What is Visual Question Answering (VQA)?
The Core of VQA Technology
Visual Question Answering (VQA) combines computer vision and natural language processing to help users interact with visual content.
It enables systems to analyze images or videos and respond to natural language queries about them. For instance, asking, “What is in this picture?” can return responses like, “A cat sitting on a sofa.”
How It Works: Machine Learning in Action
VQA systems rely on deep learning algorithms. These systems are trained on extensive datasets containing labeled images and text. Through this training, they learn to recognize patterns, detect objects, and understand relationships within visuals.
Key components include:
- Image recognition models for detecting objects and scenes.
- Language models for interpreting and answering user questions.
- Integration layers to combine visual and text-based insights.
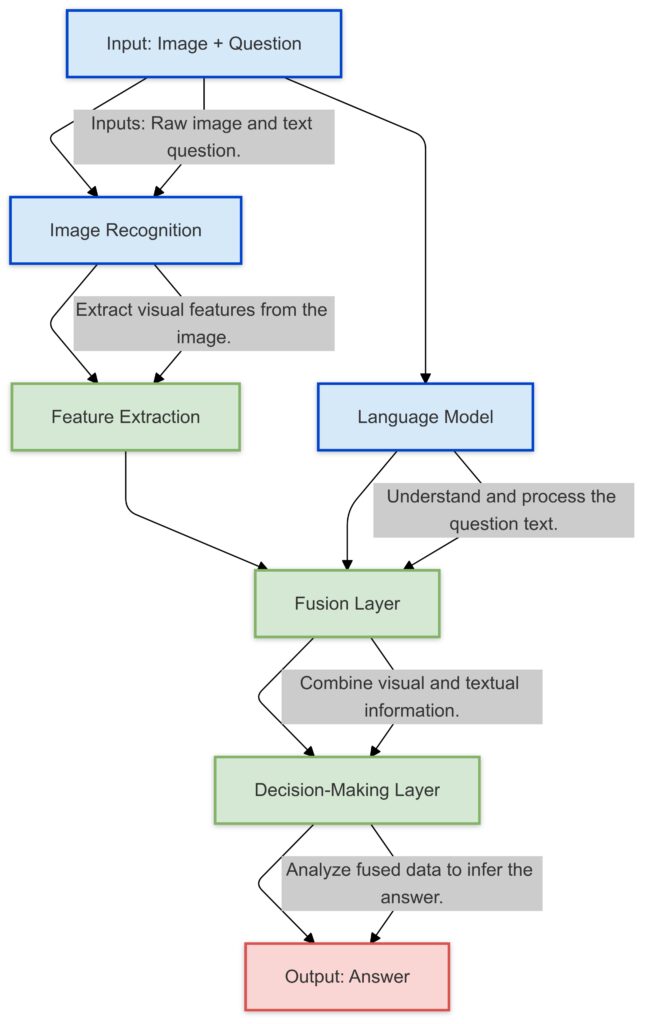
Key Features:
Flow Representation: Clear arrows show the step-by-step progression of data.
Annotations: Highlight the role of each node in the pipeline.
Real-World Examples of VQA in Use
Many platforms, like Microsoft’s Seeing AI or Facebook’s VQA research, use this technology. These tools are designed for accessibility, bridging the gap for visually impaired individuals to understand their surroundings better.
Accessibility: The Transformative Potential of VQA
Empowering the Visually Impaired
For individuals with visual impairments, VQA can provide real-time answers about their environment. Imagine scanning a product label or capturing a photo of a busy street and receiving descriptive feedback instantly.
Benefits include:
- Enhanced independence in daily activities.
- Better access to education and employment opportunities.
Inclusive Design for a Broader Audience
While designed for accessibility, VQA also supports universal usability. Parents can use it to identify misplaced items, or students might explore museum exhibits more interactively. The goal is to make interaction seamless, regardless of ability.
Key Accessibility Features of VQA
- Customizable Outputs like voice, text, or braille.
- Compatibility with screen readers and assistive devices.
- Context-sensitive answers, adjusting based on user needs or preferences.
Challenges in Implementing VQA
Data Diversity and Bias
One significant hurdle is ensuring that datasets reflect diverse real-world scenarios. Without this, systems might struggle to recognize objects in various contexts or fail to account for cultural differences.
Computational Limitations
High processing power is often required for VQA systems, especially for real-time applications. Making these tools lightweight yet effective is essential for broader adoption.
