
Zero Trust and AI-driven passwordless authentication have become buzzwords—but they’re much more than hype. They’re the future of secure access in modern enterprises.
Let’s dive into how these two technologies converge to redefine digital identity, improve security, and simplify user experiences.
Understanding the Zero Trust Model in Cybersecurity
What Is Zero Trust, and Why Does It Matter?
The Zero Trust model shifts away from traditional “trust but verify” approaches. Instead, it adopts a “never trust, always verify” stance.
Every access request, whether internal or external, is evaluated continuously.
This model is essential in today’s remote work culture. Employees, contractors, and third-party vendors access networks from diverse locations and devices, leaving traditional perimeter-based defenses obsolete.
Zero Trust Pillars: The Foundation of Strong Security
Zero Trust relies on these principles:
- Continuous verification: Access is constantly reevaluated.
- Least privilege access: Users get only the access they need.
- Assume breach: Operate as though intrusions are inevitable.
These principles reduce vulnerabilities by ensuring only authenticated, authorized users gain entry.
Challenges Enterprises Face Without Zero Trust
Without a Zero Trust strategy, enterprises face common risks, including:
- Credential-based breaches.
- Lateral movement of attackers across systems.
- Poor visibility into who is accessing what.
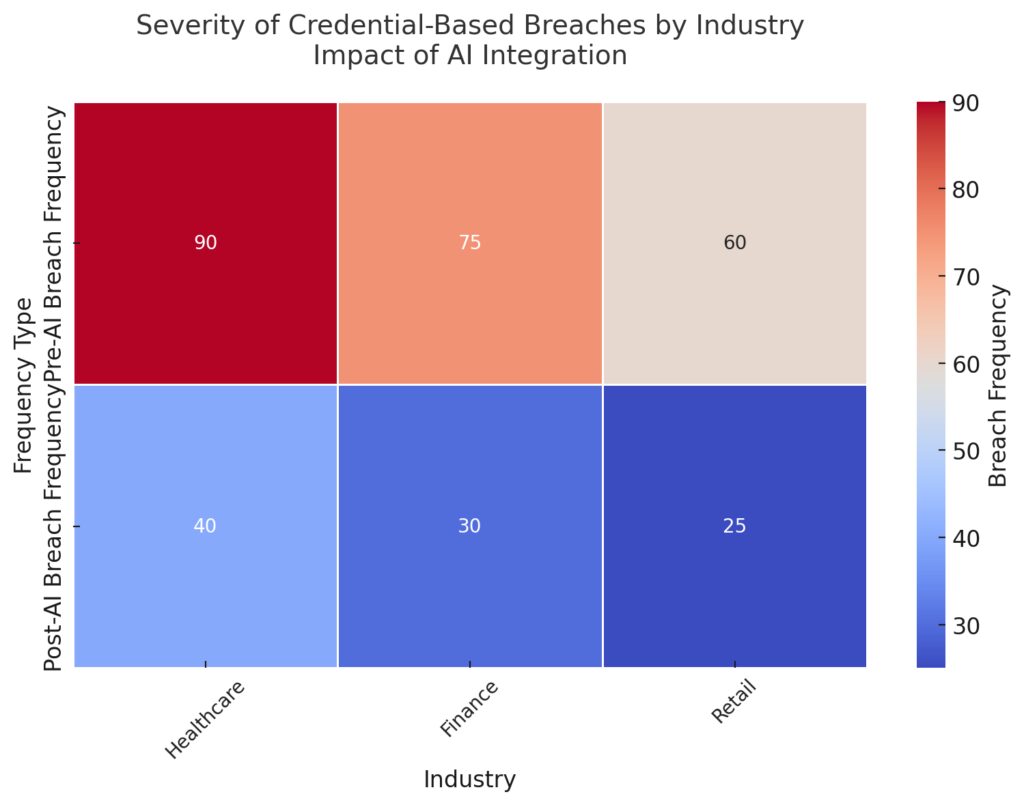
The cool-to-warm color gradient emphasizes the decreasing intensity of threats after AI implementation. AI integration clearly mitigates risks across all industries, with significant reductions in breach frequency.
Adopting Zero Trust mitigates these risks by scrutinizing each request and enforcing strict security measures.
The Rise of Passwordless Authentication
What Is Passwordless Authentication?
Passwordless authentication replaces traditional passwords with advanced technologies like biometrics, cryptographic keys, or device-based login. Think fingerprint scanning or push notifications over the cumbersome password-recall process.
It’s the user-friendly cousin of multi-factor authentication (MFA), eliminating a known security weak spot: passwords.
