- Agriculture: Smart irrigation systems adjust water usage based on weather and soil data.
How can individuals contribute to smarter grids?
Consumers play a vital role in the success of smarter grids by adopting energy-efficient practices and technologies. Using smart home devices like thermostats and energy-monitoring apps helps manage energy usage more effectively.
For example, a smart thermostat adjusts heating and cooling automatically based on your schedule and energy rates, lowering both costs and grid strain.
What is the future of jobs in this sector?
The adoption of 5G and Edge ML is creating opportunities in fields like data analytics, IoT development, and grid maintenance. Jobs requiring expertise in cybersecurity, renewable energy systems, and AI applications are especially in demand.
Educational programs focusing on smart grid technology are being introduced to prepare the workforce for this growing industry.
How does energy-sharing work with smarter grids?
Energy-sharing allows households or businesses to sell their surplus energy, like excess solar power, to others within the grid.
For example, a home with solar panels can share unused electricity with a neighbor during the day, while pulling energy from the grid at night. This creates a decentralized, sustainable energy ecosystem.
Are there any downsides to adopting these technologies?
While the benefits are clear, challenges exist:
- High Initial Costs: Implementing 5G and Edge ML infrastructure requires significant investment.
- Privacy Concerns: Continuous data collection from smart devices raises questions about personal information security.
- Learning Curve: Consumers and utilities may need time to fully adopt and understand the new technologies.
Addressing these challenges through policy, education, and technological advancements will ensure smoother adoption.
Are smarter grids resilient to natural disasters?
Yes! Smarter grids are designed to be more resilient. With real-time monitoring and rapid response capabilities, they adapt quickly during natural disasters like hurricanes or earthquakes.
For example, microgrids can isolate themselves from the main grid during an outage, ensuring hospitals or emergency services continue operating.
What policies are driving the adoption of smarter grids?
Governments worldwide are implementing initiatives to accelerate smart grid adoption. Policies focus on:
- Subsidizing renewable energy projects.
- Encouraging private-public partnerships for 5G and Edge ML infrastructure.
- Mandating utilities to reduce carbon footprints and improve energy efficiency.
For instance, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Smart Grid Investment Grant program funds projects that modernize energy grids and integrate renewable energy.
How soon will smarter grids be mainstream?
The timeline for mainstream adoption depends on infrastructure development, policy support, and public acceptance. Urban areas with advanced infrastructure may fully implement smarter grids within the next 5-10 years, while rural regions may take longer.
As 5G expands and edge computing becomes more cost-effective, adoption rates are expected to rise significantly. Global collaboration among governments and industries will further accelerate the transition.
Conclusion
With their transformative potential, 5G and Edge ML-powered smarter grids are driving the future of energy management. From increasing renewable energy adoption to empowering individuals with energy-saving tools, these technologies promise a more efficient, resilient, and sustainable energy landscape.
Resources
Government and Industry Reports
- U.S. Department of Energy (DOE): Smart Grid Resource Center
Offers detailed reports and case studies on modernizing energy systems in the U.S. - International Energy Agency (IEA): Digitalization and Energy
Comprehensive analysis of how digital technologies, including 5G and ML, are shaping the energy landscape. - European Commission: Smart Grids Task Force
Focuses on the policy frameworks driving smart grid adoption across Europe.
Educational Tools and Courses
- Coursera: Smart Grid Technologies
A range of online courses from universities like Stanford and Imperial College London on energy management and grid modernization. - edX: Digital Transformation in Energy
Learn how digital technologies, including 5G and ML, are revolutionizing the energy industry.
Real-World Examples
- Siemens Smart Infrastructure: Case Studies
Real-world examples of smart grid projects integrating 5G and Edge ML. - Schneider Electric: Smart Grid Solutions
Explore innovative tools and systems enabling smarter energy grids worldwide.
Industry News and Updates
- Greentech Media: Energy Grid Insights
Stay updated on the latest trends, news, and breakthroughs in smart grid technology. - Renewable Energy World: Energy Management Innovations
In-depth coverage of renewable energy and its integration into smarter grids.