
Generative AI has seen incredible advancements in recent years. From text generation to artificial creativity, AI is reshaping industries across the board. But just when you thought the possibilities were limitless, a new development is pushing boundaries even further: the rise of AI agents. These autonomous entities represent the next frontier in AI, and they promise to revolutionize how we interact with technology. So, what exactly are these agents, and how will they change the game?
What Are AI Agents?
At its core, an AI agent is a self-operating software program designed to perform tasks autonomously. Unlike traditional AI models, which often require human intervention to function, these agents can make decisions, execute actions, and even adapt to new situations without direct oversight. Think of them as a hybrid between traditional AI and autonomous robots—but without the physical form.
Why AI Agents Matter
The appeal of AI agents lies in their potential to automate complex processes that currently require human oversight. By leveraging machine learning and neural networks, these agents can learn from their environments, make informed decisions, and carry out tasks that were previously too nuanced for automated systems. For businesses, this means reducing overhead costs and improving efficiency by automating intricate workflows.
This diagram illustrates how generative AI agents work.
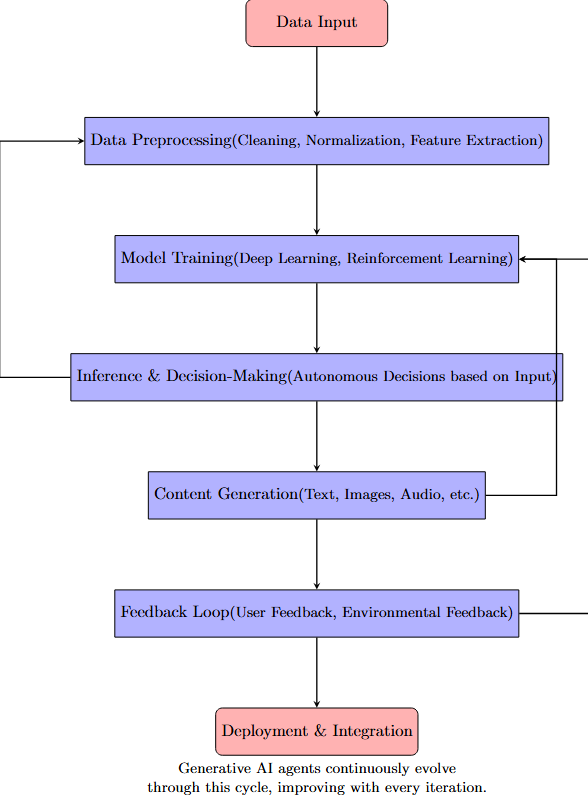
Key Differences Between Generative AI Agents and Traditional AI
1. Autonomy
- Traditional AI: Requires human oversight for operation and decision-making. Tasks are typically static and predefined.
- Generative AI Agents: Operate autonomously, making decisions and adapting to new situations without direct human input. They can manage dynamic and complex environments independently.
2. Adaptability
- Traditional AI: Often struggles with tasks outside its specific training. It excels in controlled environments but lacks flexibility.
- Generative AI Agents: Highly adaptable, these agents can learn from new data, adjust their actions, and even improve their decision-making over time.
3. Creativity
- Traditional AI: Limited to processing existing data and following predefined rules. It does not generate new ideas or concepts.
- Generative AI Agents: Capable of creating new content, whether it’s text, images, or even strategies for problem-solving. They simulate aspects of human creativity, offering novel solutions.
4. Task Complexity
- Traditional AI: Best suited for tasks with clear, predictable outcomes, such as data analysis, classification, or simple decision-making.
- Generative AI Agents: Handle more complex, multifaceted tasks that require a deeper understanding of context, such as autonomous project management or interactive customer service.
Comparison Chart: Generative AI Agents vs. Traditional AI
| Feature | Generative AI Agents | Traditional AI Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Autonomy | High autonomy; capable of making decisions without human input | Low to moderate autonomy; often requires human intervention or pre-programmed rules |
| Adaptability | Highly adaptable; learns and evolves with minimal human oversight | Limited adaptability; requires reprogramming or retraining to adjust to new tasks |
| Creativity | High creativity; generates novel content and ideas (e.g., art, text, designs) | Low creativity; follows specific, predefined rules or templates |
| Task Complexity | Capable of handling complex, open-ended tasks | Best suited for well-defined, structured tasks |
| Learning Approach | Uses deep learning, reinforcement learning, and unsupervised learning techniques | Primarily uses supervised learning and rule-based systems |
| Data Requirements | Requires large amounts of diverse data for training | Can work with smaller, more specific datasets |
| Interaction Style | More natural and human-like; can engage in complex dialogues and generate context-aware responses | Limited interaction capabilities; often provides straightforward, predetermined responses |
| Use Cases | Content creation, conversational agents, artistic generation, adaptive systems | Data analysis, automation, predictive analytics, and rule-based decision making |
| Scalability | Highly scalable; can be deployed across various applications and industries | Scalable within specific domains but less versatile |
| Innovation Potential | High potential for innovation; can create previously unimaginable solutions | Limited innovation; focuses on optimization within predefined constraints |
Real-World Applications
Generative AI agents are making waves across various industries. In healthcare, they are used to personalize treatment plans and predict patient outcomes. In finance, they can autonomously manage portfolios, assess risks, and even execute trades. Traditional AI, while still powerful, remains largely confined to tasks like fraud detection, customer segmentation, and automated reporting.