Why Passwords Are a Security Risk
Passwords are infamous for being reused, guessed, or stolen. A 2023 Verizon Data Breach Report revealed that over 80% of breaches involve weak or stolen passwords. Passwordless systems sidestep this issue entirely.
Imagine no more “forgot your password” emails or password-reset hassles for your IT team. Passwordless methods mean stronger security and happier users.
How AI Improves Passwordless Authentication
AI algorithms add another layer of protection by analyzing user behavior, devices, and access patterns in real time.
For example, AI can detect anomalies like unusual locations or access attempts outside regular hours, blocking potential threats proactively.
How AI Transforms the Zero Trust Approach
AI takes Zero Trust strategies to new heights by automating threat detection, analyzing vast datasets, and enabling real-time decision-making. With AI, enterprises can:
- Identify malicious actors faster through behavioral analysis.
- Pinpoint access anomalies that traditional systems might miss.
- Automate risk-based decisions, like requiring additional verification for suspicious logins.
AI complements Zero Trust by providing dynamic, adaptive security rather than static rules.
Behavioral Biometrics: A Game Changer
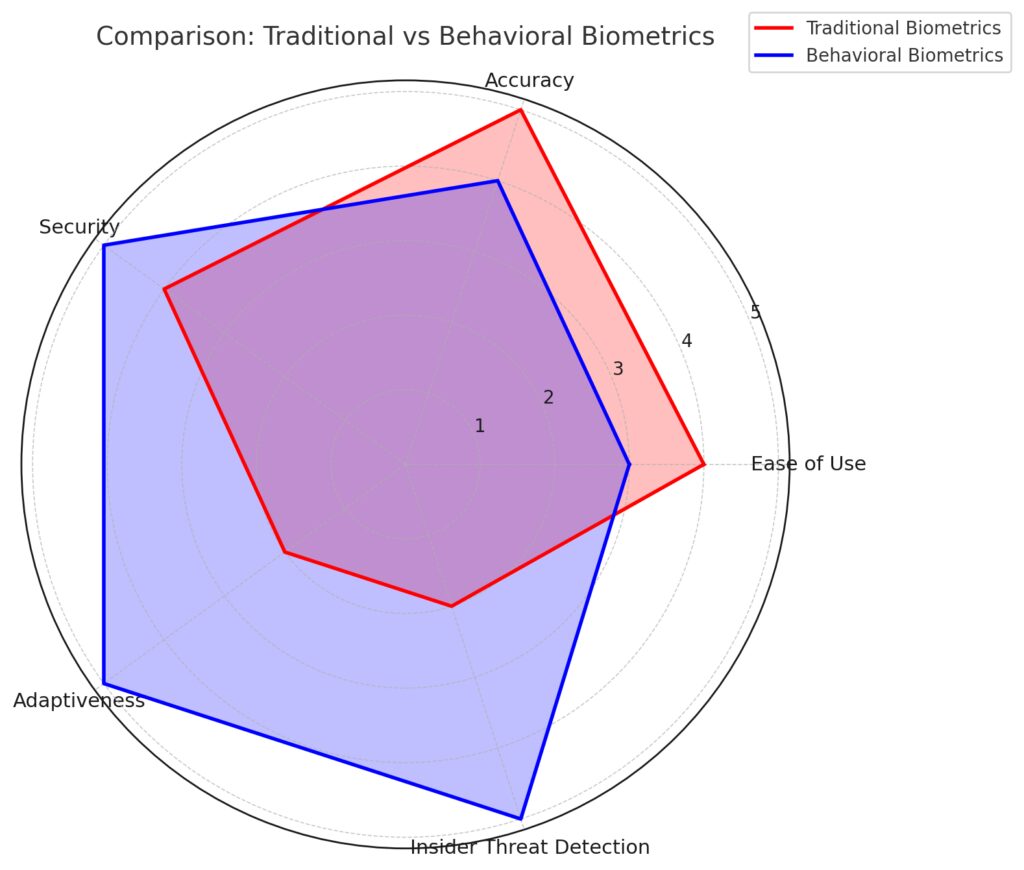
Behavioral biometrics enhance security by analyzing user interaction patterns, complementing traditional authentication methods.
Behavioral biometrics, powered by AI, monitor subtle patterns like typing speed, mouse movements, or smartphone tilt. If a user’s behavior deviates significantly from the norm, the system can flag or block access.
This goes beyond basic MFA to provide nuanced, context-aware authentication.