Privacy Concerns
Since many VQA tools require image capture, safeguarding user data becomes critical. Developers must prioritize encryption and anonymization to ensure compliance with global privacy standards like GDPR.
VQA Applications: Redefining Accessibility Across Sectors
Education and Learning
Visual Question Answering is transforming education for students with disabilities, enabling access to visual content that would otherwise remain inaccessible.
Interactive Learning Tools
With VQA, learners can ask questions about images in textbooks, infographics, or educational videos. Responses provide context and meaning, helping students grasp visual concepts more effectively.
For example, a student might ask, “What does this diagram represent?” and receive a detailed explanation tailored to their query.
Student 1: Exploring a science diagram, gaining insights into complex processes.
Student 2: Analyzing historical artifacts, uncovering context and details.
Student 3: Solving interactive math problems with visual aids.
Benefits
Improved STEM Access: VQA provides visual explanations that make challenging topics more accessible.
Interactive Learning: Real-time Q&A fosters engagement, curiosity, and deeper understanding.
Enabling STEM Access
Subjects like science and mathematics heavily rely on visuals like graphs and charts. VQA can interpret and describe these materials, leveling the playing field for visually impaired students.
Healthcare Innovations
In healthcare, VQA offers assistance to patients and practitioners alike, addressing both accessibility and convenience.
Assisting Patients
For visually impaired patients, VQA can help with reading prescription labels, identifying medications, or navigating hospital signage. Asking, “What is written on this bottle?” could save lives by avoiding medication errors.
Supporting Healthcare Providers
Healthcare professionals might use VQA for analyzing medical images or charts, especially in fast-paced settings. For example, a provider might ask, “What abnormalities are visible in this X-ray?”
Retail and E-commerce
Shopping becomes more inclusive with VQA technology, breaking barriers for individuals with disabilities.
Navigating Physical Stores
VQA-enabled devices can guide users through stores, answering queries like, “What items are on this shelf?” or “What is the price of this product?” This makes independent shopping a reality for those with visual impairments.
Online Shopping Accessibility
For e-commerce, VQA bridges gaps by describing product images, answering questions about design, or highlighting features not captured by standard alt-text.
VQA’s Role in Public Spaces
Enhancing Navigation
Public spaces like airports, train stations, and government buildings can be overwhelming, especially for individuals with disabilities. VQA tools integrated into mobile devices can describe surroundings, signage, or landmarks to help users navigate confidently.
Access to Art and Culture
Museums and galleries are now more accessible, thanks to VQA. Users can take a photo of an exhibit and ask questions like, “Who painted this?” or “What does this sculpture represent?” This brings art and history to life for everyone.
Future Trends in VQA Technology
AI Advancements
As AI evolves, VQA systems will become even more intuitive. Improved natural language understanding will allow these systems to provide context-aware, conversational answers.
Personalization Through AI
Future VQA tools may adapt to user preferences, offering detailed or concise responses based on individual needs. For instance, a user might prefer brief descriptions or more nuanced answers depending on the situation.
Integration with Wearables
Wearable devices, such as smart glasses, are likely to become the primary interface for VQA. These tools will offer hands-free, real-time accessibility, seamlessly blending technology into daily life.
Multimodal Interfaces
The combination of audio, visual, and haptic feedback will enhance interaction for users, ensuring multi-sensory communication.
Collaborative AI Ecosystems
VQA will integrate with other AI systems, such as voice assistants or navigation apps, creating comprehensive ecosystems that support accessibility in every aspect of life.

Addressing Ethical and Social Implications of VQA
Ensuring Fair Representation in VQA Models
VQA systems must handle diverse cultures, languages, and perspectives. Bias in datasets can lead to inaccurate or incomplete answers, which disproportionately impacts underrepresented groups.
Building Inclusive Datasets
Developers need to curate datasets that reflect global diversity, covering various environments, objects, and interactions. Collaboration with advocacy groups ensures that marginalized communities are not left behind.
Language and Localization
Multilingual support is vital for accessibility. VQA should recognize and respond to queries in various languages while respecting regional contexts and idioms.
Prioritizing Privacy and Security
Since VQA often involves capturing sensitive images, safeguarding user privacy is a non-negotiable priority.
Robust Data Encryption
VQA systems should implement end-to-end encryption to protect images and queries from unauthorized access. Security protocols must comply with international standards like GDPR and HIPAA.