In creative industries, generative AI agents are being used to produce original music, art, and literature, something traditional AI could never achieve. Meanwhile, traditional AI continues to excel in tasks like optimizing supply chains, improving manufacturing processes, and enhancing cybersecurity measures.
Advantages of Generative AI Agents
The primary advantage of generative AI agents is their ability to operate independently and adapt to changing conditions. This allows them to handle tasks that would be too complex or time-consuming for traditional AI systems. Additionally, their creative capabilities open up new possibilities for innovation, from personalized marketing campaigns to entirely new product designs.
Enhancing Customer Experience
One of the most promising applications of AI agents is in customer service. By harnessing the power of natural language processing (NLP), these agents can understand and respond to customer inquiries in real-time. Unlike traditional chatbots, AI agents are not limited to scripted responses; they can generate personalized replies, make decisions on the fly, and even escalate issues to human operators when necessary.
Revolutionizing the Workplace
In the workplace, AI agents could become invaluable assets. Imagine having an AI assistant that not only schedules meetings and manages emails but also analyzes business data, provides strategic recommendations, and manages projects autonomously. This is the future that AI agents could bring to fruition, allowing employees to focus on higher-level tasks while routine operations are handled by intelligent agents.
Ethical Considerations
With great power comes great responsibility. As AI agents become more prevalent, ethical considerations must be addressed. How do we ensure these agents make decisions that align with human values? What safeguards need to be in place to prevent misuse? These are crucial questions that developers, businesses, and policymakers must tackle as we move forward.
The Role of Human Oversight
Despite their autonomy, AI agents will still require some level of human oversight. This is especially true in high-stakes industries like healthcare and finance, where errors can have significant consequences. Ensuring that AI agents operate within predefined parameters and are regularly audited will be essential for maintaining trust and safety.
The Evolution of AI Agents
The technology behind AI agents is still in its infancy, but it’s evolving rapidly. As algorithms improve and computational power increases, we can expect AI agents to become more sophisticated and capable. Future developments may include agents that can learn from minimal data, operate in highly dynamic environments, and even collaborate with other AI systems.
The Future of AI: A Symbiotic Relationship
It’s important to recognize that generative AI agents and traditional AI systems are not mutually exclusive. In fact, they can complement each other beautifully. For example, a traditional AI system might handle data collection and initial analysis, while a generative AI agent uses that data to create actionable insights or innovative solutions.
Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
When deciding between generative AI agents and traditional AI, the key is to consider the specific needs of your task or project. Traditional AI is ideal for tasks requiring precision, speed, and efficiency in a controlled environment. Generative AI agents, on the other hand, excel in situations that require creativity, adaptability, and autonomous decision-making.
Challenges on the Horizon
While the potential of AI agents is vast, there are significant challenges to overcome. Data privacy concerns, the complexity of integrating these agents into existing systems, and the risk of job displacement are all issues that need careful consideration. Addressing these challenges will be key to ensuring the successful adoption of AI agents.
Final Thoughts: Embracing the Agent Revolution
The emergence of AI agents marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of technology. As these autonomous systems become more integrated into our daily lives and workspaces, they will fundamentally alter how we interact with the digital world. The promise of increased efficiency, personalized experiences, and enhanced decision-making is within reach, but this potential comes with responsibilities. Ethical considerations, human oversight, and strategic planning will be crucial in navigating this new frontier.
As we embrace this next wave of generative AI, we must do so with a clear understanding of both its incredible potential and its inherent challenges. The future of AI agents is not just about technological advancement; it’s about creating a symbiotic relationship between humans and machines, where both can thrive. By harnessing the power of these agents thoughtfully and responsibly, we can unlock new possibilities and lead the way into a more intelligent and interconnected world.