Predictive Analytics and Risk Scoring
AI can predict potential threats through risk scoring. For instance, if an employee logs in from an unusual country, AI assigns a high-risk score, prompting additional identity verification measures.
This predictive power makes AI critical for defending against increasingly sophisticated attacks.
Enterprise Benefits of Combining Zero Trust and AI
Stronger Security, Reduced Breaches
By combining Zero Trust with AI-powered passwordless authentication, enterprises can mitigate risks like phishing, credential stuffing, and brute-force attacks. Every login attempt is scrutinized—AI ensures no red flags slip through.
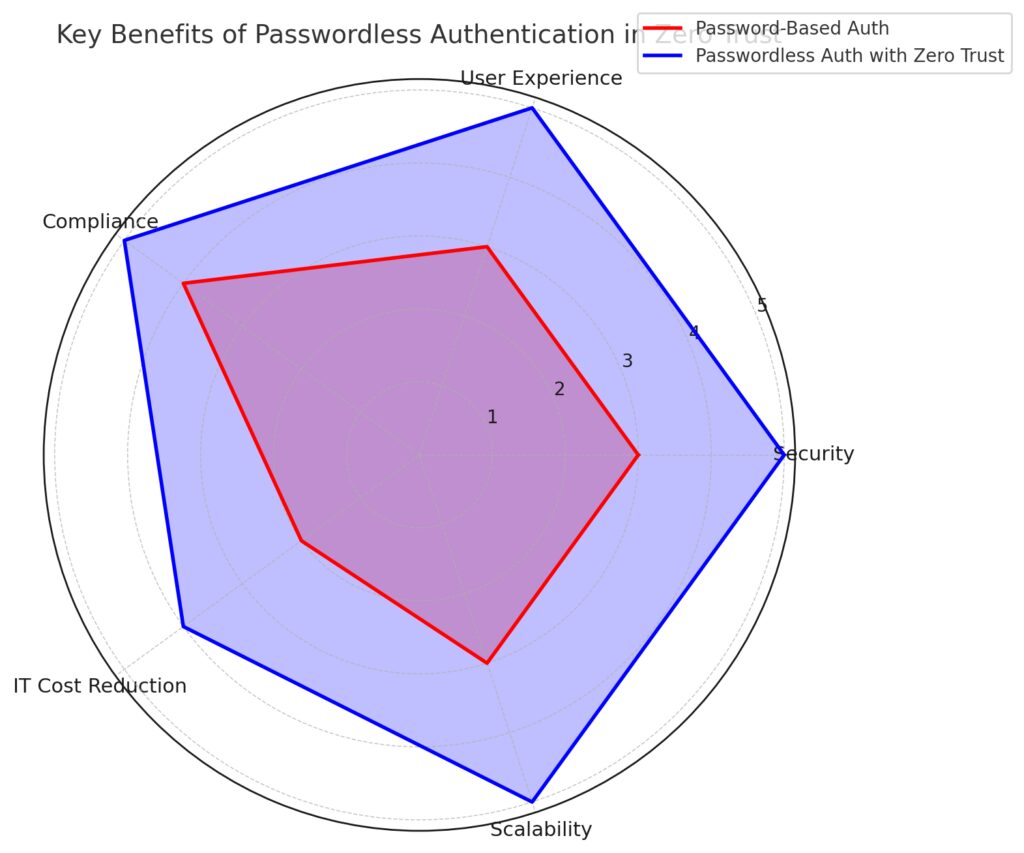
The chart highlights the superior performance of passwordless systems, particularly when combined with a Zero Trust framework.
Seamless User Experience
AI streamlines authentication without compromising security. Instead of requiring users to remember complex passwords, enterprises can implement frictionless login solutions like:
- Face recognition.
- Device-based cryptographic tokens.
- One-touch mobile approvals.
The result? Employees spend less time logging in and more time being productive.
Reduced Costs for IT Teams
Password management is a major IT expense, from resetting forgotten credentials to responding to phishing incidents. Going passwordless eliminates this overhead, saving resources and reducing downtime caused by compromised accounts.
Real-World Applications in Enterprise Security
Case Study: A Tech Giant’s Shift to Passwordless Login
A major technology company implemented AI-driven passwordless authentication across its workforce. By leveraging Zero Trust and behavioral biometrics, it:
- Reduced unauthorized access by 60%.
- Slashed password-reset requests by 80%.
- Achieved faster login times, boosting productivity.
Industries Benefiting Most from This Model
Certain industries are ahead in adopting Zero Trust and passwordless tech:
- Healthcare: Protects patient data from breaches while complying with HIPAA.