Ethical AI Use Policies
Companies must establish transparent policies outlining how VQA systems handle data. User consent and anonymization are key to maintaining trust and compliance.
Bridging the Digital Divide
Accessibility is a human right, but technological gaps persist. Affordability and usability remain challenges for widespread VQA adoption.
Affordable Access
Innovative partnerships between governments and tech companies can subsidize VQA tools, making them affordable for underserved communities.
Simplifying Interfaces
User-friendly designs ensure that VQA tools are accessible, even to those unfamiliar with complex technologies.
Advanced VQA Applications: Beyond the Basics
Augmented Accessibility for Dynamic Environments
Traditional accessibility tools often struggle in dynamic, unpredictable environments like crowded streets or events. VQA’s real-time capabilities allow users to ask complex questions such as:
- “Which direction is the nearest exit?”
- “How many people are in this space?”
These features enable users to navigate independently in environments where static tools fall short.
Emotional and Contextual Understanding
Future VQA systems may detect emotions and contexts within visuals. For example:
- Instead of simply answering, “This is a family photo,” a VQA system might add, “This is a cheerful family gathering at sunset.”
This kind of enriched feedback goes beyond object identification, offering a narrative that makes the visual world more meaningful.
AI-Driven Personalization in VQA Systems
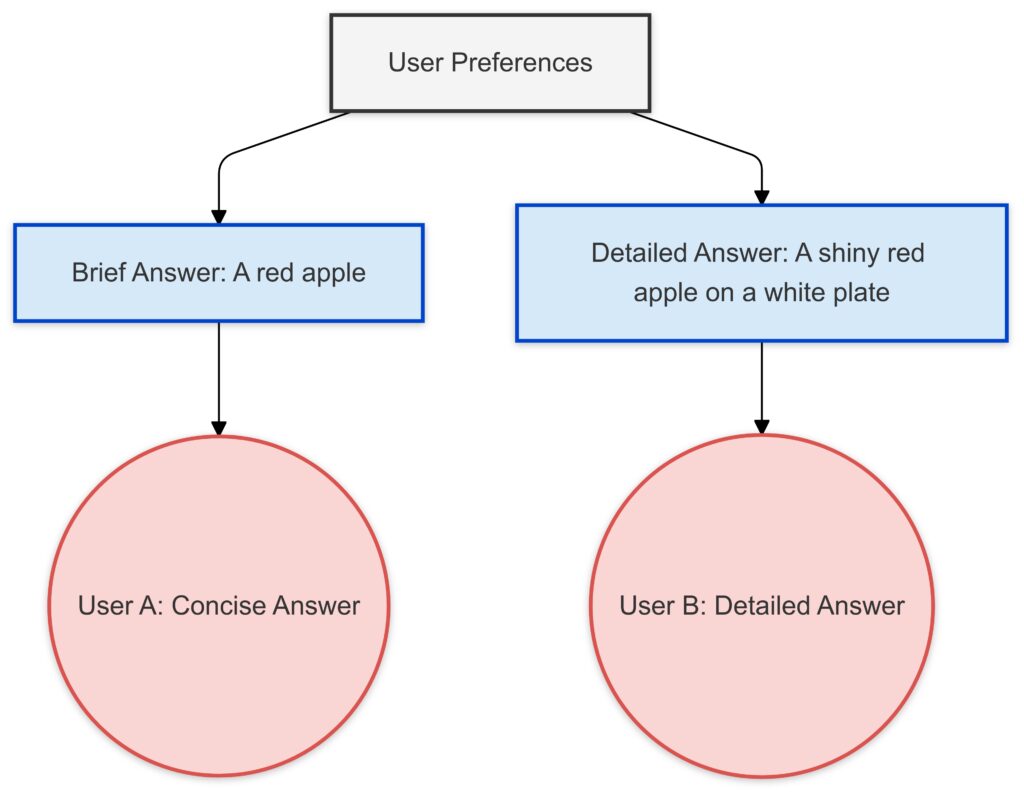
User Preferences:
- Central node representing user-defined preferences for response style.
Responses:
- Brief Answer: For users preferring concise descriptions, e.g., “A red apple.”
- Detailed Answer: For users wanting more context, e.g., “A shiny red apple on a white plate.”
Examples:
User B: Prefers detailed, descriptive responses.
User A: Prefers concise answers.
Adaptive Learning for Individual Users
Advanced VQA systems could personalize responses by learning user preferences over time. For instance:
- A user who values brevity might receive concise answers like, “A red apple on a plate.”