- Finance: Safeguards sensitive financial records and reduces fraud.
- Retail: Protects e-commerce platforms from credential-stuffing attacks.

Implementing Passwordless Authentication in a Zero Trust Framework
Key Technologies Powering Passwordless Authentication
Several cutting-edge technologies enable passwordless authentication within the Zero Trust model:
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scans ensure access relies on unique personal identifiers.
- FIDO2 and WebAuthn: These open standards enable secure, device-based authentication without storing sensitive information on servers.
- Smartcards and Tokens: Hardware security modules generate cryptographic keys, adding an extra layer of protection.
By deploying these technologies, enterprises can achieve robust security while enhancing usability.
Building a Zero Trust Ecosystem
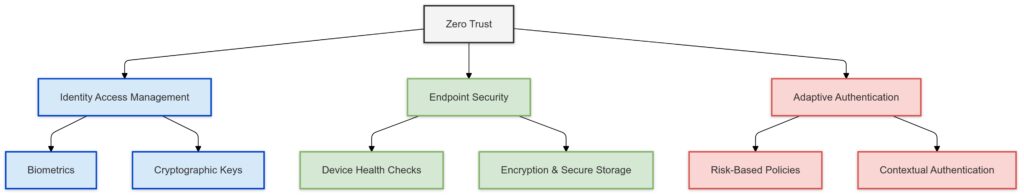
To successfully integrate passwordless authentication, enterprises must establish a Zero Trust ecosystem with:
- Identity Access Management (IAM): Centralized tools like Okta or Azure AD to enforce authentication policies.
- Endpoint Security: AI-powered monitoring to assess the risk of devices requesting access.
- Adaptive Authentication: Context-aware systems that adjust security measures based on user behavior.
Overcoming Challenges in Deployment
Adopting Zero Trust and passwordless methods may face hurdles like:
- Legacy systems that aren’t compatible with modern authentication.
- Resistance to change among users or leadership.
- High initial costs of deploying new technology at scale.
Solutions include phased rollouts, employee training, and partnering with experienced vendors to ensure seamless integration.
The Technical Backbone of Zero Trust and Passwordless Authentication
How AI Powers Contextual Authentication
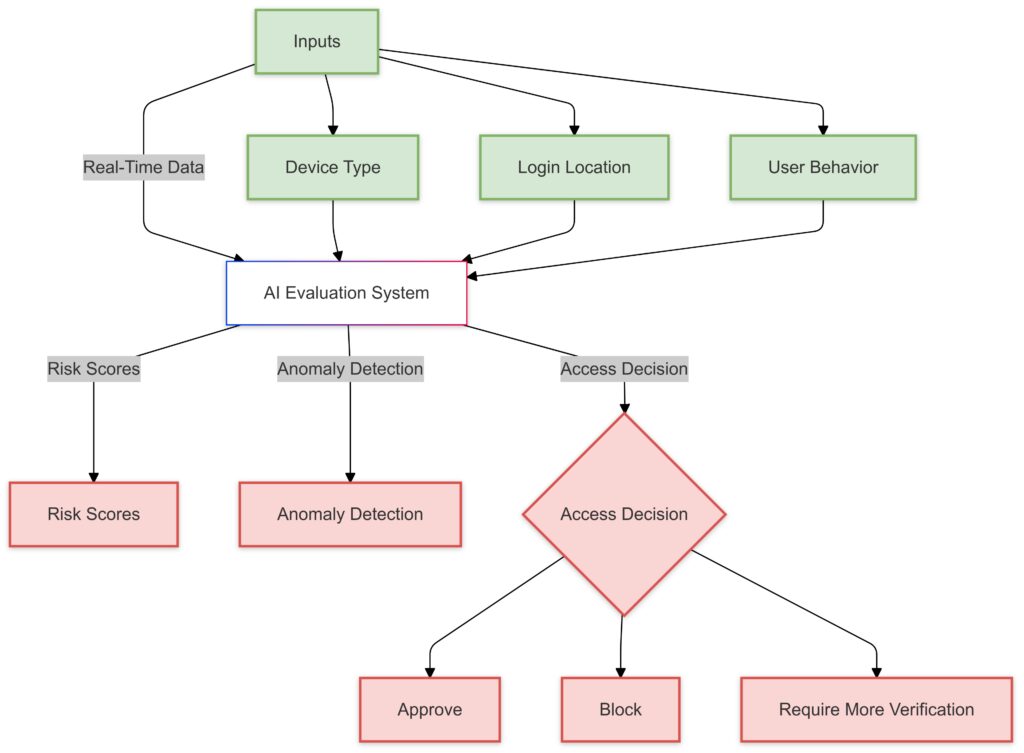
AI introduces a new level of contextual authentication by continuously analyzing and adapting based on real-time data. Here’s how:
- User Behavior Analysis: AI tracks login times, locations, devices, and even typing patterns. For example, an employee who usually logs in from New York at 9 AM will trigger alerts if attempting access from Tokyo at midnight.
- Device Trustworthiness: AI inspects devices for indicators like jailbreaking, outdated software, or unusual activity, labeling them as “trusted” or “untrusted.”
- Anomaly Detection: AI flags access requests deviating from baseline behavior. This means even if credentials are stolen, unauthorized use is blocked.
By integrating these elements, AI ensures enterprises dynamically authenticate users without relying on static policies.
Passwordless Authentication Technology in Action
To truly eliminate passwords, enterprises can adopt a blend of technologies:
- Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): PKI uses cryptographic keys for secure, passwordless logins. Users authenticate by proving ownership of a private key stored securely on their device.
- Proximity-Based Authentication: Bluetooth and NFC technologies authenticate users when their verified device is nearby, enabling seamless access.
- Biometric Fusion: Combining multiple biometrics, such as face and fingerprint scans, further enhances security by making impersonation virtually impossible.
When paired with AI, these technologies provide a seamless, layered approach to security.
Advanced Security Strategies in a Passwordless Environment

Continuous Access Monitoring
One-time authentication isn’t enough in a Zero Trust model. Continuous Access Monitoring (CAM) ensures security beyond the initial login by verifying users throughout their session.
- AI detects session hijacking by monitoring unexpected behavior, such as IP changes mid-session.
- Risk levels adjust dynamically; for example, sensitive data access might trigger additional verification steps, even mid-workflow.
This approach ensures even insiders or hijacked sessions can’t go unchecked.
Role of Multi-Factor Authentication in Passwordless Systems
Although MFA and passwordless authentication might seem interchangeable, they complement one another. In cases where passwordless solutions raise risk flags, MFA acts as a fallback.
Examples include:
- Using a biometric scan paired with a one-time device key.
- Prompting for a trusted second device verification if a login attempt deviates from usual patterns.
Passwordless solutions supported by MFA ensure users remain authenticated while offering a flexible safety net.
Strengthening Privileged Access with Passwordless AI Tools
Privileged access, like admin logins or access to financial data, remains a major target for attackers. AI-integrated passwordless tools can enforce:
- Just-in-Time Access (JIT): Permissions granted only when explicitly needed, then revoked immediately after.
- Granular Control: Differentiating levels of access based on real-time assessments of trustworthiness.
- Biometric Escalation: Requiring multiple biometrics for high-risk operations, such as transferring funds or modifying critical systems.
This tailored approach strengthens security for enterprise-critical assets.
Key Metrics for Evaluating Passwordless Zero Trust Deployments
Reducing Breach Risk and Credential Abuse
Passwordless authentication eliminates the risks of weak, stolen, or reused passwords. Enterprises implementing these systems report:
- Up to a 95% reduction in credential stuffing attacks (source: IBM Cybersecurity Report).
- 50% fewer phishing incidents, as attackers can no longer exploit password resets or stolen credentials.
Measuring Usability Improvements
User adoption is critical for success. Metrics showing the success of passwordless Zero Trust strategies include:
- Faster authentication times: Studies show biometric logins are up to 10x faster than typing passwords.
- Lower password-related IT costs: Enterprises save $70 per password reset on average.
Enhanced Visibility with AI-Driven Analytics
AI provides enterprises with a centralized view of all access attempts, successful or blocked, via real-time dashboards. This not only improves visibility but helps audit compliance with regulatory requirements such as GDPR or HIPAA.
The Role of Decentralized Identity in Zero Trust
Shifting Toward Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) allows individuals to own and control their digital identities rather than relying on centralized databases. By leveraging blockchain, SSI eliminates the need for companies to store sensitive user information, reducing data breach risks.
Key features include:
- Decentralized Verification: Users authenticate through cryptographic proofs stored in blockchain wallets.
- Data Minimization: Only essential attributes (e.g., “over 18” rather than birth date) are shared, enhancing privacy.
This fits perfectly within a Zero Trust framework, where user identity is verified at every step but without compromising security or privacy.
Implementing Decentralized Identity Systems
Integrating SSI into enterprise authentication systems can require:
- Partnering with decentralized identity providers like Sovrin or Microsoft ION.