- Those who prefer detail might get, “A shiny red apple sitting on a white ceramic plate, placed on a wooden dining table.”
Predictive Querying
Next-gen VQA could anticipate user needs without explicit prompts. For example, after taking a photo of a train station, the system might suggest:
- “The platform to your left leads to the express train. The ticket counter is ahead.”
Such predictive functionality reduces effort and enhances usability.
Tackling Dataset Bias: A Deeper Dive
The Hidden Risks of Bias
Bias in datasets can result in misinterpretations, leading to inaccurate or culturally insensitive answers. For example:
- Traditional South Asian clothing could be misidentified as “fabric” instead of “sari.”
- Rural African settings might be labeled “undeveloped land” rather than “village farm.”
These errors not only undermine trust but also perpetuate stereotypes.
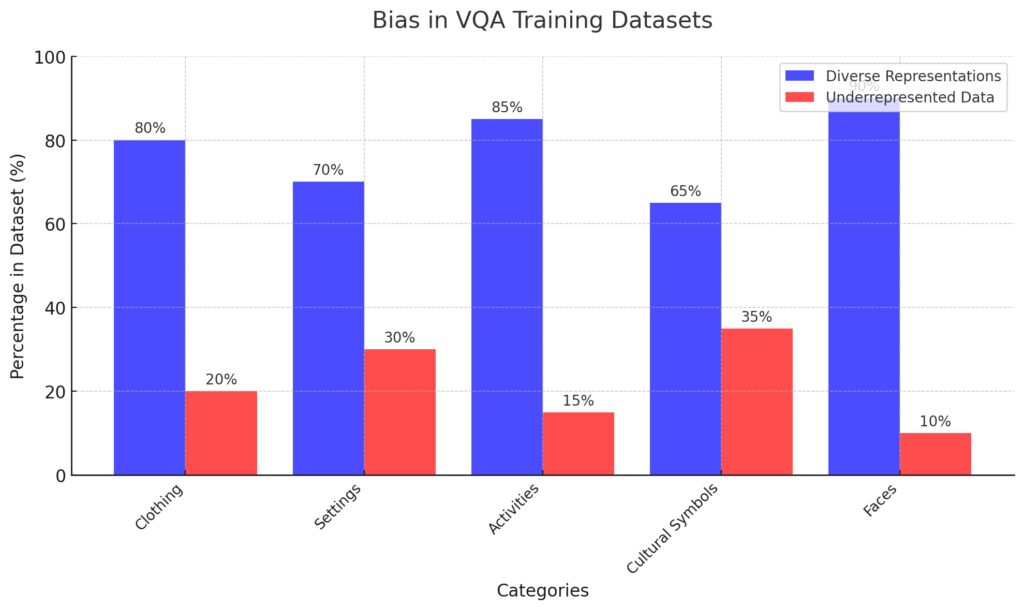
This visualization emphasizes disparities in training data distribution, underscoring the need for inclusivity and fairness in VQA systems
Solutions to Dataset Limitations
To mitigate bias, developers can:
- Use Synthetic Data: Simulate diverse scenarios, such as regional clothing, architecture, and objects, to train AI systems.
- Engage Community-Sourced Labeling: Collaborate with local communities to ensure accurate and culturally sensitive annotations.
The Future of VQA in Public Policy and Infrastructure
Empowering Civic Participation
Governments can deploy VQA to enhance inclusivity in public services. Examples include:
- Making voting ballots accessible by describing options to visually impaired voters.
- Answering queries about city maps or public notices for those with visual or cognitive disabilities.
Smart Cities Integration
Smart cities could integrate VQA with IoT infrastructure for seamless accessibility. For example:
- A smart bus stop might answer, “When is the next bus arriving?” while also describing nearby landmarks for better navigation.
Neuro-AI and Cognitive Accessibility
Supporting Cognitive Disabilities
VQA has the potential to assist individuals with cognitive impairments by simplifying complex visual information. For example:
- Breaking down dense subway maps into clear, step-by-step navigation instructions.
- Converting product labels or instructions into concise, actionable statements.
Multi-Sensory Feedback Systems
Combining VQA with haptic feedback and sound cues creates tools that engage multiple senses. For users with dual sensory loss, tactile vibrations paired with audio outputs could provide accessible and intuitive guidance.