- Training users and IT teams to adopt blockchain-based wallets for secure identity management.
- Developing smart contracts to manage identity verification workflows.
Long-Term Vision: AI, Zero Trust, and Automation
Fully Autonomous Security
AI’s role in Zero Trust and passwordless systems is only set to grow. The future will likely see:
- Automated Incident Response: AI blocking attacks in milliseconds without human intervention.
- Self-Healing Systems: AI repairing compromised devices or access points by quarantining and patching them autonomously.
- Proactive Threat Hunting: AI scanning global attack patterns to identify vulnerabilities before they’re exploited.
Convergence with IoT and Edge Computing
As IoT devices proliferate, their access needs also grow. Passwordless systems powered by AI-driven Zero Trust can secure billions of endpoints, adapting dynamically to unique risks posed by edge devices.
Embracing AI Ethics in Identity Systems
The increased reliance on AI raises important ethical questions:
- Bias in biometric data: Developers must eliminate inaccuracies that could disproportionately impact users based on race or gender.
- Data ownership: Enterprises must balance security with privacy, ensuring AI doesn’t infringe on user rights.
Addressing these challenges is crucial to creating systems that are secure, fair, and widely accepted.
Enterprises that fully integrate Zero Trust, AI, and passwordless authentication will lead the charge into a future of frictionless, secure access. The potential to streamline operations while bolstering defenses is unmatched—but success depends on understanding and harnessing the intricate technologies behind these innovations.
FAQs
Can Zero Trust and passwordless systems coexist with legacy infrastructure?
Yes, enterprises can integrate Zero Trust and passwordless systems with older infrastructure by adopting a phased implementation strategy. Compatibility tools like secure gateways or modern IAM platforms (e.g., Okta) bridge the gap.
Example: A healthcare provider can start by deploying passwordless solutions for its HR department while maintaining legacy systems for patient records, gradually transitioning to a fully Zero Trust model.
How does AI identify unusual access attempts?
AI analyzes access patterns over time, creating a baseline for normal user behavior. It evaluates factors like:
- Login locations: Logging in from an unexpected country.
- Access timing: A login attempt at 3 AM when a user typically works 9-5.
- Device type: Using an unregistered device or outdated software.
For example, an employee logging in from a new device while on vacation might trigger a verification prompt, ensuring security without assuming malice.
What happens if biometrics fail in a passwordless system?
Passwordless systems often include fallback options like trusted devices or backup verification methods. If a fingerprint scanner fails to recognize the user, they could use a push notification on their smartphone or a pre-configured security key.
For example, a traveling employee unable to access a fingerprint scanner can still authenticate through their phone’s Face ID or a hardware token.
Are passwordless authentication systems suitable for small businesses?
Absolutely! Small businesses benefit greatly from passwordless systems as they:
- Reduce reliance on IT teams for password resets.
- Mitigate risks from phishing attacks.
- Provide a seamless, professional experience for users.
For example, a small e-commerce business could deploy a FIDO2-based solution, allowing employees to securely access customer data without passwords.
What industries benefit most from Zero Trust and passwordless authentication?
Industries with high security and compliance needs stand to gain the most, including:
- Healthcare: Protect sensitive patient data.
- Finance: Secure financial transactions and combat fraud.
- Retail: Safeguard e-commerce platforms against credential theft.
For instance, a bank can secure online banking logins with biometrics, ensuring only the account holder can access funds.
How do passwordless systems handle compliance requirements?
Passwordless systems improve compliance by reducing risks like credential theft while offering features like detailed logging. Most systems support adherence to regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS by:
- Enforcing strong authentication measures.
- Maintaining access logs for auditing.
For example, a pharmaceutical company can meet HIPAA standards by using biometrics and AI-driven risk assessments to control access to sensitive research data.
What’s the ROI for implementing passwordless authentication in enterprises?
Enterprises see returns through:
- Lower IT costs: Fewer password-reset requests save time and money.
- Increased productivity: Faster login times mean employees can focus on work.
- Stronger security: Avoiding costly data breaches caused by weak passwords.
For instance, a global tech company reported saving millions annually by switching to passwordless logins and reducing support calls.
Is passwordless authentication the future of cybersecurity?
Yes! With its ability to simplify access, eliminate password vulnerabilities, and integrate with Zero Trust principles, passwordless authentication is becoming a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity.
Enterprises adopting this approach are better equipped to defend against emerging threats while providing a superior user experience. As more organizations implement AI-enhanced systems, passwordless technology will likely become the new standard for securing digital access.
How does passwordless authentication protect against phishing attacks?
Passwordless authentication removes the need for users to input passwords, eliminating the primary target of phishing scams. Attackers cannot trick users into revealing credentials if there are no credentials to steal.
For example:
- Instead of entering a password, a user approves login via a push notification or biometric scan.
- Even if an attacker sends a fake link, they cannot access the authentication methods tied directly to the user’s device or identity.
Can Zero Trust and passwordless systems work with BYOD (Bring Your Own Device)?
Yes, Zero Trust and passwordless authentication are well-suited for BYOD environments. They rely on AI-driven risk assessments and endpoint checks rather than assuming devices are secure.
Features like device attestation ensure only registered, trusted devices can access enterprise systems. For instance, an employee using their personal phone can log in securely if it meets specific security policies, like having the latest OS version.
What are behavioral biometrics, and how do they fit into passwordless systems?
Behavioral biometrics analyze unique user behaviors, such as typing speed, mouse movements, or how someone holds their smartphone. These patterns are hard to mimic, providing an additional layer of authentication.
Example:
- A hacker may steal access to a device but fail to replicate the user’s typing rhythm or gesture patterns.
- AI identifies the mismatch and blocks the attempt, even without requiring additional user input.
Behavioral biometrics make authentication both seamless and more secure.
How does passwordless authentication address insider threats?
Passwordless systems reduce insider threat risks by relying on identity-based access control and continuous monitoring. Every action is tied to a verified user and device, making it harder for insiders to access systems anonymously.
For example:
- A disgruntled employee trying to log in from an unauthorized device would be flagged by AI as suspicious.
- Additionally, role-based access limits what they can see or do, minimizing damage.
With detailed audit trails, enterprises can quickly trace malicious actions back to specific users.
How scalable are passwordless authentication systems for large enterprises?
Passwordless systems are highly scalable. They integrate with existing IAM platforms and support thousands—or even millions—of users without bottlenecks.
For example:
- A global retail company can deploy FIDO2-based passwordless authentication for its workforce across multiple regions.
- Each user’s login is processed locally on their devices, reducing the load on central servers.
The decentralized nature of passwordless methods makes scaling much easier compared to password-dependent systems.
What’s the role of cryptographic keys in passwordless authentication?
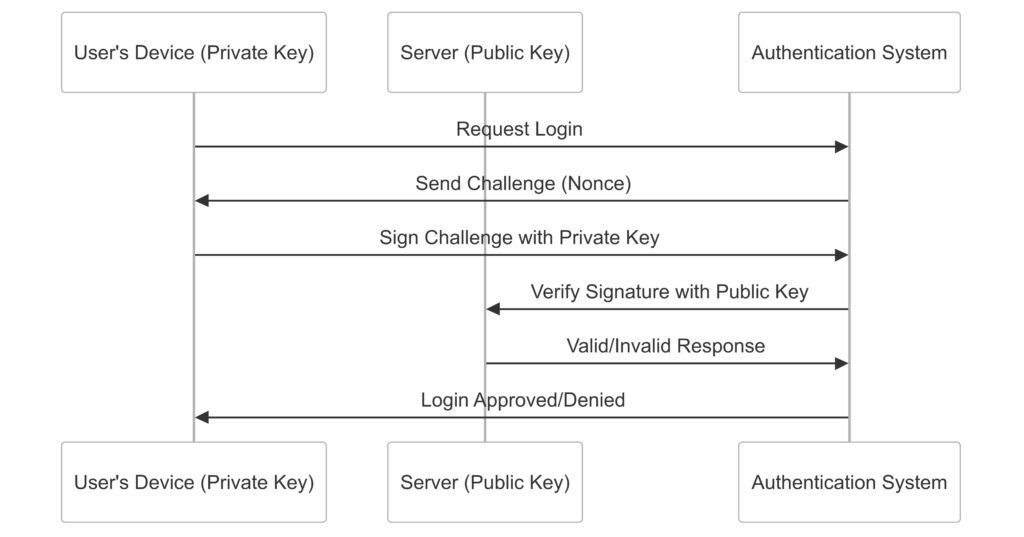
Cryptographic keys are the foundation of many passwordless methods. A user’s device generates a public-private key pair during setup.
Here’s how it works:
- The private key stays securely on the device and never leaves.
- The public key is shared with the server for verification.
When a user tries to log in, the private key signs a challenge from the server, proving identity without sharing sensitive data.