Privacy in the AI Age: Going Beyond Encryption
Ethical Considerations for Image Storage
Cloud-based VQA systems may expose users to privacy risks. Edge computing offers a solution by processing data locally on the device, eliminating the need for image uploads.
Transparency in AI Decisions
Users deserve to understand how VQA systems arrive at answers. Explainable AI (XAI) can offer clarity, showing how specific objects or features led to the response. For example:
- “This answer is based on detecting a stop sign and a pedestrian crossing.”
Breaking Barriers with Affordability
Open-Source VQA Platforms
To democratize access, open-source VQA tools can empower developers to adapt systems for regional and low-resource contexts. For instance:
- Platforms tailored for underserved languages.
- Lightweight VQA models optimized for low-bandwidth environments.
Low-Tech VQA Solutions
Even users with basic devices, such as feature phones, could benefit from simplified VQA systems. These might deliver text-based outputs via SMS or voice calls, ensuring access in rural or economically challenged areas.
The Road Ahead for VQA and Accessibility
Visual Question Answering is more than a technological innovation—it’s a revolution for inclusive design and universal access. By enhancing independence, improving opportunities, and fostering equity, VQA has the potential to redefine accessibility across the globe.
Advancements in AI, combined with collaborative efforts to address challenges, will ensure that VQA continues to evolve into a game-changing tool for empowerment. As adoption grows, it will serve as a powerful reminder that technology, when designed thoughtfully, can truly transform lives.
FAQs
What devices or platforms support VQA?
VQA is available on various platforms, including:
- Smartphone apps like Seeing AI and Envision AI, which allow users to snap photos or record videos for real-time feedback.
- Wearable devices such as smart glasses, which can integrate VQA for hands-free operation.
- IoT-enabled systems like smart home assistants, making daily tasks more accessible.
Example: A visually impaired user could ask their wearable device, “What’s on this restaurant menu?” and receive a detailed description.
Is VQA only for people with disabilities?
No, VQA benefits everyone by enhancing human-technology interaction. It can help users in diverse scenarios, such as:
- Identifying misplaced items: “Where is my phone in this room?”
- Assisting travelers: “What does this road sign mean?”
- Engaging museum visitors: “Who painted this artwork?”
The technology’s versatility makes it valuable beyond accessibility.
Does VQA work in real time?
Many VQA systems support real-time processing, especially when integrated into wearables or mobile apps. This allows users to receive instant feedback on their surroundings.
Example: A user walking through a park could ask, “What animals are nearby?” and the system might reply, “A squirrel is climbing the tree to your left.”
However, real-time functionality often depends on processing power and internet connectivity.
Can VQA describe emotions or abstract concepts?
Emerging VQA technologies aim to describe emotions, moods, and abstract details. For example:
- A user might ask, “What is happening in this picture?”
- The system could respond, “Two children are playing happily in a sunny backyard.”
Such advancements are particularly useful for creating a richer experience in storytelling, education, or social interactions.
Can VQA identify text in images or documents?
Yes, VQA can process and interpret text within images, making it invaluable for reading signs, documents, or labels. By combining Optical Character Recognition (OCR) with contextual understanding, it delivers meaningful results.
Example:
- If a user asks, “What does this sign say?” while pointing their camera at a traffic sign, the VQA system might reply: “The sign says, ‘No Parking from 9 AM to 5 PM.’”
For visually impaired users, this bridges gaps in environments where text-based information dominates.
How accurate are VQA systems?
The accuracy of VQA systems depends on the quality of their training datasets and algorithms. While most systems handle basic queries reliably, complex or ambiguous scenarios may lead to errors.
For example:
- A simple query like “What color is this car?” will likely produce accurate results.
- A more nuanced question like “Is this car environmentally friendly?” might struggle due to its subjective nature.
Developers are constantly working to refine these systems to improve context awareness and precision.
Can VQA help in emergencies?
Yes, VQA has the potential to assist during emergencies by providing quick, relevant information. For instance:
- A user in an unfamiliar location might ask, “Where is the nearest fire extinguisher?” or “What does this emergency exit sign say?”
- First responders could use VQA-enabled tools to analyze live visuals, like asking, “Where are the injured people in this area?”
Such applications make VQA a valuable tool for safety and crisis management.
How does VQA handle ambiguous questions?
VQA systems use contextual analysis and machine learning to clarify ambiguous queries. However, if the system cannot determine an accurate answer, it might respond with clarifying questions or probabilistic answers.