For example, a user logging into a secure app on their phone triggers the private key to authenticate silently in the background. This method prevents phishing since the private key can’t be intercepted or guessed.
What are the biggest challenges of going passwordless?
While passwordless systems offer undeniable advantages, enterprises may face challenges like:
- User Resistance: Employees accustomed to passwords may need training to adopt new methods like biometrics.
- Legacy System Integration: Older applications or systems may lack compatibility with passwordless protocols.
- Initial Costs: Deploying devices with biometric capabilities or hardware tokens can be expensive upfront.
For example, an enterprise transitioning to passwordless logins may need to prioritize high-risk departments (e.g., finance) before extending the solution organization-wide.
How can enterprises measure the success of Zero Trust and passwordless systems?
Enterprises can track key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the impact of Zero Trust and passwordless authentication, such as:
- Reduction in breaches: Fewer incidents caused by compromised credentials.
- User adoption rates: Percentage of employees using passwordless methods without issue.
- Authentication times: Speed of access compared to traditional methods.
For instance, a financial institution might report an 80% drop in account lockouts after switching to passwordless systems, reducing IT workload and user frustration.
Are passwordless systems more expensive than traditional authentication?
While initial deployment costs may be higher, passwordless systems often lead to long-term savings by reducing IT overhead and breach-related expenses.
Savings examples include:
- Eliminating password reset tickets, which cost an average of $70 per incident.
- Avoiding fines or legal fees associated with breaches caused by compromised credentials.
For example, a mid-sized enterprise saved hundreds of thousands annually after switching to passwordless authentication by reducing helpdesk tickets and preventing credential-based attacks.
What regulatory frameworks support passwordless authentication?
Passwordless systems align well with security and privacy regulations, including:
- GDPR: Limits the collection of sensitive data (e.g., passwords) and enforces strong user identity protections.
- HIPAA: Ensures secure authentication for healthcare workers accessing patient data.
- PCI DSS: Meets strong authentication requirements for handling payment card data.
For example, an e-commerce platform implementing FIDO2 can comply with PCI DSS standards by using device-based keys instead of password storage, reducing the risk of stolen credentials.
Resources
Research Papers and Case Studies
- “Passwordless Authentication in the Enterprise: A Gartner Research Overview”
Explains trends in passwordless technology adoption and how it improves business outcomes. - “Implementing Zero Trust for Hybrid Work Environments” by Forrester Research
A case study on how organizations integrate Zero Trust with passwordless access to protect remote teams. - “The Future of Identity: Passwordless Authentication with AI” from NIST
A technical report on advanced identity management systems supported by AI and biometrics.
Online Courses
- “Zero Trust Security Fundamentals” on Coursera (by Palo Alto Networks)
Learn the core principles and strategies for deploying Zero Trust in enterprise environments. - “FIDO2 and Passwordless Authentication for Developers” on Pluralsight
A technical course for building FIDO2-compliant authentication systems. - “AI for Cybersecurity” on Udemy
Teaches how to leverage AI for threat detection, behavioral analytics, and adaptive security.
Tools and Frameworks
- Microsoft Azure Active Directory
A comprehensive platform supporting Zero Trust policies and passwordless authentication with tools like Windows Hello and FIDO2 keys. - Okta Identity Cloud
Provides adaptive, passwordless access and integrates seamlessly with Zero Trust strategies. - Duo Security (Cisco)
Offers multi-factor and passwordless authentication, with built-in device trust and contextual AI. - Ping Identity
Specializes in passwordless solutions through AI-driven identity orchestration.
Blogs and Articles
- Microsoft Security Blog: “Securing the Future with Passwordless Authentication”
(https://www.microsoft.com/security/blog)
Regular updates on passwordless technologies and Zero Trust principles. - Okta Blog: “From MFA to Passwordless: Why Zero Trust is the Key to Modern Authentication”
(https://www.okta.com/blog)
Insights into enterprise deployments and benefits of passwordless systems. - Dark Reading: “The Role of AI in Strengthening Zero Trust Frameworks”
(https://www.darkreading.com)
Explores cutting-edge AI tools that enhance Zero Trust and authentication systems.
Standards and Organizations
- FIDO Alliance (Fast Identity Online)
Website: https://fidoalliance.org
A leading organization advancing passwordless standards like FIDO2 and WebAuthn. - NIST Cybersecurity Framework
Website: https://www.nist.gov
A trusted source for cybersecurity guidelines, including identity management and Zero Trust strategies. - OWASP (Open Web Application Security Project)
Website: https://owasp.org
Provides best practices for secure authentication and passwordless methods.