Example:
- Query: “What is on the table?”
- Response: “There are several items on the table: a coffee mug, a book, and a pair of glasses. Which one do you mean?”
This feature allows the system to adapt to user intent, reducing confusion.
Can VQA describe scenes in videos?
Yes, some VQA systems are designed to process video content, analyzing multiple frames to answer dynamic questions about moving objects or evolving scenarios.
Example:
- A user watching a wildlife documentary might ask, “What animal just entered the frame?”
- The system could answer, “A cheetah is entering from the left, chasing a gazelle.”
Such capabilities are useful for entertainment, education, and accessibility in real-time or pre-recorded videos.
Does VQA work offline?
While many VQA systems rely on cloud processing for complex tasks, offline functionality is increasingly supported through edge computing and local AI models.
For example:
- An offline VQA system on a smartphone could answer, “What is this fruit?” by analyzing an image of an apple using pre-installed AI models.
Offline modes are particularly valuable in rural areas, during travel, or in emergencies where internet access is limited.
Can VQA interpret artistic or abstract images?
Interpreting artistic visuals, like paintings or abstract art, is challenging for VQA. However, advanced systems trained on cultural and artistic datasets can provide meaningful interpretations.
Example:
- A user might ask, “What does this painting represent?”
- The VQA system could answer, “This is a surrealist painting by Salvador Dalí, featuring melting clocks to symbolize the fluidity of time.”
While still limited in nuance, this application broadens accessibility to cultural experiences.
Is VQA compatible with other assistive technologies?
Yes, VQA can integrate with existing assistive technologies like screen readers, voice assistants, and braille devices.
Examples:
- A screen reader could narrate VQA results aloud: “This image shows a park with people playing frisbee.”
- Braille displays might provide tactile descriptions, converting text responses into braille characters for blind users.
This interoperability enhances accessibility for people with multiple disabilities.
Are there industries beyond accessibility using VQA?
Yes, VQA is being adopted in industries like healthcare, retail, and security for innovative use cases.
Examples:
- Healthcare: Doctors might use VQA to interpret X-rays, asking, “What abnormalities are visible in this scan?”
- Retail: Shoppers can ask, “What are the features of this product?” by scanning its label with a VQA app.
- Security: Surveillance systems equipped with VQA can respond to queries like, “Is there anyone in this restricted area?”
These applications demonstrate the broad potential of VQA technology across diverse sectors.
How accessible is VQA for non-tech-savvy users?
VQA systems are designed to be intuitive, often using voice or touch-based interfaces for ease of use. Many systems prioritize user-friendly interactions, such as:
- Simple commands like “Describe this scene.”
- Step-by-step onboarding to help new users navigate the tool.
For instance, an elderly user could use a VQA app to ask, “What’s in this pantry?” and receive a clear, spoken description without needing technical expertise.
Will VQA ever replace human assistance?
While VQA is highly advanced, it is unlikely to completely replace human assistance. Instead, it serves as a complementary tool that reduces dependency and enhances independence.
Example:
- A visually impaired person might use VQA to navigate their home but still rely on human guidance for nuanced social interactions, like choosing an outfit for a specific event.
This balance highlights the importance of combining technology with human support for the best outcomes.
Resources
Research Papers and Academic Resources
- “Visual Question Answering: Datasets, Algorithms, and Future Challenges”
A comprehensive paper exploring the foundations of VQA, including datasets, methodologies, and challenges. Link to paper - “VQA: Visual Question Answering Dataset”
This seminal paper introduced one of the first large-scale VQA datasets, laying the groundwork for modern VQA systems. Read it here - ACL Anthology
A repository of research papers on natural language processing, including VQA-related studies. Explore ACL
Open-Source Tools and Frameworks
- VQA Demo from VisualGenome
An interactive demo to test VQA capabilities using publicly available datasets. Try it here - PyTorch Tutorials on VQA
Learn to implement basic VQA models using PyTorch. Includes step-by-step instructions and datasets. - Hugging Face Transformers
Pretrained models for language and vision tasks, including VQA applications. Get started
Accessible VQA Apps and Platforms
- Microsoft Seeing AI
A powerful app for visually impaired users that combines VQA with OCR, object detection, and navigation tools. Download it here - Envision AI
A mobile app that helps visually impaired users describe objects, scenes, and text in real time. Learn more - Google Lookout
A tool designed for Android users that offers real-time image and text recognition.





